Introduction
Introduction
- Government of India has set the University Grants Commission (UGC) Quality Mandate as the target. The idea is to ensure that at least half of the students completing their degree program through the higher education system should find suitable employment by 2022.
- Therefore, the Government of India launched a Scheme for Higher Education Youth for Apprenticeship and Skills (SHREYAS).
- This scheme comprises of the joint initiatives taken up by three central ministries, i.e., the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), and Ministry of Labour and Employment (MLE).
- The Scheme is applicable for students in non-technical degree courses. Employable skills are imbibed through learning and promoting apprenticeship.
 SHREYAS
SHREYAS
The vision of SHREYAS is;
- Aligning the education curriculum as per the needs of the industry and service sector, and
- Promoting on-the-job exposure to all candidates in the skill sets of their own choice and aptitude.
- For any further information, visit the website: www. https://shreyas.ac.in
Given below are the objectives with which SHREYAS was formed and launched.
- The primary objective of the SHREYAS Scheme is to introduce the employment relevance in the learning process of the higher education system such that it improves the employability of the students.
- The Scheme forges a close functional link between the industry or service sectors and the education on a sustainable basis..
- SHREYAS helps to establish a system of 'earn while learning' into higher education..
- Further, students are taught skills that are in demand dynamically..
- SHREYAS also aims to help businesses and industry in securing good quality manpower..
- The employment facilitating efforts of the Government are linked with the student community for better implementation.
- The SHREYAS is operating in conjunction with the National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS). NAPS provides the placing of apprentices up to 10 percent of the total workforce in every business or industry.
- The Government of India shares 25 percent of the monthly stipend under the NAPS Scheme. The maximum amount of this stipend is INR 1500 per month during the period of apprenticeship.
- Besides, an amount of up to INR 7500 is also met if needed towards the basic training cost.
- Initially, the Scheme has been implemented by the Sector Skill Councils (SSCs), the Banking Finance Insurance Sector (BFSI), Health care, retail, telecom, media, logistics, management services, apparel, ITeS.
| Stakeholder | Interest or Impact on the Scheme | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Institutions | SSCs identify the industries for apprenticeship and conduct the assessment for certification. |
|
| SSCs | The existing programs are restructured into B.A. (Professional), B.Com (Professional) or B.Sc. (Professional). |
|
| MSDE and NSDC | MSDE operates the NAPS scheme through NSDC. The entire program progresses only with the dynamic interface and information sharing between the MHRD and MSDE. |
|
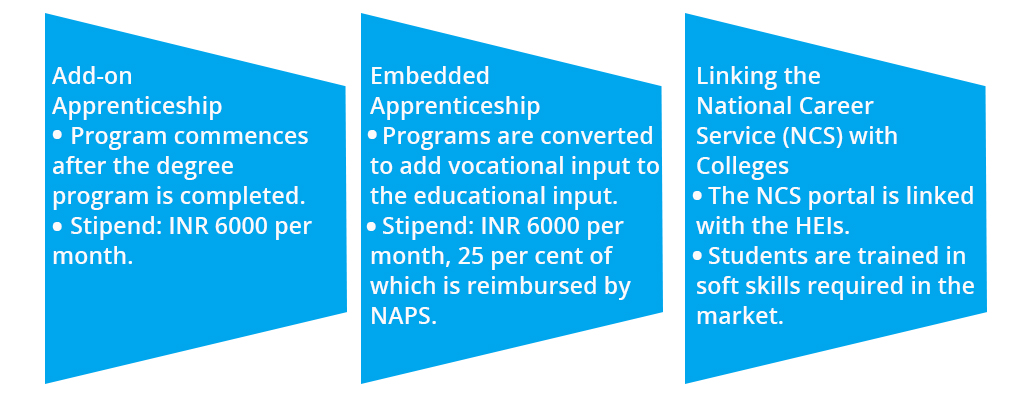
'Merging Skill into Degree Education' is the idea behind the SHREYAS. The figure below shall reveal the three main tracks crucial in the implementation of this Scheme.
- Add-on Apprenticeship: The students who have completed the degree program are invited to choose a job role of their personal choice from a selected list given by the SSC of the MSDE.
- Embedded Apprenticeship: The existing programs include educational input with the vocational input. At the end of the apprenticeship period, SSC conducts tests, and the successful candidates receive a skill certificate.
- Linking National Career Service with Colleges: Under this, NCS link the HEIs to help the students in HEIs to improve employment opportunities.
| Short Form | Full Form |
|---|---|
| SHREYAS | Scheme for Higher Education Youth for Apprenticeship and Skills |
| UGC | University Grants Commission |
| MHRD | Ministry of Human Resource Development |
| MSDE | Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship |
| MLE | Ministry of Labour and Employment |
| NAPS | National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme |
| SSCs | Sector Skill Councils (SSCs), |
| BFSI | Banking Finance Insurance Sector |
| HEIs | Higher Education Institutions |
| NCS | National Career Service |