Introduction
Introduction
UK Cooperative Bank Senior Branch Manager Recruitment Study Guide, will comprise of Objective Tests for 200 marks consisting of 6 Sections as follows. A composite time of 2 Hours will be given for answering the questions. The below sections gives the detailed information about UK Cooperative Bank Senior Branch Manager Study Guide Section.
 Pattern
Pattern
| Sr.No. | Name of Tests | Medium of Exam | No. of Questions | Maximum Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reasoning | Hindi/ English | 40 | 40 | Composite time of 2 hours |
| 2 | Quantitative Aptitude & Data Interpretation | Hindi/ English | 40 | 40 | |
| 3 | Financial Awareness | Hindi/ English | 60 | 60 | |
| 4 | English Language | English | 20 | 20 | |
| 5 | Hindi Language | Hindi | 20 | 20 | |
| 6 | Computer Knowledge | Hindi/ English | 20 | 20 | |
| Total | 200 | 200 | |||
 Syllabus
Syllabus
[Click Here] for UK Cooperative Bank Online Exam Syllabus
Note: Peanlity for Wrong Answers:
There will be penalty for wrong answers marked in the Objective Tests. For each question for which a wrong answer has been given by the candidate one fourth or 0.25 of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as penalty to arrive at corrected score. If a question is left blank, i.e. no answer is marked by the candidate; there will be no penalty for that question.
 Samples
Samples
Direction (1-5): Study the information given below and answer the questions based on it.
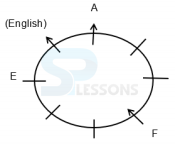
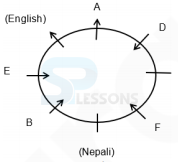
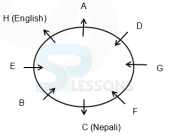
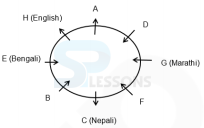
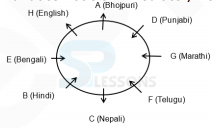
Eight persons - A, P, B, Q, C, R, D and S are sitting around a circular table, but not necessarily in the same order. Some of them are facing inside while rest of them are facing outside. Each of them likes different subject viz. Hindi, English, Nepali, Telugu, Marathi, Punjabi, Bhojpuri and Bengali.
F does not sit immediately next to A. Only two persons sit between G and H. Immediate left of A likes English, who faces the outside the centre. F and E are facing the same side and only two persons are sitting between them. The one who likes Punjabi sits immediately next to the one who likes Bhojpuri but not faces the one who likes Nepali. E sits second to the left of A. The one who likes Marathi faces the one who likes Bengali. D sits diagonally opposite to B who sits to the immediate right of E and both of them are facing same direction. The one who likes Nepali sits between F and B. The one who likes Hindi does not sit immediately next to F and F is not hindi. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F. C sits second to the left of G. The one who likes Bengali sits second to the right of the one who likes Nepali. The
one who likes Punjabi and the one who likes Telgu faces the same direction. G is facing the centre.
1. Who among the following likes Telugu?
-
A. C
B. B
C. A
D. H
E. F
- 1) Immediate left of A likes English, who faces the centre. E sits second to the left of A. F and E are facing the same side and only two persons are sitting between them. F does not sit immediately next to A. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
2) D sits diagonally opposite to B who sits to the immediate right of E and both of them are facing each other. The one who likes Nepali sits between F and B. Hence, E, D and F face the centre.
3) Only two persons sit between G and H. C sits second to the left of G. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
Hence, G faces the centre.
4) The one who likes Bengali sits second to the right of the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Marathi faces the one who likes Bengali.
5) The one who likes Punjabi sits immediately next to the one who likes Bhojpuri but not faces the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Hindi does not sit immediately next to F.
Hence, F likes Telugu.
-
A. B
B. D
C. C
D. H
E. F
- 1) Immediate left of A likes English, who faces the centre. E sits second to the left of A. F and E are facing the same side and only two persons are sitting between them. F does not sit immediately next to A. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
2) D sits diagonally opposite to B who sits to the immediate right of E and both of them are facing each other. The one who likes Nepali sits between F and B.
Hence, E, D and F face the centre.
3) Only two persons sit between G and H. C sits second to the left of G. A and C are facing
outward direction but not as F.
Hence, G faces the centre.
4) The one who likes Bengali sits second to the right of the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Marathi faces the one who likes Bengali.
5) The one who likes Punjabi sits immediately next to the one who likes Bhojpuri but not
faces the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Hindi does not sit immediately next to F.
Hence, F likes Telugu.
Hence, H sits between A and E.
-
A. A sits immediate next to D
B. G and C face the same direction.
C. D faces the person who likes Hindi.
D. H and F sit opposite to each other
E. All of the above
- 1) Immediate left of A likes English, who faces the centre. E sits second to the left of A. F and E are facing the same side and only two persons are sitting between them. F does not sit immediately next to A. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
2) D sits diagonally opposite to B who sits to the immediate right of E and both of them are facing each other. The one who likes Nepali sits between F and B.
Hence, E, D and F face the centre.
3) Only two persons sit between G and H. C sits second to the left of G. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
Hence, G faces the centre.
4) The one who likes Bengali sits second to the right of the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Marathi faces the one who likes Bengali.
5) The one who likes Punjabi sits immediately next to the one who likes Bhojpuri but not faces the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Hindi does not sit immediately next to F.
Hence, G and C do not face the same direction.
-
A. A
B. B
C. H
D. G
E. F
- 1) Immediate left of A likes English, who faces the centre. E sits second to the left of A. F and E are facing the same side and only two persons are sitting between them. F does not sit immediately next to A. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
2) D sits diagonally opposite to B who sits to the immediate right of E and both of them are facing each other. The one who likes Nepali sits between F and B.
Hence, E, D and F face the centre.
3) Only two persons sit between G and H. C sits second to the left of G. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
Hence, G faces the centre.
4) The one who likes Bengali sits second to the right of the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Marathi faces the one who likes Bengali.
5) The one who likes Punjabi sits immediately next to the one who likes Bhojpuri but not faces the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Hindi does not sit immediately next to F.
Hence, G faces the one who sits second to the right of C.
-
A. D
B. F
C. B
D. A
E. G
- 1) Immediate left of A likes English, who faces the centre. E sits second to the left of A. F and E are facing the same side and only two persons are sitting between them. F does not sit immediately next to A. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
2) D sits diagonally opposite to B who sits to the immediate right of E and both of them are facing each other. The one who likes Nepali sits between F and B.
Hence, E, D and F face the centre.
3) Only two persons sit between G and H. C sits second to the left of G. A and C are facing outward direction but not as F.
Hence, G faces the centre.
4) The one who likes Bengali sits second to the right of the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Marathi faces the one who likes Bengali.
5) The one who likes Punjabi sits immediately next to the one who likes Bhojpuri but not faces the one who likes Nepali. The one who likes Hindi does not sit immediately next to F.
Hence, A faces away from the centre while rest faces the centre.
- Step I: angry disable 55 73 medical 56 treatment 84 egg 15 over 93
Step II: angry egg disable 55 medical 56 treatment 84 15 over 73 93
Step III: angry egg over disable medical 56 treatment 84 15 55 73 93
Step IV: angry egg over disable medical 56 treatment 84 15 55 73 93
Step V: angry egg over disable medical treatment 56 84 15 55 73 93
Step V, is the last step of the above arrangement as the intended arrangement is obtained.
-
A. VI
B. V
C. IV
D. VII
E. None of these
Explanation:
In this input output question only one word and one number is arranged in each step. As a first step let us first understand the logic behind the question. If we will see the final output we will observe the following:
(1) For words – If the first letter of the word is a vowel then it is arranged first from left to right. If two words have first letter a vowel then they are arranged according to the English alphabet. The words does not starting with a vowel is arranged as arranged in the English dictionary.
(2) For numbers – The numbers are arranged according to the odd and even concept. The highest odd number is arranged first from right to left followed by the arrangement of even numbers.
INPUT: shift 54 36 routine 49 lunch 59 dinner 11 breakfast class 89
7. In step IV, which of the following word/ number would be on the fifth position (from the right)?
- Step I: breakfast shift 54 36 routine 49 lunch 59 dinner 11 class 89
Step II: breakfast class shift 54 36 routine 49 lunch dinner 11 59 89
Step III: breakfast class dinner shift 54 36 routine lunch 11 49 59 89
Step IV: breakfast class dinner lunch shift 54 36 routine 11 49 59 89
Step V: breakfast class dinner lunch routine shift 36 54 11 49 59 89
-
A. 11
B. routine
C. 36
D. 54
E. shift
-
A. 51
B. 25
C. 29
D. 31
E. None of these
-
A. routine
B. 54
C. shift
D. 11
E. 36
-
A. lunch
B. routine
C. dinner
D. 36
E. 54
1. Interest earned on an amount after 2 years at 20% p.a compounded yearly is Rs.2552. Find the interest earned on
same amount after 4 years at 17 %p.a at Simple interest.
-
A. Rs. 3564
B. Rs. 3944
C. Rs. 4235
D. Rs. 4456
E. Rs. 3644
-
A. 6460
B. 6160
C. 4400
D. 5760
E. 6660
-
A. 210.5 min
B. 160 min
C. 240.7 min
D. 110.4 min
E. None of these
-
A. a > b
B. a ≤ b
C. a < b
D. a ≥ b
E. a = b
-
A. Only III
B. Only either I or III
C. Only II
D. Only either I or II
E. Question can’t be answered even with the help of all the three statements.
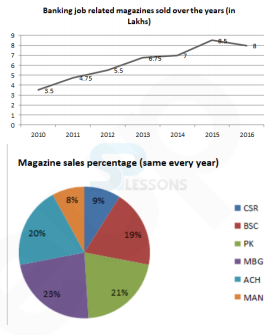
-
A. 140000
B. 132000
C. 92000
D. 123750
E. None of the above
-
A. PK by ₹280000
B. CSR by ₹280000
C. PK by ₹240000
D. CSR by ₹320000
E. PK by ₹290000
-
A. 234000
B. 124000
C. 154000
D. 184000
E. 194000
-
A. ₹95
B. ₹65
C. ₹115
D. ₹50
E. ₹150
-
A. ₹1920000
B. ₹1620000
C. ₹2920000
D. ₹1580000
E. ₹1250000
1. What is the full form of BHIM?
-
A. Bank Interface for Money
B. Balance Interface for Mobile
C. Bharat Interface for Mobile
D. Bharat Interface for Money
E. Bank Interbank for Money
-
A. Dollar
B. Pound
C. Ruble
D. Rial
E. Euro
-
A. 2,000 Km
B. 1.000 Km
C. 5,000 Km
D. 4,000 Km
E. 500 Km
-
A. Fixed Deposit Account
B. Saving Account
C. Current Account
D. Recurring Account
E. Demat Account
-
A. 10 lakh
B. 15 lakh
C. 17 lakh
D. 19 lakh
E. 20 lakh
-
A. Telecom
B. Total
C. Transfer
D. Time
E. Treasury
Direction (1-7): Read the given passage carefully and answer the questions that follow. Certain words are printed in bold to help you locate them while answering some of these.
The threat of global warming can still be greatly diminished if nations cut emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases by 70 percent this century, according to a new analysis. While global temperatures would raise, the most dangerous potential aspects of climate change, including massive losses of Arctic sea ice and permafrost and significant sea level rise, could be partially avoided.
"This research indicates that we can no longer avoid significant warming during this century," says NCAR scientist Warren Washington, the lead author. "But if the world were to implement this level of emission cuts, we could stabilize the threat of climate change and avoid catastrophe."
Average global temperatures have warmed by close to 1 degree Celsius (almost 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit) since the pre-industrial era. Much of the warming is due to human-produced emissions of greenhouse gases, predominantly carbon dioxide. This heat-trapping gas has increased from a pre-industrial level of about 284 parts per million (ppm) in the atmosphere to more than 380 ppm today. With research showing that additional warming of about 1 degree C (1.8 degrees F) may be the threshold for dangerous climate change, the European Union has called for dramatic cuts in emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
To examine the impact of such cuts on the world's climate, Washington and his colleagues ran a series of global supercomputer studies with the NCARbased Community Climate System Model. They assumed that carbondioxide levels could be held to 450 ppm at the end of this century. That figure comes from the U.S. Climate Change Science Program, which has cited 450ppm as an attainable target if the world quickly adapts conservation practices and new green technologies to cut emissions dramatically. In contrast, emissions are now on track to reach about 750 ppm by 2100 if unchecked. The team's results showed that if carbondioxide were held to 450 ppm, global temperatures would increase by 0.6 degrees C (about 1 degree F) above current readings by the end of the century.
In contrast, the study showed that temperatures would rise by almost four times that amount, to 2.2 degrees C (4 degrees F) above current readings, if emissions were allowed to continue on their present course. Holding carbondioxide levels to 450 ppm would have other impacts, according to the climate modelling study. Sea level rise due to thermal expansion as water temperatures warmed would be 14 centimetres (about 5.5 inches) instead of 22 centimetres (8.7 inches). Significant additional sea level rise would be expected in either scenario from melting ice sheets and glaciers.
Arctic ice in the summertime would shrink by about a quarter in volumes and stabilize by 2100, as opposed to shrinking at least three-quarters and continuing to melt. Some research has suggested the summertime ice will disappear altogether this century if emissions continue on their current trajectory. Arctic warming would be reduced by almost half, helping preserve fisheries and populations of sea birds and Arctic mammals in such regions as the northern Bering Sea.
1. Which of the following is the central concern of the passage?
I. The central theme of the passage is the ways in which global warming has affected human life in this century.
II. The passage explains how global warming can be prevented from increasing in this century.
III. The passage explains the fact that global warming is the main difference between today's world and a pre–industrial era.
-
A. Only I and II
B. Only II and III
C. Only II
D. Only I and III
E. All I, II and III
-
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only III
D. Only I and II
E. All I, II and III
-
A. Climate impact as a function of global temperature.
B. Climate models stimulating global warming.
C. Earth’s climate is approaching a dangerous point.
D. Avoiding dangerous climate change.
E. None of these
-
A. If countries cut down on greenhouse emissions, the threat of global warming will cease to remain a threat.
B. If countries stop emitting 70% of their greenhouse gases, the great loss of Arctic sea ice can be prevented.
C. If countries add any more to the emissions of greenhouse gases, especially carbon dioxide, the temperature will increase by 1 degree Celsius.
D. If countries together reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by 70%, the significant rise in sea level could be contained, at least to an extent.
E. If countries cut down on their greenhouse gas emissions by a large margin, global warming will continue but no dangerous instances of climate change will be felt.
-
A. Only I
B. Only I and II
C. Only III
D. Only I and III
E. All I, II and III
-
A. Dramatic cut in carbon dioxide emissions, reduce sea level rise.
B. The worst impact of climate change, increase sea level rise.
C. The climate is approaching dangerous point continuing major cuts through the century.
D. Cuts in greenhouse gas emissions would save Arctic ice, reduce sea level rise.
E. None of the above
-
A. Embrace
B. Virtuoso
C. Consummate
D. Accede
E. Accustom
1. The ________ button on the Quick Access Toolbar allows you to cancel your recent commands or actions.
-
A. Search
B. Cut
C. Document
D. Undo
E. None of these
-
A. Java
B. system software
C. DBMS
D. application software
E. None of these
-
A. Motionware
B. Anigraphics
C. Videoscapes
D. Multimedia
E. None of these
-
A. QBE
B. SQL
C. OLAP
D. Sequel Server
E. None of these
-
A. 4
B. 8
C. 16
D. 32
E. 64