Introduction
Introduction
Analytical Reasoning skills are crucial in every field that involves Numerical Reasoning, Logic, Math , Deductions & Inductions and fields where data needs to be analysed to discern patterns within the data. Analytical Reasoning is thus defined as the ability to look at the data/information and to find patterns or rules or connection between items in the information. Analytical Reasoning questions in competitive exams include both verbal & non-verbal questions and also involve a series of diagrams and pictures.
The article Analytical Reasoning Practice Quiz 4 lists different types of Analytical Reasoning questions with solutions useful for candidates preparing for different competitive examinations like RRB .RRB ALP/Technical Exams/Junior Engineer Recruitment Exams, SSC CGL,SSC CHSL, IBPS, SBI PO, SBI Clerks, CAT and etc.
 Quiz
Quiz
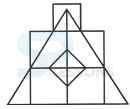
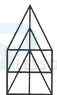
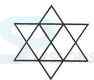
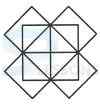
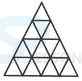
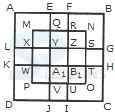
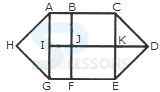
1. Count the number of triangles and squares in the given figure.
- A. 21 triangles, 7 squares
B. 18 triangles, 8 squares
C. 20 triangles, 8 squares
D. 22 triangles, 7 squares
- A. 11
B. 21
C. 24
D. 26
- A. 21, 17
B. 19, 13
C. 21, 15
D. 19, 17
- A. 22
B. 20
C. 18
D. 14
- A. 8
B. 11
C. 12
D. 15
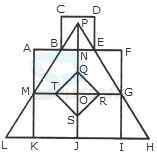
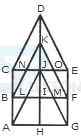
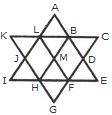
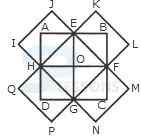
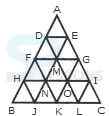
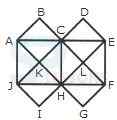
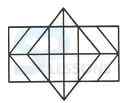
1. Count the number of convex pentagons in the adjoining figure.
- A. 16
B. 12
C. 8
D. 4
- A. 20
B. 18
C. 16
D. 15
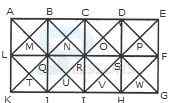
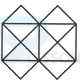
- A. 28 triangles, 10 squares
B. 28 triangles, 8 squares
C. 32 triangles, 10 squares
D. 32 triangles, 8 squares
- A. 47
B. 45
C. 41
D. 39
- A. 23
B. 22
C. 21
D. 18
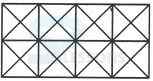
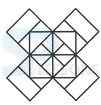
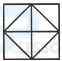
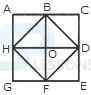
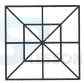
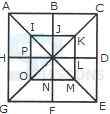
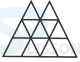
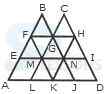
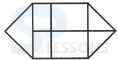
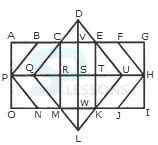
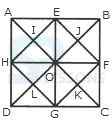
1. Count the number of squares in the given figure.
- A. 18
B. 19
C. 25
D. 27
- A. 11
B. 13
C. 15
D. 21
- A. 10
B. 9
C. 8
D. 7
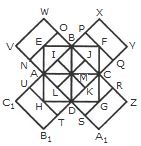
- A. 30, 5
B. 32, 3
C. 28, 5
D. 30, 3
- A. 44 triangles, 10 squares
B. 14 triangles, 16 squares
C. 27 triangles, 6 squares
D. 36 triangles, 9 squares