Introduction
Introduction
RRB NTPC (Non-Technical Popular Categories) 2019 – Second Stage Computer Based Test (CBT), conducted in online Mode, has: a duration of 90 minutes [120 Minutes for eligible PwBD candidates accompanied with Scribe], consists of 3 sections, namely – General Awareness, Mathematics and General Intelligence & Reasoning. The total number of questions are 120. The 3 sections are not separately timed. There is a Negative marking in RRB NTPC Second Stage CBT and 1/3rd marks are deducted for each wrong answer. The below sections gives the detailed information about RRB NTPC Reasoning in the Second Stage CBT.
 Pattern
Pattern
| Exam Duration in Minutes | No. of Questions (each of 1 mark) from | Total No. of Questions | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Awareness | Mathematics | General Intelligence and Reasoning | ||
| 90 | 50 | 35 | 35 | 120 |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
[Click Here] for RRB NTPC Second Stage CBT Syllabus
Note:
Negative Marking: There will be negative marking and 1/3 mark shall be deducted for each wrong answer.
 Samples
Samples
Analogies
1. Elated is to despondent as enlightened is to
- A. aware
B. ignorant
C. miserable
D. tolerant
- A. gloomy
B. mean
C. petty
D. helpful
- A. petal
B. stem
C. daisy
D. alligator
- A. symphony
B. musician
C. piano
D. percussion
- A. massive
B. solid
C. elastic
D. inflexible
- A. 44
B. 45
C. 46
D. 47
- A. 42
B. 51
C. 81
D. 91
- A. 12
B. 13
C. 14
D. 15
- A. 324
B. 243
C. 210
D. 162
- A. 14
B. 16
C. 18
D. 24
- A. CBT
B. ABR
C. BCT
D. RBB
- A. xyzyy
B. yyyzz
C. yxzyx
D. xyyzz
- A. xyyyzz
B. xyzyzy
C. yxzyxy
D. yzxyxy
- A. FXW
B. EFX
C. FEY
D. HDW
- A. xxxyy
B. xyxyy
C. yxyxy
D. yxyyx
- A. MFEDJJOE
B. EOJDEJFM
C. MFEJDJOE
D. EOJDJEFM
- A. 9
B. 2
C. 1
D. 8
- A. SHFDQ
B. HFDSQ
C. RSAFD
D. QDFHS
- A. EDRIRL
B. DCQHQK
C. ESJFME
D. DEQJQM
- A. 39
B. 41
C. 44
D. 46
- A. x, x, x
B. -, +, x
C. x, +, x
D. +, -, x
- A. 18
B. 28
C. 31
D. 103
- A. 80
B. 25
C. 24
D. 5
- A. 4 + 8 - 12 = 12
B. 4 - 8 + 12 = 0
C. 8 + 4 - 12 = 24
D. 8 - 4 + 12 = 8
- A. 20
B. 29
C. 28
D. 24
- A. Dress
B. Panda
C. Bear
D. Fox
- A. CPU
B. Monitor
C. Kangaroo
D. Keyboard
- A. Thirty
B. Fifty
C. Seventy
D. Camera
- A. Time
B. Chain
C. Bangle
D. Bracelet
- A. Week
B. Head
C. Year
D. Month
Relationships
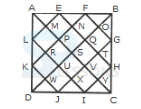
1. If X is the brother of the son of Y`s son, how is X related to Y?
- A. Son
B. Brother
C. Cousin
D. Grandson
E. Uncle
- A. Mother
B. Aunt
C. Sister
D. Daughter
E. Grandmother
- A. Son
B. Brother
C. Nephew
D. Father
- A. Daughter
B. Brother-in-Law
C. Husband
D. Sister-in-Law
- A. Nil
B. One
C. Two
D. Three
- A. 16
B. 18
C. 14
D. 15
- A. 18
B. 20
C. 28
D. 34
- A. 20
B. 24
C. 28
D. 32
- A. 11
B. 14
C. 16
D. 17
- A. 28
B. 32
C. 36
D. 40
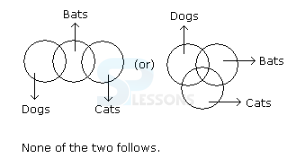
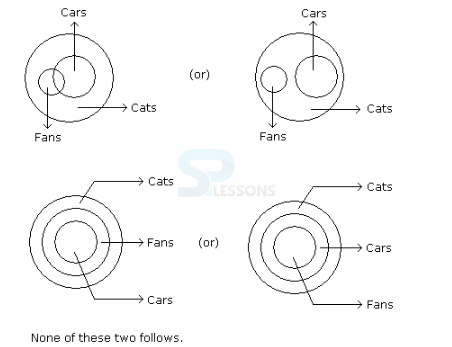
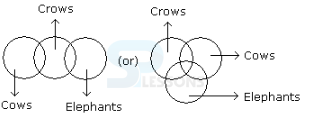
- A. If only (1) conclusion follows
B. If only (2) conclusion follows
C. If either (1) or (2) follows
D. If neither (1) nor (2) follows and
E. If both (1) and (2) follow.
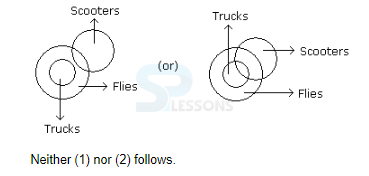
- A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
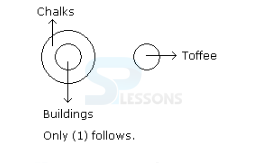
- A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
- A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
- A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
- A. Only (1) conclusion follows
B. Only (2) conclusion follows
C. Either (1) or (2) follows
D. Neither (1) nor (2) follows
E. Both (1) and (2) follow
- A. D and A
B. B and C
C. A and B
D. A and C
E. None of these
- A. A
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. B
- A. A
B. B
C. C
D. E
E. D
- A. A and D
B. B and E
C. C and E
D. C and D
E. A and C
- A. B
B. C
C. E
D. D
E. A
- A. 10
B. 11
C. 12
D. 13
- A. 3
B. 1
C. 6
D. 14
- A. 3
B. 5
C. 1
D. 7
- A. 13
B. 2
C. 11
D. 1
- A. 34
B. 12
C. 2
D. 1
Data Sufficiency
Direction (1 - 5): In each of the questions below consists of a question and two statements numbered I and II given below it. You have to decide whether the data provided in the statements are sufficient to answer the question. Read both the statements and
Give answer
A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement II alone are not sufficient to answer the question
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question, while the data in statement I alone are not sufficient to answer the question
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient to answer the question
D. If the data given in both statements I and II together are not sufficient to answer the question and
E. If the data in both statements I and II together are necessary to answer the question.
1. How is T related to K?
Statements:
I. K has two sons; one of the sons is A.
II. The mother of T has only two sons - Aand B.
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. I alone is sufficient while II alone is not sufficient
B. II alone is sufficient while I alone is not sufficient
C. Either I or II is sufficient
D. Neither I nor II is sufficient
E. Both I and II are sufficient
- A. The only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. The only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. The only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. The only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. The only conclusion I follows
B. Only conclusion II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. Only I follows
B. Only II follows
C. Either I or II follows
D. Neither I nor II follows
E. Both I and II follow
- A. be a graduate with at least 50 % marks.
B. have secured at least 40 % marks in the written test.
C. is not less than 24 years and more than 29 years as on 10th October 1997.
D. should have work experience of at least two years as an officer.
E. fulfills all other criteria except at (4) above but has a diploma in Marketing Management, his/her case is to be referred to General Manager, Marketing.
F. fulfills all other criteria except at (3) above but has worked as Maketting Officer at least for three years, his/her case is to be referred to Director, Marketing.
- A. be a graduate with at least 50 % marks.
B. have secured at least 40 % marks in the written test.
C. is not less than 24 years and more than 29 years as on 10th October 1997.
D. should have work experience of at least two years as an officer.
E. fulfills all other criteria except at (4) above but has a diploma in Marketing Management, his/her case is to be referred to General Manager, Marketing.
F. fulfills all other criteria except at (3) above but has worked as Marketing Officer at least for three years, his/her case is to be referred to Director, Marketing.
- A. be a graduate with at least 50 % marks.
B. have secured at least 40 % marks in the written test.
C. is not less than 24 years and more than 29 years as on 10th October 1997.
D. should have work experience of at least two years as an officer.
E. fulfills all other criteria except at (4) above but has a diploma in Marketing Management, his/her case is to be referred to General Manager, Marketing.
F. fulfills all other criteria except at (3) above but has worked as Marketing Officer at least for three years, his/her case is to be referred to Director, Marketing.
- A. be a graduate with at least 50 % marks.
B. have secured at least 40 % marks in the written test.
C. is not less than 24 years and more than 29 years as on 10th October 1997.
D. should have work experience of at least two years as an officer.
E. fulfills all other criteria except at (4) above but has a diploma in Marketing Management, his/her case is to be referred to General Manager, Marketing.
F. fulfills all other criteria except at (3) above but has worked as Marketing Officer at least for three years, his/her case is to be referred to Director, Marketing.
- A. be a graduate with at least 50 % marks.
B. have secured at least 40 % marks in the written test.
C. is not less than 24 years and more than 29 years as on 10th October 1997.
D. should have work experience of at least two years as an officer.
E. fulfills all other criteria except at (4) above but has a diploma in Marketing Management, his/her case is to be referred to General Manager, Marketing.
F. fulfills all other criteria except at (3) above but has worked as Marketing Officer at least for three years, his/her case is to be referred to Director, Marketing.
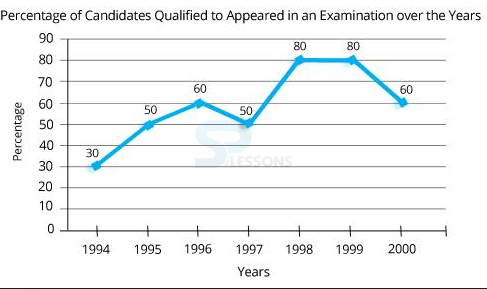
- A. 1994 and 1995
B. 1997 and 1998
C. 1998 and 1999
D. 1999 and 2000
- A. 1995 and 1997
B. 1995 and 2000
C. 1998 and 1999
D. Data inadequate
- A. 32000
B. 28500
C. 26500
D. 25000>
- A. 34700
B. 32100
C. 31500
D. Data inadequate
- A. 24500
B. 22000
C. 20500
D. 19000