Introductions
Introductions
Noun is a word which describes the name of a person, place, animal, thing or an idea.
Various examples of nouns are as follows.
| Name | Examples |
|---|---|
| A person: |
|
| A Place |
|
| An animal: |
|
| A thing: |
|
| An idea: |
|
 Classification
Classification
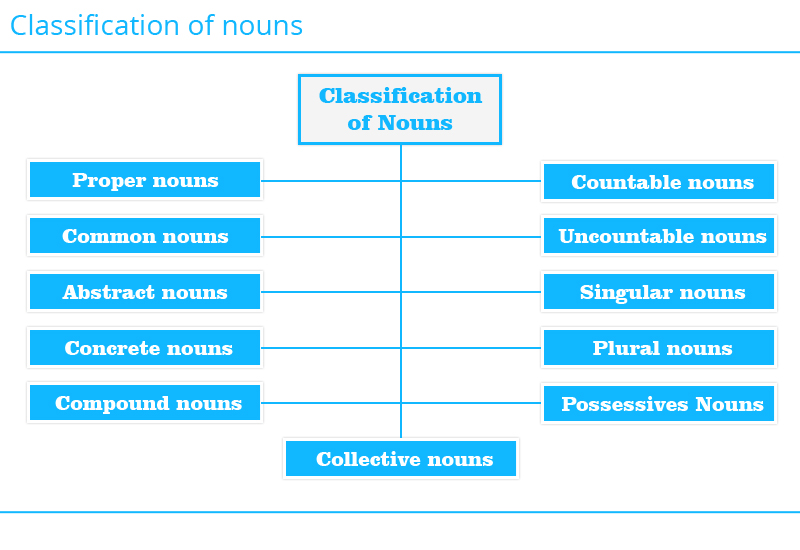
Classification of Nouns:
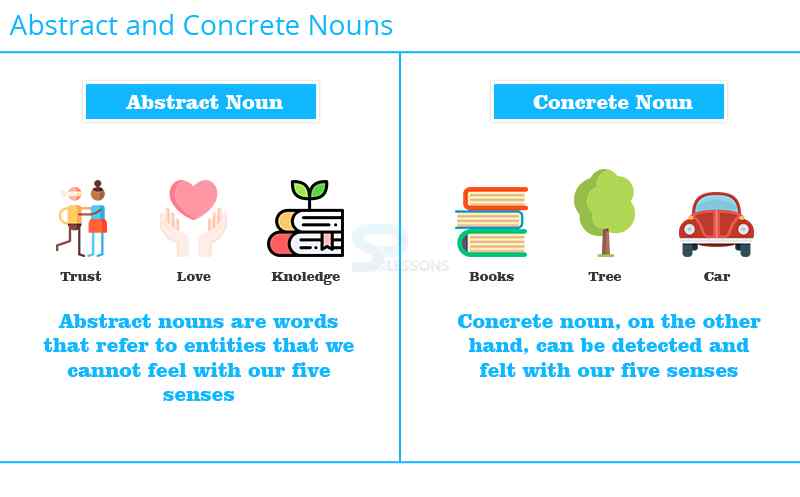
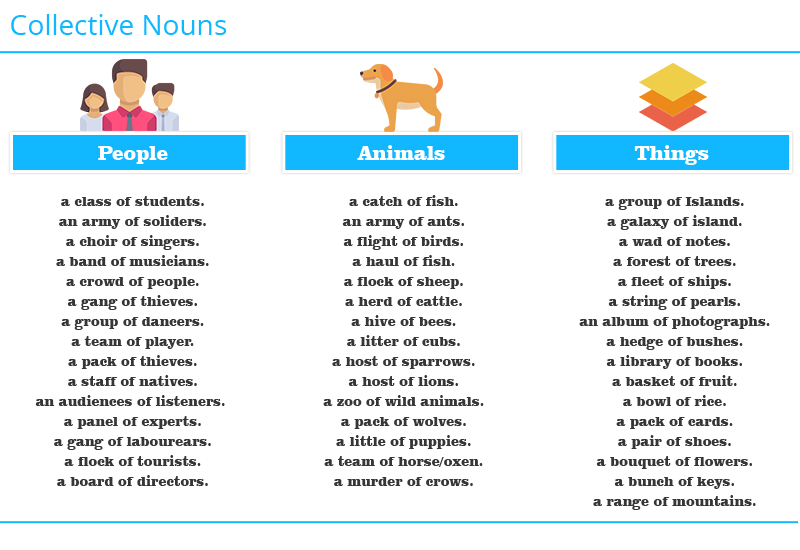
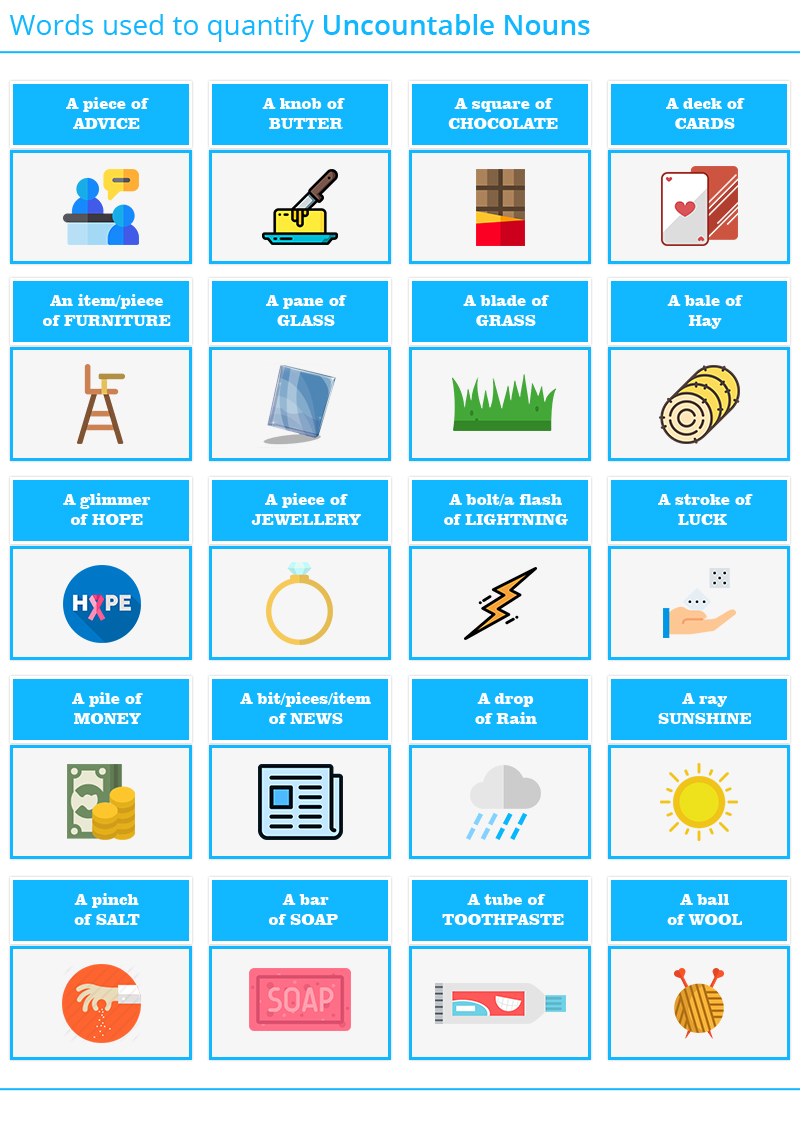
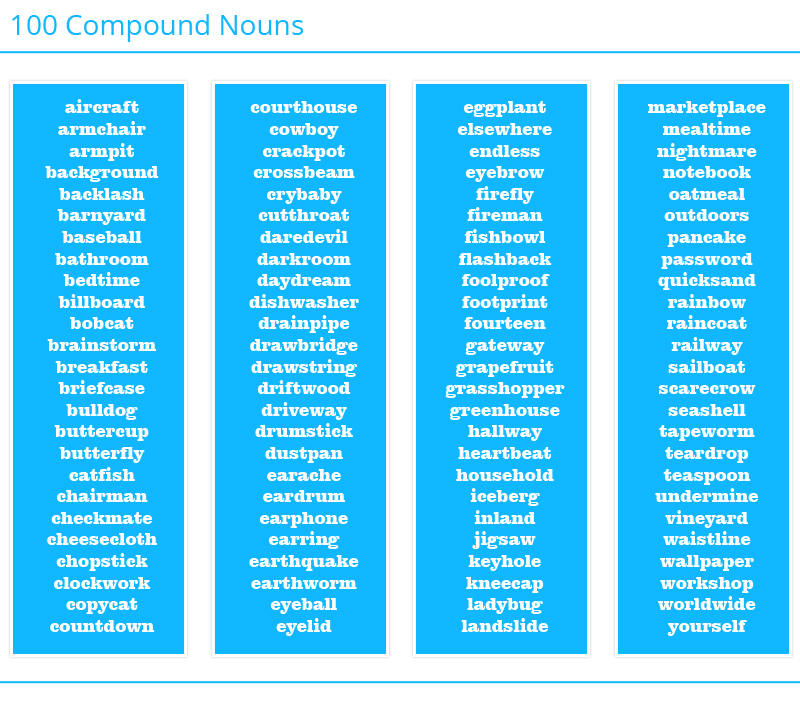
Different types of nouns are proper nouns, common nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, compound nouns, collective nouns, compound nouns, countable nouns, uncountable nouns, singular nouns, plural nouns and possessive nouns.
1. Proper Nouns: A noun that is a name of a certain person, place or thing is called a Proper Noun. They always begin with a capital letter.
For example:
- Asia is the largest continent.
- Wednesday is a holiday.
- A group of boys is standing at the bus stop.
- The countries near the equator have hot temperature.
- She has an incredible love for dogs.
- The young girl received an award for her bravery.
- Your muffler is made of fine wool.
- Can you please pass me the pickles?
- The band of musicians performed amazingly.
- The audience clapped after the dance performance.
- There are five books on the bookshelf.
- I have ten new dresses for the occasion.
- There was snow outside our school.
- The wheat fell out of the sack.
- The daughter-in-law respects her new family members.
- The sunlight entered the room from between the curtains.
- I gifted her photo frame.
- The monkey was in the backyard of the house.
- He has bought a new pen for his mother.
- There were six bottles in the box.
- The children were playing with the kittens.
- That is his pencil.
- Her mom’s scooter was hit by a fast approaching scooter.
- This bouquet of flowers belongs to the girl in the red dress.
 Functions
Functions
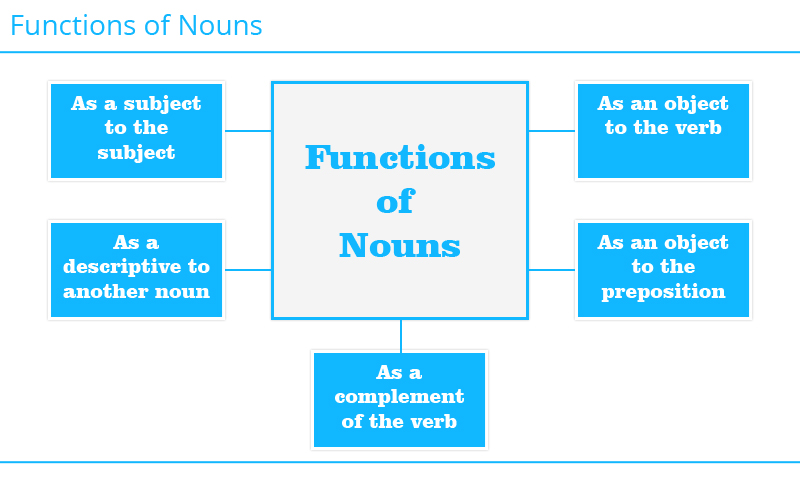
Nouns are the most important part of the speech which is used in the sentences. They are very important and equally important are their functions.
The most important functions of nouns are as follows:
1. Subject of the Verb: All the sentences have subjects which tell the reader what the sentence is all about. The subject is a noun. So we can say that the foremost function of the noun is to work as a subject.
For example:
- Michael threw the ball. So, Michael is the subject of the verb threw.
- He is sleeping. He is the subject of the verb sleeping.
- The ship was crossing the river. So in the sentence, the river is the object of the verb crossing.
- My uncle gave me the chocolate. So in the sentence, me is the direct object, and chocolate is the indirect object of the verb gave.
- The boy is a trader.
- Tyson is the winner.
- I have to give the project report to the professor.
- Let us go with Matt.
- All the highlighted words coming after the prepositions are said to be object of preposition.
- The teacher, Mrs. Kohli was retired from the school. In this sentence, Mrs. Pike is giving meaning to the noun teacher.
- Prem Sharma, as the president of the organization, has decided. In this sentence, the president adds meaning to Prem Sharma.
 Rules & Tips
Rules & Tips
Rules and Tips While Using Nouns:
As simple as nouns may seem, there are certain rules that need to be followed for the use of nouns in sentences.
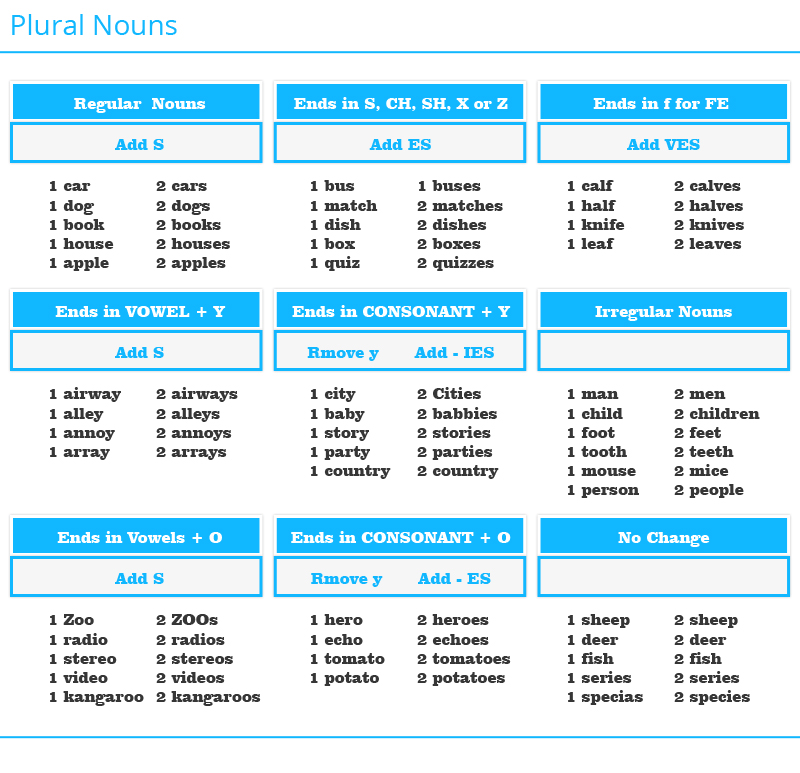
Rule 1: Some nouns always exist in plural forms. Thus‘s’ cannot be removed from them to make them singular words.
For example: tongs, scissors, trousers, troops, gallops.
- I have bought a pair of earrings.
- My mother uses tongs while making chapattis.
- Athletics is a field chosen only by the few people.
- Physics is a very boring subject.
- The cattle are grazing in the field.
- The children are playing in the ground.
- She has colored her hair red.
- The scenery of Srinagar has captivated us.
- A sheep is sleeping.
- Two sheep are sleeping.
- She has five hundred rupees only.
- Mr. Mehta donated two million rupees to the NGO.
- Child after child was arriving.
- Every student was doing his own task individually.
- The teacher must treat all his students equally.
- Bat- Bats
- Rat- Rats
- Kiss- Kisses
- Boss- Bosses
- Quiz- Quizzes
- Gas- Gasses
- Wolf- Wolves
- Half- Halves
- Marry- Marries
- Fancy- Fancies
- Portray- Portrays
- Pray- Prays
- Do- Does
- Volcano- Volcanoes
- Syllabus- Syllabi
- Bronchus- Bronchi
- Parenthesis- Parentheses
- Phenomenon- Phenomena
- Fish- Fish
- Deer- Deer
- Person- People
- Foot-Feet