Description
Description
Finance is a field that deals with the study of investments. It includes the dynamics of assets and liabilities over time under conditions of different degrees of uncertainty and risk. Finance aims to price assets based on their risk level and their expected rate of return.
 Concepts
Concepts
The goal of the finance is to create value for the firms legal owners. thus the goal of the firm is to "maximize shareholder wealth" by maximizing the price of the existing common stock.
The principles of finance:
It is necessary to understand these principles in order to understand finance.
Cash Flow of a firm:
- accounting profits are not equal to cash flows. it is possible for a firm to generate accounting profits but not have cash or to generate cash flows but not report accounting profits in the books.
- Cash flow and not profits drive the value of a business.
- we must determine incremental cash flows when making financial decisions.
- Incremental cash flow is the difference between the projected cash flows if the project is selected, versus what they will be, if the project is not selected.
- A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future.
- since we can earn interest on money received today, it is better to receive money earlier rather than later.
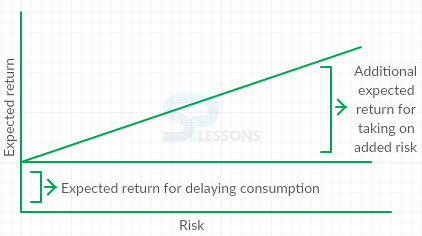
- we won't take on additional risk unless we expect to be compensated with additional to reward.
- Investors expect to be compensated for delaying consumption and taking on risk.
- Thus investors expect a return when they put their savings in a abank and they expect to earn a higher rate of return on stocks relative to bank savings account.
- In an efficient market, the prices of all traded assets at any instant in time fully reflect all available information.
- Thus stock prices are useful indicator of the value of the firm. prices changes reflect changes in expected future cash flows. good decisions will tend to increase the stock prices.
- There are inefficiencies in the market that may distort the prices.
- The separation of management and the ownership of the firm creates an agency problem. managers may make decisions that are not consistent with the goal of maximizing shareholder wealth.
- Agency conflict is reduced through monitoring, compensation schemes, and market mechanisms.
- Capital budgeting decision
- Capital structure decision
- Working capital decision
- The factors effecting a firm's financial objective are timing, risk, accounting, "long-run" value.
- Maximizing current market value is the only plausible financial objective.
- Current market value incorporates present value of all current and future cash flows, adjusted for timing and risk.
- Market value rule is independent of shareholders differences.
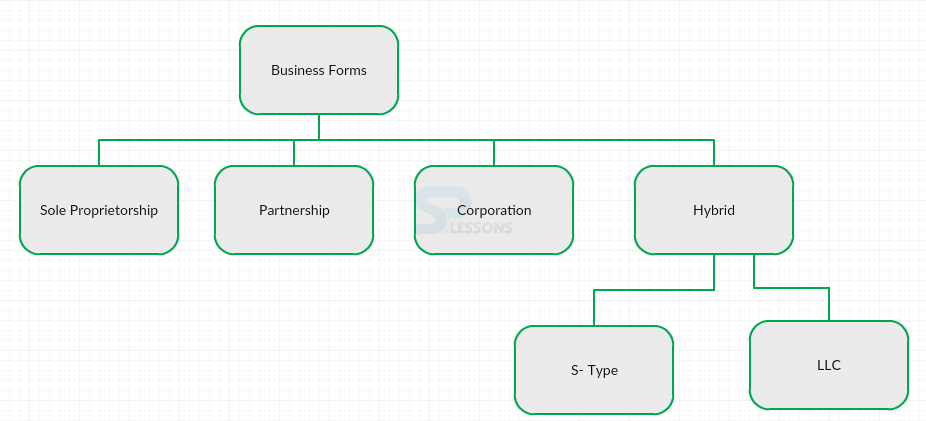
- Business owned by an individual.
- Owner maintains title to assets and profits.
- unlimited liability.
- Termination occurs on owners death or by owners choice.
- Two or more persons come together as co-owners.
- General Partnerships: All partners are fully responsible for liabilities incurred by the partnerships.
- Limited Partnerships: One or more partners can have limited liability, restricted to the amount of capital invested in the partnerships. there must be at least one general partner with unlimited liability. limited partners cannot participate in the management of the business and their names cannot appear in the name of the firm.
- Legal functions separate and apart from its owners.
- Owners dictate direction and policies of the corporation, oftentimes through elected board of directors.
- Life of corporation doesn't depend on owners. corporation continues to exist through easy transfer of ownership.
- Shareholders liability is restricted to amount of ownership.
- Taxed separately.
- Benefits: Limited liability, easy to transfer ownership, easy to raise capital, unlimited life.
- Drawbacks: No secrecy of information, may be delays in decision making, greater regulation, double taxation.
- Limited liability
- Taxed as partnerships
- Owners must be people so cannot be used for joint ventures between two corporations.
- Limited liability
- Taxed like a partnership
- Qualifications vary from state to state.
- Cannot appear like a corporation otherwise it will be taxed like one.
- U.S. corporations are looking to international expansion to discover profits.
- In addition to US firms going abroad, we have also witnessed many foreign firms making their mark in the united states.
- Internationalization of business has been spurred by collapse of communism, acceptance of free market system, technology, improved transportation.
- Country risk: changes in government regulations, unstable government, economic changes in foreign country.
- Currency risk: fluctuations in exchange rates.
- Cultural risk: differences in language, traditions, ethical standards.
 Model Questions
Model Questions
1. Finance is a field that deals with the study of?
A. investments
B. Purchase
C. Banking
D. None of the Above
Answer-A
2. Country risk means fluctuations in?
A. Interest rates
B. Exchange rates
C. Purchase rates
D. investment rates
Answer-B
3. U.S. corporations are looking to international expansion to discover?
A. Investments
B. Losses
C. Profits
D. Increase rates
Answer-C
4. What is the benefit of Limited liability Companies?
A. Profits in business
B. Increase rates
C. Partnership
D. Limited liability
Answer-D
5. What is the Drawback of the Trade-offs?
A. Double taxation
B. Easy to raise capital
C. unlimited life
D. Limited liability
Answer-A
6. What is the benefit of the Trade-offs?
A. Double taxation
B. Limited liability
C. May be delay in decision making
D. Greater regulation
Answer-B
7. How many types of Hybrid organisation?
A. 4
B. 3
C. 2
D. 1
Answer-C
8. All partners are fully responsible for liabilities incurred by the partnership is called?
A. Limited partnership
B. Multinational partnership
C. Unlimited partnership
D. General Partnership
Answer-D
9. Sole Proprietorship means?
A. Business owned by an individual
B. Business owned by an team
C. Business owned by a committee
D. Business owned by an organisation
Answer-A
10. What are the principles of finance?
A. Cash Flow of a firm
B. Money has a time value
C. Risk requires reward
D. All of the above
Answer-D