Description
Description
Servlet Form, The functionality of using servlet concept is to provide efficient maintenance, develop web applications. While working on big projects, client may need credentials to utilize an application so following example describes how to build an application using servlet, in the following example SPlessons have taken one requirement that is how to use splessons services before that user has to register by providing details. Any credentials will need a database to store the data like that here used MySQL, here by using commands first create a table and based on the table columns developer prepare the fields to enter the details. Following is the practice example which elaborates more regarding this chapter.
 Example
Example
Servlet Form - Following is an example to register user details and how details will store in the database.
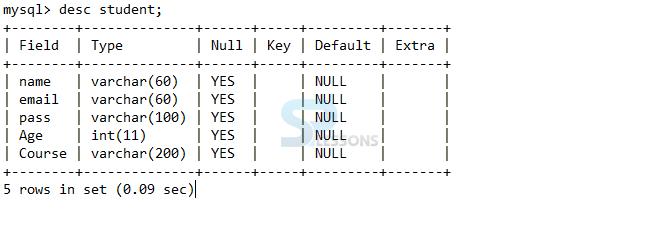
create database
First create the database as follows.
index.html
[html]<html>
<head>
<title>Register form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="post" action="register">
<table cellpadding="2" width="20%" align="center"
cellspacing="2">
<tr>
<td colspan=2>
<center><font size=4><b>SPlesson Registration Form</b></font></center>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Name:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="name" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="pass" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Email ID:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="email" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> Age:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="Age" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> Course:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="Course" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="register" onclick="();" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
<body bgcolor="skyblue">
</body>
</html>[/html]
HTTP POST asks for supply extra information from the clent (program) to the server in the message body.
Register.java
[java]package servletregistrationform;
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import java.sql.*;
public class Register extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String name = request.getParameter("name");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
String pass = request.getParameter("pass");
String Age = request.getParameter("Age");
String Course = request.getParameter("Course");
try{
//loading drivers for mysql
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//creating connection with the database
Connection con=DriverManager.getConnection
("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test_db","root","root");
PreparedStatement ps=con.prepareStatement
("insert into Student values(?,?,?,?,?)");
ps.setString(1, name);
ps.setString(2, email);
ps.setString(3, pass);
ps.setString(4, Age);
ps.setString(5, Course);
int i=ps.executeUpdate();
if(i>0)
{
out.println("Hi Man, You are sucessfully registered");
}
else
{
out.println("please enter your details");
}
}
catch(Exception se)
{
se.printStackTrace();
}
}
}[/java]
The doPost() shall be used when comparatively large amount of sensitive data has to be sent. Examples are sending data after filling up a form or sending login id and password. Sets the content type of the response being sent to the client, if the response has not been committed yet. The given content type may include a character encoding specification.
The java.lang.Class.forName(String name, boolean introduce, ClassLoader loader) strategy gives back the Class object connected with the class or interface with the given string name, utilizing the given class loader. The predetermined class loader is utilized to stack the class or interface.
The PreparedStatement interfaces characterize the strategies and properties that empower you to send SQL or PL/SQL orders and get information from your database. They likewise characterize techniques that scaffold information sort contrasts amongst Java and SQL information sorts utilized as a part of a database.
web.xml
[xml]<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>register</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>servletregistrationform.Register</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>register</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/register</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>[/xml]
Output
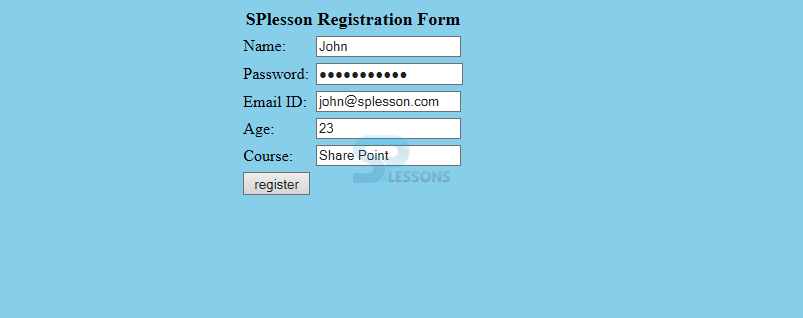
When compile the code registration form will be displayed as follows. Where enter the details as follows.
When click on register button following message will be displayed.
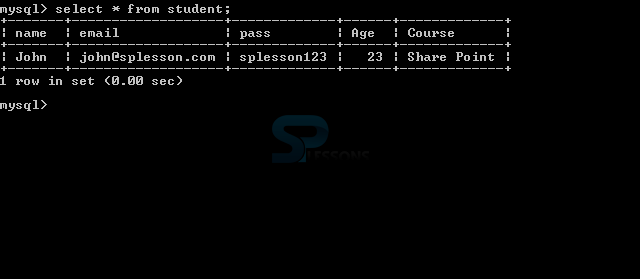
Check the database where details will be stored.
 Description
Description
The following are the some important differences between getAttribute() and getParameter().
getParameter()
- The getParameter will give back the value of a parameter that was put together by a HTML shape or that was incorporated into a query string
- Here the string is the return type of a parameter.
- The request.getParameter() is utilized for authenticating variable from JSP or HTML .
- The getAttribute gives back a protest that client have set in the demand, the main way you can utilize this is in conjunction with a RequestDispatcher. Client utilize a RequestDispatcher to forward a request to another resource.
- Here the object is the return type of a attribute.
- The RequestDispatcher.forward() and request.getAttribute() in JSP are used for accessing variables
 Key Points
Key Points
- Servlet Form - Make sure to add MySQLconnector jar file.
- Servlet Form - Make sure to mention database name, user name, password.
- Create the database before start coding.