Introduction
Introduction
Career in Banking is one of the most lucrative and most sought after careers. In India, Bank Recruitment Exams are primarily conducted for recruitment of Probationary Officers, Clerks & Specialist Officers. India currently[2019] has 93 commercial and 27 public sector banks out of which 19 are nationalized and 6 are SBI and its associate banks and rest two are IDBI Bank and Bharatiya Mahila Bank, which are categorized as other public sector banks. Recruitment for Bank Probationary Officers, Management Trainees, Clerks and for various other posts generally follow a 3 step recruitment process: Preliminary Exam + Mains Exam + Interview & Group Discussion. The article SBI CLERK Mains Practice Quiz presents a practice set for the most sought after SBI CLERK recruitment. Until the year 2013, All Public Sector Banks used to conduct their own entrance test, GDs and Personal Interview for recruiting candidates. However, after 2014, IBPS started conducting recruitment Tests for 12 PSU Banks. SBI holds a separate entrance test for recruitment.
Mains exams are very important to clear every government sector or bank related recruitment process in India. Only those candidates who are selected in the Mains round are allowed to move further up in the recruitment process. The marks obtained in the Mains exams are considered for the final merit list. Mains exams usually consist of 4 sections, with 155 questions with a time duration of 3 hours. Mains exams most certainly have negative marking.
 Quiz
Quiz
1. Which of the following symbols should replace the question mark in the given expression in order to make the expressions ‘K ≤ H’ and ‘M > J’ definitely true?
H ≥ I = J ? K H 3 I = J ? K ≤ L < M L < M
-
A. >
B. 3
C. ≤
D. Either < or ≤
E. =
-
A. P > Q ≥ R = S
B. S ≤ R ≤ Q < P
C. R = P > Q ≥ S
D. S > Q ≥ R < P
E. S < Q ≤ R < P
-
A. 19
B. 29
C. 4
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
-
A. 20
B. 40
C. 10
D. 60
E. None of these
-
A. 720
B. 228
C. 108
D. 93
E. None of these
-
A. 240
B. 80
C. 120
D. Can not be determined
E. None of these
-
A. 40 # 40 * 10
B. 40 $ 40 % 10
C. 40 @ 40 ⓒ 10
D. 40 · 40 l 10
E. None of these
-
A. bond 86 goal 46 like 12 33 high.
B. bond 86 goal 46 high 33 12
C. bond 86 goal 46 high 33 like 12.
D. There will be no such step.
E. None of these
-
A. VI
B. IV
C. V
D. VII
E. None of these
-
A. Four
B. Five
C. Three
D. Two
E. None of these
-
A. 18 25 wear 49 long for car 73
B. 73 18 car 25 wear 49 long for
C. 18 73 25 car wear 49 long for
D. Cannot be determined
E. None of these
-
A. Four
B. Five
C. Six
D. Seven
E. None of these
-
A. Only (A)
B. Only (B)
C. Only (C)
D. ONly (D)
E. (A), (B ) and (C)
-
A. Only (A)
B. Only (B)
C. Only (C)
D. Only (D)
E. None of the above
-
A. Only (C)
B. Only (D)
C. Only (E)
D. Only (F)
E. Both (E) and (F)
-
A. The speaker is a die-hard colonist
B. The speaker has the good of the nation at heart
C. The speaker is addressing an issue related to a colonial empire
D. None of the above
E. All of these
-
A. All the people of the society should progress at an equitable rate and there should be no disparities and private property does bring about a tremendous disparity.
B. One should not strive for the common good of humanity at all, instead one should be concerned with maximizing one’s own wealth.
C. One should learn from the experiences of former communist nations and should not repeat their mistakes at all.
D. Even prosperous capitalist countries like the USA have their share of social problems.
E. None of these
- V sits second to the right of his wife.
- S sits third to the right of V.
- W sits second to the right of her husband Z. Z is not an immediate neighbor of V’s wife.
- T is a male and Y is not an immediate neighbor of V.
- R sits second to the right of Q.
-
A. Second to the left
B. Immediately to the right
C. Third to the left
D. Second to the right
E. Third to the right
-
A. S is one of the male members of the group.
B. Both the immediate neighbors of S are females.
C. S sits third to the left of T.
D. W is an immediate neighbor of S.
E. S sits second to the right of Q.
-
A. Q
B. Y
C. R
D. T
E. None of these
-
A. Y
B. R
C. Q
D. S
E. None of these
-
A. T is an immediate neighbor of Z’s wife.
B. No male is an immediate neighbor of T.
C. Q sits second to the right of T.
D. The one who sits third to the left of T is a male.
E. All are true.
-
A. RQ
B. WZ
C. YV
D. WY
E. None of these
-
A. database
B. DBA
C. users
D. SQL
E. separate files
-
A. field
B. data
C. file
D. batch
E. group
-
A. debugging a program
B. running a program
C. compiling a program
D. coding program
E. assembling a program
-
A. System program
B. Compiler program
C. Object program
D. Source program
E. Data program
-
A. cluster
B. track
C. cylinder
D. All the above
E. None of these
-
A. automatic
B. simplex
C. half-duplex
D. full-duplex
E. None of these
-
A. Integerated Standard Digital Network
B. Intelligent Services Digital Network
C. Integerated Services Digital Network
D. Integrated Services Data Network
E. None of these
-
A. date ()
B. now ()
C. today ()
D. time ()
E. current date ()
-
A. F1
B. F2
C. F3
D. F5
E. F6
-
A. First generation
B. Second generation
C. Third generation
D. Fourth generation
E. Fifth generation
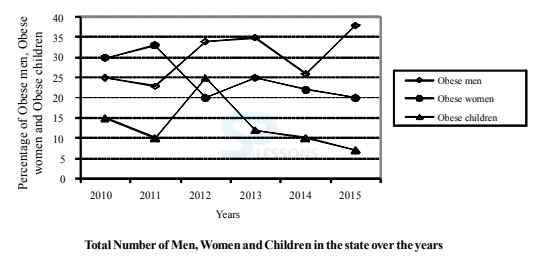
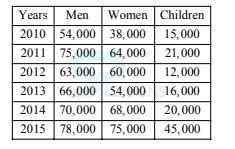
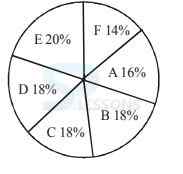
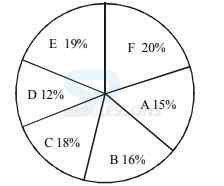
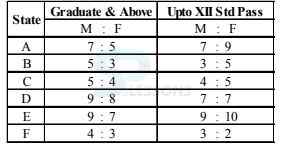
Directions Q (46 - 50): Study the following graph and table carefully and answer the questions given below them.
-
A. Integerated Standard Digital Network
B. Intelligent Services Digital Network
C. Integerated Services Digital Network
D. Integrated Services Data Network
E. None of these
-
A. 12,683
B. 12,795
C. 12,867
D. 12,843
E. 12,787
-
A. 55
B. 60
C. 50.5
D. 65.5
E. None of these
-
A. 6 : 7
B. 21 : 65
C. 15 : 73
D. 48 : 77
E. None of these
-
A. 5,475
B. 5,745
C. 4,530
D. 31,650
E. None of these
-
A. 4,350
B. 31,560
C. 4,530
D. 31,650
E. None of these
-
A. 4,350
B. 4,950
C. 4,800
D. 4,900
E. 4,850
-
A. 12,450
B. 8,400
C. 10,050
D. 10,650
E. None of these
-
A. 4 : 3
B. 3 : 2
C. 2 : 3
D. 3 : 4
E. None of these
-
A. 1,800
B. 2,250
C. 4,050
D. 36,600
E. None of these
-
A. 60.5
B. 63.5
C. 62
D. 64
E. None of these
-
A. 1521
B. 1641
C. 1651
D. 1671
E. 1691
-
A. 306
B. 316
C. 308
D. 318
E. None of these
-
A. 90
B. 70
C. 75
D. 80
E. 86
-
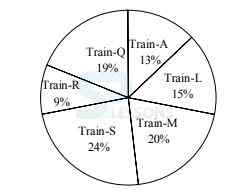
A. A
B. Q
C. S
D. M
E. L
-
A. 29
B. 49
C. 43
D. 33
E. 39
-
A. 24,000
B. 14,000
C. 28,000
D. 36,000
E. None of these
-
A. 7 : 5
B. 5 : 7
C. 16 : 15
D. 14 : 16
E. None of these
-
A. 40
B. 62.5
C. 50
D. 52.5
E. None of these
-
A. 8%
B. 12%
C. 11%
D. 9%
E. None of these
-
A. 28 : 35
B. 35 : 28
C. 32 : 45
D. 45 : 32
E. None of these
-
A. 56
B. 72
C. 68
D. 76
E. None of these
-
A. 70
B. 75
C. 68
D. 72
E. None of these
-
A. 215 : 216
B. 214 : 215
C. 217 : 215
D. 215 : 217
E. None of these
-
A. 17 : 16
B. 16 : 17
C. 64 : 51
D. 51 : 64
E. None of these
-
A. 129
B. 82
C. 77
D. 107
E. None of these
-
A. 1
B. 5
C. 3
D. 4
E. None of these
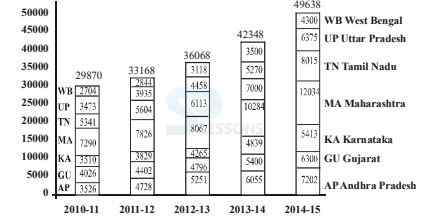
-
A. Andhra Pradesh
B. Uttar Pradesh
C. Karnataka
D. Tamil Nadu
E. None of these
-
A. Tamil Nadu
B. Karnataka
C. Gujarat
D. Andhra Pradesh
E. None of these
-
A. 2011 to 2012
B. 2012 to 2013
C. 2013 to 2014
D. 2014 to 2015
E. None of these
-
A. Karnataka
B. West Bengal
C. Uttar Pradesh
D. Tamil Nadu
E. None of these
-
A. 225%
B. 150%
C. 275%
D. 240%
E. None of these
-
A. Rs. 1,40,000
B. Rs. 1,50,000
C. Rs. 1,60,000
D. Rs. 1, 80,000
E. None of these
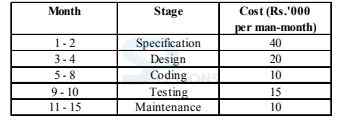
-
A. Testing
B. Specification
C. Coding
D. Design
E. None of these
-
A. 1- 5
B. 9 - 13
C. 11 - 15
D. 5 - 8
E. None of these
-
A. Rs. 30,000
B. Rs. 60,000
C. Rs. 70,000
D. Rs. 40,000
E. None of these
Directions Q (81 - 84): Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given below. Certain words are printed in bold to help you locate them answering some of the questions.
A nine-membered international task force on conservation of forests has identified India as one of the 56 countries of the world which are critically affected by widespread deforestation and steady destruction of natural watersheds. It has also warned that unless urgent conservation measures are taken, the country will face a serious food crisis in the next century. The report correctly describes the Himalayan eco system as the most critical watershed in the world, the degradation of which now threatens the very processes of life in the Indo-Gangetic plain. The report documents some aspects of the process of environmental destruction that is at work in this country and calls for an expenditure of about Rs.1,450 crores over the next five years to reverse some of the damage that has taken place. While the task force’s report is a welcome reminder of the urgency to the task of halting and rolling back the most awesome form of destruction that this country has ever witnessed, it regrettably underestimates the magnitude of the effort involved and hence falls short of suggesting a comprehensive solution to the problem. For instance, the five-year plan. Its recommendation bears no relationship to the resources that will be actually needed to reach a net rate of zero deforestation. At present deforestation is proceeding at the furious pace of 1.3 million hectares a year.
Past experience shows that more than Rs. 300 crores in government expenditure alone is needed over four to five years at today’s prices merely to plant less than a million hectare. Realistically speaking, resources of the order of Rs. l,000 crores a year will be necessary for the next five years to sustain a plan that actually provides a forest cover to badly denuded land and an underestimation of the magnitude of such a plan is not the only flaw in the report. An even more serious one, related to the first, lies in its failure to establish a coherent set of priorities among the different functions that an afforestation programme must perform. To take just one example, the vital task of planting fuel wood and fodder trees is put at par with the planting of trees to meet raw materials requirement of industries. Owing to confusion, the task force falls short of recommending the kind of radical measures. Wood-based industries step against the spreading of mono cultures and entrusting afforestation programmes.
81. The author’s chief concern appears to be –
-
A. conservation of forests
B. destruction of natural watersheds
C. degradation of Himalayan eco systems
D. to take radical measures for afforestation
E. to discuss the report of international task force
-
A. 300 crores
B. 1000 crores
C. 1450 crores
D. 2450 crores
E. 5000 crores
-
A. Danger of famine
B. Scarcity of water
C. Scarcity of food grains
D. Report of the international task force on conservation of forests
E. 5000 crores
-
A. suggested a comprehensive scheme for dealing with the problem of deforestation
B. emphasized the urgency of tackling the problem
C. underestimated the magnitude of problem of deforestation
D. underestimated the intensity of the problem of the natural watersheds
E. 5000 crores
-
A. Momentum
B. Rate
C. Progress
D. Gain
E. Measure
-
A. Substantial
B. Negligible
C. Secondary
D. Large
E. Unduly
-
A. endowed, criticized
B. afflicted, downtrodden
C. consistent, damaged
D. associated, vulnerable
E. imbued, exposed
-
A. management, voluminous
B. higher, vulnerable
C. neglects, better
D. refuses, higher
E. denies, superior
-
A. fabulously, intricate
B. meticulously, extensive
C. leisurely, complete
D. hardly, national
E. closely, scattered
-
A. witnessing, ambitious
B. observing, listless
C. recovering, debt
D. demonstrating, efficient
E. succumbing, lean
-
A. (B) and (E)
B. (A) and (C)
C. (A) and(F)
D. (B) and (D)
E. (C) and (E)
-
A. (D) and (F)
B. (A) and (C)
C. (C) and (F)
D. (D) and (E)
E. (B) and (D)
-
A. (C) and (F)
B. (A) and (E)
C. (C) and (E)
D. (D) and (F)
E. (A) and (C)
-
A. (B) and (C)
B. (C) and (F)
C. (A) and (E)
D. (A) and (D)
E. (D) and (E)
-
A. (A) and (D)
B. (B) and (C)
C. (C) and (E)
D. (E) and (F)
E. (C) and (D)
-
A. If one pray
B. One if prays
C. If one will praying
D. If one prayed
E. No correction required
-
A. am looking forward to seeing
B. are looking to see forward
C. are looking forward seeing
D. are looking forward to seeing
E. no correction required
-
A. are waiting
B. are awaiting to
C. have been a waiting
D. have been waiting for
E. no correction required
-
A. If he ask
B. had he asked
C. He had asked
D. If he asked
E. no correction required
-
A. will have discovered
B. might discovered
C. have discovered
D. must discover
E. no correction required
-
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. F
-
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. E
E. F
-
A. B
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. F
-
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
-
A. A
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. F
-
A. on
B. in
C. with
D. for
E. from
-
A. short
B. long
C. small
D. tall
E. high
-
A. see
B. look
C. do
D. recognise
E. realise
-
A. plenty
B. scarce
C. minute
D. enough
E. minimum
-
A. really
B. coldly
C. badly
D. happily
E. seriously
-
A. effect
B. result
C cause
D. wisdom
E. affect
-
A. cause
B. rest
C. consequence
D. result
E. get
-
A. revolution
B. pollution
C. resolution
D. evolution
E. solution
-
A. ecological
B. biological
C. logical
D. chronological
E. geographical
-
A. by
B. in
C. out
D. through
E. from
116. RBI increased the validity period of the in-principle approval of setting up of new banks from one year to
-
A. 14 months
B. 16 months
C. 18 months
D. 20 months
E. None of these
-
A. to define and implement the monetary policy for the Eurozone
B. to conduct foreign exchange operations
C. to maintain price stability within the Eurozone.
D. to take care of the foreign reserves of the European System of Central Banks and operation of the financial markets.
E. None of these
-
A. Article 2 of the Constitution of India
B. Article 239 A of the Constitution of India
C. Article 358 of the Constitution of India
D. Article 371-D of the Constitution of India
E. None of these
-
A. Bharat Electronics Limited
B. Indian Oil Corporation
C. Airports Authority of India
D. Rural Electrification and Corporation Limited
E. None of these
-
A. Kempegowda International Airport
B. Kochi International Airport
C. Indira Gandhi International Airport
D. Rajiv Gandhi International Airport
E. None of these
-
A. grocery industry
B. railroad industry
C. word-processing industry
D. banking industry
E. None of these
-
A. Marketing makes the company loose money due to high cost.
B. Marketing is not important in profit- making companies
C. Marketing sharpens the mind set of the employees
D. Marketing is a time-bound seasonal function
E. Marketing is a waste
-
A. 12
B. 14
C. 15
D. 16
E. None of these
-
A. Cash Rate Requirements
B. Cash Reserve Ratio
C. Credit Rate Requirements
D. Credit Reserve Requirements
E. None of these
-
A. Pulitzer prize
B. Magsaysay award
C. Booker prize
D. Right livelihood award
E. None of these
-
A. Myanmar
B. Sri Lanka
C. Bhutan
D. Maldives
E. None of these
-
A. Devkinandan Khatri
B. Sharat Chand Chaudhary
C. Vrindavanlal Verma
D. Mahadevi Verma
E. None of these
-
A. Jindal Group
B. Reliance Group
C. Future Group
D. Aditya Birla Group
E. None of these
-
A. Allow the merger and acquisition of banks so that only few big banks exist and continue to cater to the need of corporate sector.
B. Providing insurance cover to each and every citizen so that he/she can live a healthy and long life.
C. Expanding the network of banks of such a way that people from lower strata of society also get the benefit of services provided by banks
D. To manage banking operations smoothly and merge nationalised banks for further financial settlements.
E. None of these
-
A. financing of irrigation projects by banks
B. development of forestry by banks
C. financing of environment friendly projects by banks
D. Managing fishery by banks.
E. None of these
-
A. Narayan Lakshman
B. Greg Lindsay
C. Khushwant Singh
D. Salman Rushdie
E. None of these
-
A. South Asian Preferential Trade Agreement
B. South Asian Post Trade Agreement
C. SAARC Preferential Trade Agreement
D. SAARC Post Trade Agreement
E. None of these
-
A. Journalism
B. Social work
C. Peace initiatives
D. Films
E. None of these
-
A. NRDP
B. IRDP
C. ASHA
D. Bharat Nirman
E. All of these
-
A. Kalinga Prize
B. Dhyanchand Award
C. Arjun Award
D. Moortidevi Award
E. Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award
-
A. Wolf hall
B. Sea of Poppies
C. Silent Spring
D. The Grass is Singing
E. None of these
-
A. Issue management
B. Market maker in capital market
C. Capital structuring/restructuring
D. All of the above
E. None of these
-
A. Bank of India
B. Canara Bank
C. State Bank of India
D. Indian Bank
E. None of these
-
A. contribution by the employees of a business enterprise in the provident fund scheme
B. fund created by commercial banks and other eligible financial institutions for floating new shares in the market to earn a higher profit
C. the business of acquisition, holding managment, trading or disposal of securities participation certificates or any other instruments, income or growth
participation business and Unit Trust schemes
D. All of the above
E. None of these
-
A. real estate and plantation projects
B. capital market instruments such as shares, debentrures and other securities
C. gilt-edged securities only
D. government securities only
E. None of these
-
A. collection of funds from the public
B. investment of the resources raised in capital markets
C. holding investment in trust and ensuring proper management of investment portfolio
D. All of the above
E. None of these
-
A. World Bank
B. Asian Development Bank
C. IMF
D. It is known by its name
E. None of these
-
A. Asian Development Bank
B. IMF
C. International Developmental Association
D. International Finance Corporation
E. None of these
-
A. Asian Development Bank
B. IMF
C. International Developmental Association
D. International Finance Corporation
E. None of these
-
A. decrease in the internal value of money
B. decrease in the external value of money
C. decrease both in the external and internal values of money
D. increase in the internal value of money
E. None of these
-
A. bearer cheques
B. credit cards
C. demand drafts
D. gift cheques
E. None of these
-
A. 1975
B. 1947
C. 1956
D. 1960
E. None of these
-
A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Only 3
D. All
E. None of these
-
A. Union Government
B. Reserve Bank of India
C. Ministry of Finance
D. Supreme Court
E. None of these
-
A. Howrah Rajdhani
B. Swarna Jayanti Rajdhani
C. August Kranti Rajdhani
D. ibrugarh Rajdhani
E. None of these
-
A. Reorganize, Restructure Rejuvenate Indian Railways: 'Chalo, Milkar Kuch Karen'
B. Chalo, Milkar Kuch Naya Karen: 'Navinikaran, Sashaktikaran, Shodh aur Vikas'
C. Nav Arjan, Nav Manak, Nav Sanranchna: 'Chalo, Milkar Kuch Karen'
D. Reorganize, Restructure Rejuvenate Indian Railways: 'Nav Arjan, Nav Manak, Nav Sanranchna'
E. None of these
-
A. Israel
B. Philippines
C. United States
D. Russia
E. None of these
-
A. State Bank of India
B. ICICI Bank
C. DCB Bank
D. Axis Bank
E. None of these
-
A. April 3
B. April 4
C. April 5
D. April 6
E. None of these
-
A. Reserved accommodation on trains available on demand and time tabled freight trains.
B. High end technology to improve safety record, elimination of all unmanned level crossings and higher average speed of freight trains.
C. Semi high speed trains running along the golden quadrilateral and zero direct discharge of human waste
D. All of the above
E. None of these