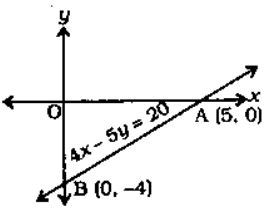
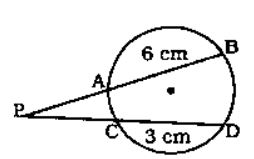
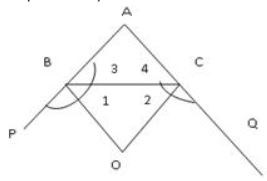
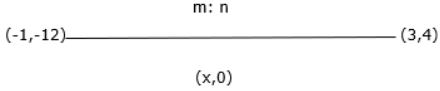Introduction
Introduction
What is Quantitative Aptitude?
Quantitative aptitude is one of the top competitive subject which will students really want to learn and to be expert. Quantitative Aptitude Tests evaluate numerical ability and problem solving skills of candidates. This test forms the major part of a number of important entrance exams for different fields.
The article RRB JE 2019 Quantitative Aptitude Quiz provides Quantitative aptitude questions with answers useful to the candidates preparing for Competitive exams, Entrance exams, Interviews etc. Railway Recruitment Board (RRB) has released RRB JE 2019 Official Notification to recruit eligible candidates for the post of it Railway JE Recruitment 2018-19 will be held to recruit candidates for the posts of Junior Engineer(JE), Junior Engineer(Information Technology), Depot Material Superintendent(DMS) and Chemical & Metallurgical Assistant(CMA). Quantitative Aptitude plays major role to qualify examination. The article RRB JE 2019 Quantitative Aptitude Quiz will assist the students understand the type of questions expected from the topic Quantitative Aptitude .
Click Here for RRB JE official website
 Quiz
Quiz
1. If 7x - 5y = 13 and 2x - y = 5, then (x - y) is
- A.3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 1
- A.10 percent
B. 5 percent
C. 20 percent
D. 16percent
- A.xy
B. xz/y
C. xy/z
D. xyz
- A.385 marks
B. 410 marks
C. 360 marks
D. 435 marks
- A.28, 28
B. 32, 24
C. 30, 26
D. 29, 27
- A. 6.4 percent loss
B. 3.2 percent gain
C. 6.4 percent gain
D. 3.2 percent loss
- A. 48 : 35
B. 28 : 15
C. 24 : 20
D. 20 : 21
- A. 54 km
B. 45 km
C. 36 km
D. 27 KM
- A. 0.6
B. 0.2
C. 9.75
D. 0.8
- A. cosec A - cot A
B. cosec A + cot A
C. [latex]\sqrt{(cosec A - cot A)}[/latex]
D. [latex]\sqrt{(cosec A + cot A)}[/latex]
1. Find the difference between the unit digits of a and b
a= [latex](437)^{253} [/latex].[latex](134)^{337} [/latex]
b= [latex](437)^{253} [/latex][latex](134)^{337} [/latex].[latex](132)^{653} [/latex][latex](559)^{381} [/latex]
- A. 2
B. 5
C. 4
D. 0
- A. 8
B. 6
C. 2
D. 4
- A. 4
B. 6
C. 8
D. 2
- A. 1
B. 3
C. 7
D. 9
- A. 0
B. 1
C. 3
D. 2
- A. 1
B. 4
C. 9
D. 0
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 0
- A. 0
B. 1
C. 7
D. 21
- A. 0
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
- A. 7
B. 2
C. 8
D. 1
1. x + [latex]\frac{1}{x}[/latex], then the value of [latex]x^{7}[/latex] + [latex]\frac {1}{x^ {5}}[/latex] is
- A. [latex](2)^{12}[/latex]
B. 2
C. [latex](2)^{5}[/latex]
D. [latex](2)^{7}[/latex]
- A. abc + 3
B. 6
C. 0
D. 3
- A. 3 + [latex]\sqrt {5}[/latex]
B. 3 - [latex]\sqrt {5}[/latex]
C. 5 + [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]
D. 5 - [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]
- A. 15 years
B. 12 years
C. 10 years
D. 20 years
- A. 2
B. 3
C. 5
D. 6
- A. 9600
B. 9200
C. 10500
D. 9540
- A. 12.5
B. 15
C. 20
D. 25
- A. 420
B. 630
C. 840
D. 1680
- A. 22 days
B. 24 days
C. 30 days
D. 20 days
- A. [latex]\frac{\sqrt{3} + 1}{2\sqrt{2}}[/latex]
B.[latex]\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2\sqrt{2}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{\sqrt{3} - 1}{-\sqrt{2}}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{\sqrt{3} - 1}{2\sqrt{2}}[/latex]
1. What is the HCF (highest common factor) of 57 and 513?
- A. 10
B. 57
C. 3
D. 27
- A. 668
B. 693
C. 674
D. 680
- A. 15
B. 7
C. 19
D. 16
- A. 53
B. 45
C. 33
D. 43
- A. 13
B.[latex]\frac{9}{11}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{7}{35}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{4}{35}[/latex]
- A. 15 and 228
B. 9 and 380
C. 45 and 76
D. 46 and 75
- A. 8
B. 12
C. 16
D. 20
- A. 9
B. 10
C. 11
D. 13
- A. 7
B. 8
C. 9
D. 10
- A. 12
B. 24
C. 36
D. 48
1. The sum of the ages of husband and wife at present is 100. Ten years ago the ratio of their ages was 9:7. What is the age of the husband?
- A. 45 years
B. 55 years
C. 65 years
D. 40 years
- A. 55
B. 77
C. 70
D. 96
- A. 5
B. 14
C. 81
D. 8
- A. 52
B. 65
C. 60
D. 32
- A. 5
B. 30
C. 8
D. 48
- A. 28, 28
B. 32, 24
C. 30, 26
D. 29, 27
- A. 81
B. 63
C. 56
D. 80
- A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
- A. 8 years
B. 10 years
C. 12 years
D. 16 years
- A. 28 years
B. 30 years
C. 24 years
D. 26 years
1. A is 4 years younger than B while C is 4 years younger than D but 1/5th times as old as A. If D is 8 years old, how many times as old is B as C?
- A. 6 times
B. 4 times
C. 5 times
D. 2 times
- A. 64 and 32
B. 48 and 16
C. 42 and 18
D. 48 and 20
- A. 15 : 14
B. 14 : 13
C. 16 : 15
D. 17 : 16
- A. 48 years
B. 60 years
C. 84 years
D. 96 year
- A. 18 years
B. 20 years
C. 24 years
D. 32 years
- A. 40 years
B. 55 years
C. 52 years
D. 65 years
- A. 30 years
B. 27 years
C. 25 years
D. 22 years
- A. 18 years
B. 15 years
C. 12 years
D. 20 years
- A. 15 years
B. 13 years
C. 19 years
D. 17 years
- A. 1 year
B. 2 year
C. 3 year
D. 4 year
1. In a class of 55 students there are 34 girls. The average weight of these girls is 51 Kg and average weight of the full class is 55.2 kgs. What is the average weight of the boys of the class?
- A. 62
B. 59.4
C. 56.8
D. 60
- A. Rs 83 lakhs
B. Rs 79 lakhs
C. Rs 77 lakhs
D. Rs 81 lakhs
- A. 51.3
B. 50.6
C. 52
D. 53.4
- A. 53.7
B. 54.4
C. 53
D. 55.8
- A. 50.3
B. 49.6
C. 51
D. 52.4
- A. 3 years
B. 2 years
C. 1 years
D. 1.5 years
- A. 25
B. 18.75
C. 10
D. 2.50
- A. 10 percent
B. 25 percent
C. 14 percent
D. 15 percent
- A. 88
B. 68
C. 126
D. 100
- A. Rs. 98 lakhs
B. Rs. 94 lakhs
C. Rs. 96 lakhs
D. Rs. 92 lakhs
1. Three persons walk from place A to place B. their speed are in the ratio 4 : 3 :5. The ratio f the times taken by them to reach B will be :
- A. 10 : 15 : 13
B. 2 : 3: 4
C. 15 : 20 : 12
D. 16 : 18: 15
- A. 300
B. 400
C. 500
D. 600
- A. 124
B. 104
C. 114
D. 144
- A. 4,200
B. 4,800
C. 7,200
D. 8,000
- A. 1.1 kg
B. 1 kg
C. 0.9 kg
D.1.5 kg
- A. 1 : 3 : 6 : 12 : 16
B. 2 : 4 : 6 : 9 : 16
C. 3 : 4 : 8 : 12 : 16
D. 3 : 6 : 8 : 12 : 16
1. What number should be added to each of 6, 14, 18 and 38 so that the resulting numbers make a proportion?
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 13 : 11
B. 11 : 13
C. 13 : 110
D. 110 : 13
- A. 8
B. 4
C. 6
D. 7
- A. 3 : 4
B. 4 : 5
C. 5 : 9
D. 20 : 27
- A. 14 : 12 : 13
B. 15 : 12 : 16
C. 10 : 9 : 12
D. 12 : 10 : 11
- A. 16 : 9 : 18
B. 25 : 18 : 10
C. 18 : 25 : 10
D. 15 : 8: 30
- A. [latex]\frac {9}{15}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {14}{9}[/latex]
C. -[latex]\frac {9}{14}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {14}{8}[/latex]
- A. 5
B. 3
C. -3
D. -5
- A. 380
B. 300
C. 200
D. 180
- A. 60 : 65: 156
B. 65: 156: 60
C. 156 : 65 : 60
D. 13 : 12 : 5
1. Ticket for an adult is Rs 1600 and a child is Rs 1200. 1 child goes free with two adults. If a group has 23 adults and 10 children what is the discount the group gets?
- A. 25.95 percent
B. 24.59 percent
C. 25.77 percent
D. 31.69 percent
- A. 60.94 percent
B. 156 percent
C. 30.47 percent
D. 78 percent
- A. 275 marks
B. 250 marks
C. 300 marks
D. 325 marks
- A. 3%
B. 7.11%
C. 3.09%
D. 2.69%
- A. 125
B. 130
C. 135
D. 145
- A. 100%
B. 105%
C. 108%
D. 111%
- A. 3.3
B. 3.0
C. 2.9
D. 2.7
- A. 500
B. 550
C. 565
D. 620
- A. 24
B. 27
C. 36
D. 42
- A. [latex]16 \frac {4} {5}[/latex]
B. [latex]16 \frac {1} {3}[/latex]
C. [latex]16 \frac {2} {3}[/latex]
D. [latex]16 \frac {2} {7}[/latex]
1. The price of a certain television set is discounted by 10% and the reduced price is then discounted by 10%. The equivalent successive discount is ______.
- A. 20%
B. 19%
C. 18%
D. 11%
- A. 810
B. 800
C. 560
D. 740
- A. 6
B. 5
C. 5.50
D. 7
- A. 460
B. 475
C. 480
D. 500
- A. 1200
B. 1250
C. 1350
D. 1500
- A. 24%
B. 25%
C. 22%
D. 23%
- A. [latex]\frac {20} {3}[/latex]%
B. [latex]\frac {20} {3}[/latex]%
C. 10%
D. 15%
- A. Rs. 1080
B. Rs. 1125
C. Rs. 850
D. Rs. 925
- A. [latex] 12 \frac {1} {2}[/latex]
B. [latex] 14 \frac {2} {3}[/latex]
C. [latex] 16 \frac {2} {3}[/latex]
D. [latex] 33 \frac {1} {3}[/latex]
- A. ?740
B. 700
C. 730
D. 777
1. Which of the following successive discount series is the best of all for a customer?
- A. 30%, 20%, 10%
B. 25%, 20%, 15%
C. 30%, 10%, 15%
D. 25%, 15%, 10%
- A. 6[latex]\frac{2}{3}[/latex]%
B. 20%
C. 25%
D. 80%
- A. 20
B. 21
C. 24
D. 28
- A. 49
B. 51
C. 57
D. 60
- A. 300
B. 900
C. 110
D. 270
- A. 80
B. 120
C. 110
D. 100
- A. 2280
B. 2296
C. 2380
D. 2396
- A. 12%
B. 11 [latex]\frac{1}{9}[/latex]%
C. 10 [latex]\frac{1}{9}[/latex]%
D. 10%
- A. 1000
B. 784
C. 498.4
D. 300
- A. 1,581
B. 1, 518
C. 1, 510
D. 1, 508
1. Two trains, of same length, are running in parallel tracks in opposite directions with speed 65 km/hour and 85 km/hour respectively. They cross each other in 6 seconds. The length of each train is
- A. 100 meters
B. 115 meters
C. 125 meters
D. 150 meters
- A. 18
B. 72
C. 20
D. 36
- A. 44 km/hr, 22 km/hr
B. 52 km/hr, 26 km/hr
C. 36 km/hr, 18 km/hr
D. 40 km/hr, 20 km/hr
- A. 72 km/hr
B. 68 km/hr
C. 65 km/hr
D. 60 km/hr
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
1. A missile travels at 1422 km/h. How many meters does it travel in one second?
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A.
- A. 9.44 m
B. 4.44 m
C. 5.44 m
D. 5.56 m
- A. 7.0 sec
B. 72 sec
C. 7.2 sec
D. 70 sec
1. A man can row 30 km downstream and return to the starting point in 8 hours. If the speed of the boat in still water is four times the speed of the current, then the of the speed current is
- A. 1 km/hour
B. 2 km/hour
C. 4 km/hour
D. 3 km/hour
- A. 4 kmph and 3 kmph
B. 4.5 kmph and 0.5 kmph
C. 4 kmph and 2 kmph
D. 5 kmph and 2 kmph
- A. 2 km/hour
B. 2.5 km/hour
C. 3 km/hour
D. 3.5 km/hour
- A. 0.5 km/hr
B. 1.5 km/hr
C. 1 km/hr
D. 3 km/hr
- A. 2.5
B. 3
C. 3.5
D. 4
- A. 1.5
B. 3
C. 2
D. 1.75
- A. 2 kmph
B. 4 kmph
C. 6 kmph
D. 8 kmph
- A. 4.5 km/h and 3 km/h
B. 4.5 km/h and 0.5 km/h
C. 4 km/h and 2 km/h 5 km/h and 2 km/h
D. 5 km/h and 2 km/h
- A. 8 : 3
B. 5 : 3
C. 9 : 5
D. 8 : 3
- A. 185 min
B. 115 min
C. 170 min
D. 225 min
1. Mihir can do a piece of work in 30 hours. If he is joined by Jigya who is 50% more efficient, in what time will they together finish the work?
- A. 24 hours
B. 12 hours
C. 6 hours
D. 3 hours
- A. 12 days
B. 6 days
C. 18 days
D. 24 days
- A. 4 days
B. 12 days
C. 8 days
D. 16 days
- A. 30 days
B. 40 days
C. 10 days
D. 20 days
- A. 7 hours
B. 3.5 hours
C. 14 hours
D. 2.5 hours
- A. 20 days
B. 10 days
C. 40 days
D. 50 days
- A. 6 hours
B. 3 hours
C. 9 hours
D. 10 hours
- A. 25 days
B. 20 days
C. 80 days
D. 24 days
- A. [latex]6 \frac{2}{3}[/latex]
B. [latex]8 \frac{2}{3}[/latex]
C. 6
D. 7
- A. 14 days
B. 12 days
C. 7 days
D. 49 days
1. A, B and C are three taps connected to a tank. A and B together can fill the tank in 6 hours, B and C together can fill it in 10 hours and A and C together can fill it in [latex]7 \frac{1}{2}[/latex]hours. In how much time will C alone fill the tank?
- A. 10 hours
B. 12 hours
C. 20 hours
D. 30 hours
- A. 6
B. 30
C. 34
D. 75
- A. 30 days
B. 60 days
C. 20 days
D. 10 days
- A. 12 hours
B. 10 hours
C. 11 hours
D. 13 hours
- A. 11
B. 13.2
C. 20
D. 21
- A. [latex]13 \frac{1}{3}[/latex] days
B. 14 days
C. 15 days
D. [latex]16 \frac{2}{3}[/latex] days
- A. 16
B. 14
C. 13
D. 12
- A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 1 : 3
D. 4 : 1
- A. 36 minutes
B. 42 minutes
C. 48 minutes
D. 44 minutes
- A. 5 days
B. 7 days
C. 11 days
D. 3 days
1. A trader had 9 Quintals of wheat. He sold a part of it at 10% profit and the rest at 20% profit, so that he made a total profit of 14 %. How much wheat did he sell at 20% profit?
- A. 540 kg
B. 360 kg
C. 180 kg
D. 720 kg
- A. 25%
B. 66 [latex]\frac{2}{3}[/latex]%
C. [latex]33 \frac{1}{3}[/latex]%
D. 75%
- A. 3 : 1
B. 4 : 1
C. 3 : 1
D. 4 : 3
- A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 2 : 3
D. 3 : 2
- A. 21
B. 16[latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
C. 36[latex]\frac{3}{4}[/latex]
D. 26[latex]\frac{3}{4}[/latex]
- A. 2 : 1
B. 1 : 2
C. 2 : 3
D. 1 : 1
- A. 4 : 3
B. 2 : 5
C. 1.8 : 24
D. 3 : 4
- A. 37 %
B. 46 %
C. 12[latex]\frac{1}{7}[/latex]%
D. 24[latex]\frac{2}{7}[/latex]
- A. 34.24 kg
B. 39.64 kg
C. 43.6 kg
D. 47.6 kg
- A. 40 liters
B. 52 liters
C. 54 liters
D. 60 liters
1. One type of liquid contains 25% of milk, the other contains 50% of milk. A container is filled with 6 parts of the first liquid and 4 parts of the second liquid. The percentage of milk in the mixture is:
- A. 25%
B. 30%
C. 35%
D. 33.68%
- A. 4500
B. 5400
C. 3000
D. 4000
- A. 2 : 7
B. 7 : 2
C. 5 : 2
D. 9 : 7
- A. 1180
B. 1182
C. 1184
D. 1056
- A. 3.5 gm
B. 5.5 gm
C. 7.5 gm
D. 4.8 gm
- A. 12
B. 15
C. 16
D. 20
- A. 350
B. 400
C. 200
D. 150
- A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 3 : 1
D. 3 : 2
- A. [latex]\frac{205}{102}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{102}{205}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{255}{102}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{107}{102}[/latex]
- A. 2 : 9
B. 5 : 7
C. 11 : 4
D. 17 : 8
1. There is 40% increase in an amount in 10 years at simple interest. What will be the compound interest of Rs. 30000 after 3 years at the same rate?
- A. Rs 3745. 92
B. 7491. 84
C. 9364. 8
D. 5618. 88
- A. 15ooo
B. 18000
C. 12000
D. 9000
- A. Rs. 650
B. Rs. 350
C. Rs. 550
D. Rs. 500
- A. ?600
B. ?675
C. ?650
D. ?625
- A. Rs. 5000
B. Rs. 6000
C. Rs. 7000
D. Rs. 4000
- A. 5 [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] years
B. 6 [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] years
C. 7 years
D. 7 [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] years
- A. 3
B. 3.5
C. 4
D. 5
- A. 4%
B. 5%
C. 2%
D. 3%
- A. [latex]{z}^{2}[/latex] = xy
B. xyz = 1
C. [latex]{x}^{2}[/latex] = yz
D. [latex]{y}^{2}[/latex] = zx
- A. 0.10%
B. 0.25%
C. 0.50%
D. 1.00%
1. A sum of money was invested at a certain rate of simple interest for 2 years. Had it been invested at 1 % higher rate, it would have fetched 24 more interest. The sum of money is _____.
- A. 1200
B. 1050
C. 1000
D. 9600
- A. 8 yrs. 6 months
B. 6 yrs. 9 months
C. 8 yrs. 4 months
D. 7 yrs. 6 months
- A. 500
B. 750
C. 1000
D. 1250
- A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 8
- A. 8.5 percent
B. 9 percent
C. 9.5 percent
D. 8 percent
- A. 10%
B. 10.5%
C. 9.5%
D. 11%
- A. 10%
B. 12%
C. 18%
D. 20%
- A. 5200
B. 6200
C. 4200
D. 3200
- A. 2031
B. 4546
C. 8488
D. None of these
- A. 30000
B. 23000
C. 20000
D. 35000
1. On what sum of money will the difference between the simple interest and the compound interest for 2 years at 8% per annum be equal to 8?
- A. Rs. 1200
B. Rs. 1300
C. Rs. 1250
D. Rs. 1350
- A. Rs. 4076
B. Rs. 4085
C. Rs. 3096
D. 4098
- A. 500
B. 750
C. 1000
D. 1250
- A. 625
B. 630
C. 640
D. 650
- A. 10%
B. 12%
C. 14%
D. 15%
- A. 1016
B. 996
C. 976
D. 966
- A. 8%
B. 7.5%
C. 10%
D. 50%
- A. Rs 3500
B. Rs 875
C. Rs 1750
D. Rs 1400
- A. 10%
B. 5%
C. 20%
D. 16%
- A. Rs 3152.5
B. Rs. 6305
C. Rs 7881.25
D. Rs 4728.75
1. A man borrowed some money from a private organization at 8% simple interest per annum. He lent 75% of his money to another person at 10% compound interest per annum. If the difference between the CI on 3/4 th amount and the SI on whole amount, that was borrowed is Rs 561.5 in 4 years. Then Find the total amount Borrowed?
- A. 30000
B. 23000
C. 20000
D. 35000
- A. 15
B. 2.5
C. 2
D. 3
- A. 50000
B. 54000
C. 25000
D. 41000
- A. 116 more
B. 116 less
C. 232 less
D. 232 more
- A. Rs 1, 24,776
B. Rs 1, 25,776
C. Rs 1, 26,776
D. Rs 1, 27,776
- A. Rs 4, 136.87
B. Rs 4, 306.81
C. Rs 3, 032.18
D. Rs 4, 265.73
- A. 70.5
B. 74.6
C. 73.8
D. 72.6
- A. 22%
B. 16 %
C. 18%
D. Cannot be determined
- A. Rs. 1000
B. Rs. 1025
C. Rs. 1050
D. Rs. 1075
- A. Rs. 520.55
B. Rs. 513.05
C. Rs. 625.50
D. Rs. 605.05
1. If [latex]{cos}^{2}\alpha + {cos}^{2}\beta = 2[/latex] then the value of [latex]{tan}^{3}\alpha + {sin}^{3}\beta[/latex] is
- A. -1
B. 0
C. 1
D. [latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
- A. A = 2B
B. A = -2B
C. 2A = B
D. 2A = -B
- A. 0
B. 1
C. -1
D. 2
- A. 60°
B. 30°
C. 0°
D. 90°
- A. 0
B. [latex]\sqrt{2}[/latex]
C. 1
D. -1
- A. -[latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
B.[latex]\frac {1}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
C. 1
D. [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
- A. 5
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 0.5
B. -0.5
C. 3.0
D. -3.0
- A. 7
B. 9
C. 4
D. 5
- A. [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
C. 3
D. 2
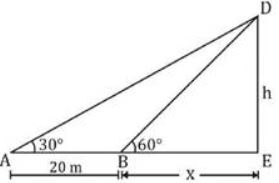
1. The distance between two pillars of length 16 metres and 9 metres is x metres. If two angles of elevation of their respective top from the bottom of the other are complementary to each other, then the value of x (in metres) is
- A. 15
B. 16
C. 12
D. 9
- A. [latex]5 \sqrt{3} [/latex] m
B. [latex]10 (\sqrt{3} + 1)[/latex] m
C. [latex]5 (\sqrt{3} + 1)[/latex] m
D. [latex]10 \sqrt{3} [/latex] m
- A. 22 m
B. [latex]22 \sqrt{3} [/latex] m
C. 20 m
D. [latex]20 \sqrt{3} [/latex] m
- A. 30º
B. 60º
C. 45º
D. 90º
- A. 12
B. 18
C. 15
D. 16
- A. [latex]30 (3 + \sqrt{3}) [/latex] m
B. [latex]40 (3 + \sqrt{3}) [/latex] m
C. [latex]20 (3 + \sqrt{3}) [/latex] m
D. [latex]10 (3 + \sqrt{3}) [/latex] m
- A. [latex]\frac{13}{\sqrt {3}} = 40[/latex] m
B. 13 m
C. 15 m
D. 3.25 m
- A. 30º
B. 45º
C. 60º
D. 90º
- A. 400 m
B. 400 [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex] m
C. 415.69 m
D. 398.62 m
- A. 193 .22
B. 144.04
C. 176.12
D. 161.05
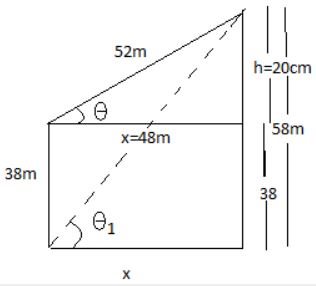
1. The distance between the tops of two building 38 metres and 58 metres high is 52 metres. What will be the distance (in metres) between two buildings?
- A. 46
B. 42
C. 44
D. 48
- A. 50 [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
B. 100 [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
C. 200 [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
D. 300 [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
- A. 210
B. 140 [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
C. 210 [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex]
D. 150
- A. [latex]20\sqrt{3}(\sqrt{3} + 1) [/latex]
B. [latex]20\sqrt{3}(\sqrt{3} - 1) [/latex]
C. [latex]10\sqrt{3}(\sqrt{3} - 1) [/latex]
D. [latex]10\sqrt{3}(\sqrt{3} + 1) [/latex]
- A. 149 m
B. 156 m
C. 173 m
D. 200 m
- A. 30º
B. 45º
C. 60º
D. 90º
- A. 10 [latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex] m
B. [latex]\frac{10}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] m
C. 10 m
D. [latex]\frac{10}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex]
- A. 42
B. 49
C. 35
D. 56
- A. [latex]\sqrt{3} [/latex] m
B. [latex]5 \sqrt{3} [/latex] m
C. [latex]10 \sqrt{3} [/latex] m
D. [latex]20 \sqrt{3} [/latex] m
- A. 45°
B. 30°
C. 60°
D. 90°
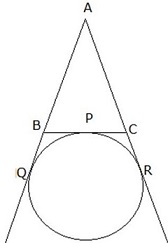
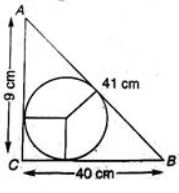
1. A circle is touching the side BC of [latex]\triangle[/latex]ABC at P and is also touching AB and AC produced at Q and R respectively. If AQ = 6 cm, then perimeter of [latex]\triangle[/latex] ABC is
- A. 6 cm
B. 10 cm
C. 12 cm
D. 18 cm
- A. 72 sq cm
B. 144 sq cm
C. 36. sq cm
D. 487.5 sq cm
- A. 3 : 2
B. 1 : 2
C. 2 : 3
D. 2 : 1
- A. [latex]3 \sqrt{3}[/latex] cm
B. 4.5 cm
C. [latex]4 \sqrt{3}[/latex] cm
D. [latex]2\sqrt{3}[/latex] cm
- A. 18 sq. cm
B. 36 sq. cm
C. 10 sq. cm
D. 16 sq. cm
- A. Incenter
B. Circumcentre
C. Centroid
D. Orthocentre
- A. 16 unit
B. [latex]5 \sqrt{10}[/latex] unit
C. [latex]8 \sqrt{2}[/latex] unit
D. 12 unit
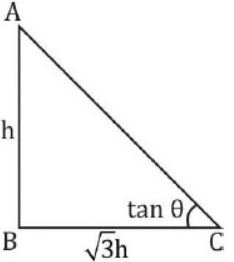
- A. 30°
B. 15°
C. 60°
D. 45°
- A. 45°
B. 90°
C. 30°
D. 60°
- A. 12 cm
B. [latex]\frac{9}{2}[/latex]
C. 4 cm
D. 9 cm
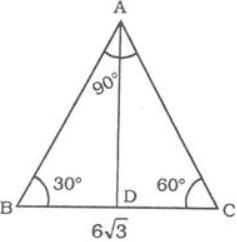
1. The diagonal of a square is [latex]10 \sqrt{2}[/latex]cm. Find its perimeter?
- A. 160 cm
B. 80 cm
C. 20 cm
D. 40 cm
- A. 10 cm
B. 12 cm
C. 16 cm
D. 9 cm
- A. 2 : 1
B. [latex]\sqrt{2}[/latex] : 1
C. [latex]\sqrt{2} : \sqrt{3}[/latex]
D. [latex]\sqrt{3} : 1[/latex]
- A. 64 [latex]\pi[/latex] sq cm
B. 25 [latex]\pi[/latex] sq cm
C. 36 [latex]\pi[/latex] sq cm
D. 49 [latex]\pi[/latex] sq cm
- A. 16 cm
B. 18 cm
C. 15 cm
D. 26 cm
- A. 2 : 1
B. 1 : 2
C. 1 : 1
D. 3 : 1
- A. 4 cm
B. 5 cm
C. 3 cm
D.
- A. 52
B. 60
C. 120
D. 100
- A. 8 cm
B. 10 cm
C. 12 cm
D. 15 cm
- A. [latex]3 \sqrt{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]5 \sqrt{2}[/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt{34}[/latex]
D. [latex]\sqrt{41}[/latex]
1. What is the area of the sector whose central angle is 90 ° and radius of the circle is 14 cm?
- A. 308 sq cm
B. 77 sq cm
C. 154 sq cm
D. 231 sq cm
- A. 28
B. 20
C. 15
D. 24
- A. 45º
B. 90º
C. 80º
D. 100º
- A. 1386 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
B. 1472 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
C. 1512 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
D. 1760 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
- A. 60º
B. 80º
C. 100º
D. 120º
- A. 21 cm
B. 14 cm
C. 7 cm
D. 28 cm
- A. [latex]\frac{\pi}{16}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{\pi}{8}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{\pi}{4}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{\pi}{12}[/latex]
- A. 45º
B. 90º
C. 30º
D. 60º
- A. 21.6 cm
B. 26.4 cm
C. 13.2 cm
D. 19.8 cm
- A. 4 (9 - [latex]\pi[/latex]) sq .cm
B. 9 (4 - [latex]\pi[/latex]) sq .cm
C. 5 (6 - [latex]\pi[/latex]) sq .cm
D. 6 (5 - [latex]\pi[/latex]) sq .cm
1. The cross section of a canal is in the shape of an isosceles trapezium which is 2 m wide at the bottom and 3 m wide at the top. If the depth of the canal is 1 m and it is 100 m long, what is the maximum capacity of this canal?
- A. 500 cubic mts
B. 250 cubic mts
C. 750 cubic mts
D. 1000 cubic mts
- A. 440 sq cms
B. 880 sq cms
C. 220 sq cms
D. 660 sq cms
- A. 28 cms
B. 7 cms
C. 21 cms
D. 14 cms
- A. 12
B. 10
C. 15
D. 20
- A. 686 cubic cms
B. 343 cubic cms
C. 171.5 cubic cms
D. 514.5 cubic cms
- A. 27.72 sq cm
B. 55. 44 sq cm
C. 9.24 sq cm
D. 13.86 sq cm
- A. p : 6
B. [latex]\sqrt {\pi} : \sqrt{6}[/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt {6} : \sqrt {\pi}[/latex]
D. 6 : p
- A. 45810
B. 45810
C. 48150
D. 48051
- A. 11385 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
B. 10395 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
C. 9900 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
D. 990 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
- A. 3 : 4
B. 9 : 16
C. 16 : 9
D. 27 : 64
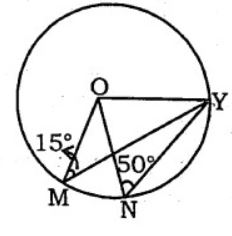
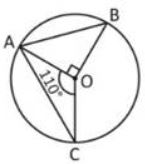
1. Let O be the in-centre of a triangle ABC and D be a point on the side BC of [latex]\triangle[/latex] ABC, such that OD ? BC. If ?BOD = 15 °, then ?ABC =
- A. 75 °
B. 45°
C. 150°
D. 90°
- A. 1 : 2
B. 1 : 1
C. 2 : 1
D. 2 : 3
- A. 18 cm
B. 24 cm
C. 22.5 cm
D. 27 cm
- A. 1 : 6
B. 6 : 1
C. 1 : 12
D. 12 : 1
- A. 32 [latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex] sq cm
B. 16 sq cm
C. 16 [latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex] sq cm
D. 32 sq cm
- A. 1 : 3
B. 2 : 3
C. 1 : 2
D. 1 : [latex]\sqrt{2}[/latex]
- A. right-angled
B. obtuse-angled
C. equilateral
D. isosceles
- A. 1 : 2
B. 1 : [latex]\sqrt{2}[/latex]
C. 4 : 1
D. 1 : 4
- A. 2
B. 4
C. 5
D. 7
- A. 10 cm
B. 8 cm
C. 6 cm
D. 5 cm
1. The perimeters of two similar triangles are 30 cm and 20 cm respectively. If one side of the first triangle is 9 cm. Determine the corresponding side of the second triangle.
- A. 13.5 cm
B. 6 cm
C. 15 cm
D. 5 cm
- A. 6.5 cm
B. 7.5 cm
C. 8.5 cm
D. 5.5 cm
- A. 3
B. [latex] \frac {1}{3} [/latex]
C. [latex] \sqrt {3}[/latex]
D. [latex] \frac {1}{\sqrt {3}}[/latex]
- A. Scalene
B. Right angled
C. Equilateral
D. Obtuse angled
- A. [latex]\frac{1}{3} \pi {r}^{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{4}{\sqrt{3}} {r}^{2}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{3 \sqrt{3}}{4} {r}^{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} {r}^{2}[/latex]
- A. [latex]{a}^{2} + {b}^{2} = {p}^{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{1}{{a}^{2}} + \frac{1}{{b}^{2}} = \frac{1}{{p}^{2}}[/latex]
C. ab = [latex]{p}^{2}[/latex]
D. a + b = p
1. The length of aside of a rhombus is 10 m and one of its diagonal is 12 m. The length of the other diagonal is
- A. 15 m
B. 18 m
C. 16 m
D. Can't be determined
- A. 60 %
B. 50%
C. 40%
D. 30%
- A. 40
B. 45
C. 60
D. 70
- A. 10 cm
B. 12. 5 cm
C. 8 cm
D. 7 cm
- A. 25 cm
B. 20 cm
C. 4 cm
D. 5 cm
- A. 24 cm
B. 12 30 cm
D. 18 cm
- A. 8 cm
B. 6 cm
C. 10 cm
D. 16 cm
- A. 1 : 3
B. 7 : 1
C. 3 : 1
D. 2 : 3
- A. (2, 0)
B. (5, 0)
C. (4, 5)
D. (0, 5)
- A. 5 cm
B. 7.35 cm
C. 6 cm
D. 4 cm
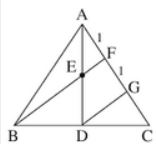
1. In the adjoining figure, sides AB and AC of a [latex]\triangle[/latex]ABC are produced to P and Q respectively. The bisectors of PBC and QCB intersect at O. then BOC is equal to:
- A. 90 - [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] BAC
B. [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]( PBC + QCB)
C. 90 + [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] BAC
D. None of these
- A. 8 cm
B. 4 cm
C. 3 cm
D. 2 cm
- A. 6 cm
B. 12 cm
C. 13.29 cm
D. 15 cm
- A. [latex]{a}^{2} = {b}^{2} + {c}^{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]{a}^{2} = {b}^{2} + {c}^{2} - bc[/latex]
C. [latex]{a}^{2} = {b}^{2} + {c}^{2} + bc[/latex]
D. [latex]{a}^{2} = {b}^{2} + 2bc[/latex]
- A. 6[latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex]
B. 3[latex]\sqrt{6}[/latex]
C. 10[latex]\sqrt{2}[/latex]
D. 5[latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex]
- A. 30
B. 45
C. 60
D. 90
- A. 3 [latex]\sqrt{5}[/latex] cm
B. [latex]\frac{3}{\sqrt{5}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt{5}[/latex]
D. 3 cm
- A. 5 : 2
B. 5 : 4
C. 3 : 4
D. 2 : 1
- A. 24 cm
B. 12 cm
C. 30 cm
D. 18 cm
- A. 8 cm
B. 10 cm
C. 11 cm
D. None of these
1. Chord PQ is the perpendicular bisector of radius OA of circle with center O (A is a point on the edge of the circle). If the length of Arc PAQ =[latex]\frac {2\pi}{3}[/latex]. what is the length of chord PQ?
- A. 2
B. [latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex]
C. 2[latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex]
D. 1
- A. 2
B. 4
C. 3
D. 6
- A. 500.5
B. 575.6
C. 521.2
D. 560.7
- A. 18
B. 24
C. 16
D. 32
- A. 56
B. 42
C. 63
D. 49
- A. 6 cm
B. 8 cm
C. 10 cm
D. 4 cm
- A. 30°
B. 40°
C. 20°
D. 70°
- A. 70°
B. 80°
C. 90°
D. 100°
- A. 60°
B. 100°
C. 120°
D. 150°
- A. 9cm
B. 4 cm
C. Can't be determined
D. None of these
1. At least two pairs of consecutive angles are congruent in a _________.
- A. Parallelogram
B. Isosceles trapezium
C. Rhombus
D. Kite
- A. 22
B. 24
C. 26
D. 20
- A. 8
B. 12
C. 10
D. 14
- A. 30
B. 16
C. 12
D. 24
- A. 60°
B. 45°
C. 120°
D. 100°
- A. 6
B. 8
C. 10
D. 12
- A. 10
B. 12
C. 6
D. 8
- A. [latex]\sqrt{168} cm[/latex]
B. 2 [latex]\sqrt{147} cm[/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt{137} cm[/latex]
D. 2 [latex]\sqrt{137} cm[/latex]
- A. 5
B. 6
C. 7
D. 8
- A.15, 12
B. 5, 6
C. 10, 8
D. 20, 16
1. If the sum of the interior angles of a regular polygon be 1080°, the number of sides of the polygon is:
- A. 6
B. 8
C. 10
D. 12
- A. 8
B. 10
C. 15
D. None of these
- A. 10
B. 20
C. 24
D. 36
- A. 7
B. 9
C. 12
D. 15
- A. 95
B. 45
C. 75
D. 65
- A. 216
B. 432
C. 512
D. 624
- A. 3 : 4
B. 5 : 3
C. 5 : 1
D. 6 : 2
- A. 120
B. 240
C. 360
D. 480
- A. 15
B. 30
C. 45
D. 60
- A. 66.66%
B. 33.33%
C. 83.33%
D. 56.41%
1. If [latex]{2}^{x} = {3}^{y} = {6}^{-z} [/latex] then [latex]\frac {1}{x} + \frac {1}{y} + \frac {1}{z}[/latex] is equal to
- A. 0
B. 1
C. [latex]\frac {3}{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {3}{2}[/latex]
- A. Rs 2000
B. Rs 1948.8
C. Rs 1411.2
D. Rs 1448
- A. 11
B. 7
C. 9
D. 13
- A. Rs. 90 and Rs. 40
B. Rs. 50 and Rs. 40
C. Rs. 40 and Rs. 60
D. Rs. 50 and Rs. 90
- A. Rs 350
B. Rs 70
C. Rs 140
D. Rs 175
- A. 16.64%
B. 6.64%
C. 16%
D. 16.46%
- A. 2160 cubic mts
B. 3240 cubic mts
C. 4329 cubic mts
D. 1080 cubic mts
- A. 45
B. 40
C. 50
D. 60
- A. 35 percent
B. 30.8 percent
C. 34 percent
D. 20.4 percent
- A. 21
B. 23
C. 25
D. 26
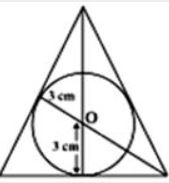
1. The distance between the centres of two equal circles each of radius 3 cm is 10 cm. The length of a transverse tangent is
- A. 4 cm
B. 6 cm
C. 8 cm
D. 10 cm
- A. 4
B. - 4
C. 0
D. 8
- A. 444
B. 496
C. 333
D. 540
- A. 900
B. 1000
C. 700
D. 800
- A. 3
B. 4
C. 45
D. 9
- A. 4
B. 12
C. 6
D. 8
- A. [latex]\sqrt {0.09}[/latex]
B. [latex]\sqrt {0.064}[3][/latex]
C. 0.5
D. [latex]\frac {3}{5}[/latex]
- A. 2
B. 44
C. 49
D. 2 [latex] \frac {3}{16}[/latex]
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. [latex]\frac {1}{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]2 \frac {1}{2}[/latex]
C. [latex]3 \frac {1}{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]9 \frac {1}{2}[/latex]
1. If sin[latex]\theta[/latex] - cos [latex]\theta[/latex] = [latex]\frac {7}{13}[/latex] and 0 < [latex]\theta[/latex] < 90, then the value of sin[latex]\theta[/latex] + cos [latex]\theta[/latex] is
- A. [latex] \frac {17}{13}[/latex]
B. [latex] \frac {13}{17}[/latex]
C. [latex] \frac {1}{13}[/latex]
D. [latex] \frac {1}{17}[/latex]
- A. 100%
B. 75%
C. 50%
D. 25%
- A. 0
B. -1
C. 1
D. 2
- A. 0
B. 1
C. [latex]\sqrt {3} [/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {1}{\sqrt {3}} [/latex]
- A. [latex]3{a}^{2} {cm}^{3}[/latex]
B. [latex]3 \sqrt {2}{a}^{2} {cm}^{3}[/latex]
C. [latex]3 \sqrt {3}{a}^{3} {cm}^{3}[/latex]
D. [latex]6{a}^{2} {cm}^{3}[/latex]
- A. 2sec A
B. 2 cosec A
C. 2 tan A
D. 2 cot A
- A. 3 : 4
B. 4 : 3
C. 3 : 8
D. 8 : 3
- A. 3 : 4
B. 4 : 3
C. 9 : 16
D. 16 : 9
- A. 60
B. 70
C. 40
D. 60
- A. 2 : 1
B. 3 : 2
C. 3 : 1
D. 1 : 4
1. Marks of two candidates P and Q are in the ratio of 2 : 5. If the marks of P are 120, marks of Q are
- A. 120
B. 240
C. 300
D. 360
- A. 6
B. 7
C. 8
D. 14
- A. 22.5
B. 25.75
C. 25
D. 20
- A. [latex] \frac {xyz}{3abc}[/latex]
B. 3 xyzabc
C. [latex] \frac {3 xyz}{abc}[/latex]
D. [latex] \frac {xyz}{abc}[/latex]
- A. 70 %
B. 40 %
C. 60 %
D. 35 %
- A. 56 [latex]{cm}^{3}[/latex]
B. 16 [latex]{cm}^{3}[/latex]
C. 64 [latex]{cm}^{3}[/latex]
D. 36 [latex]{cm}^{3}[/latex]
- A. 0.8
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. 50
B. 48
C. 36
D. 28
- A. 2
B. -1
C. 0
D. 1
- A. 80 sq cm
B. 48 sq cm
C. 60 sq cm
D. 32 sq cm
1. In a two-digit number, the digit at the unit's place is 1 less than twice the digit at the ten's place. If the digits at unit's and ten's place are interchanged, the difference between the new and the original number is less than the original number by 20. The original number is
- A. 59
B. 23
C. 35
D. 4
- A. 37.5%
B. 40%
C. 30.5%
D. 35%
- A. 50
B. 500
C. 0.05
D. 5
- A. 40 days
B. 80 days
C. 120 days
D. 20 days
- A. 1 : 1 : 2
B. 1 : 1 : 1
C. 1 : 2 : 1
D. 2 : 1 : 1
- A. 125
B. 100
C. 55
D. 50
- A. 236.25
B. 230.25
C. 240.25
D. 242 .25
- A. 10 cm
B. 20 cm
C. 30 cm
D. 40 cm
- A. 35
B. 14
C. 50
D. 24
- A. 100
B. 72
C. 40
D. 200
1. If [latex]{x}^{2} + 9{y}^{2} = 6xy[/latex] then x : y is
- A. 1 : 3
B. 3 : 2
C. 3 : 1
D. 2 : 3
- A. 356 [latex]{cm}^{2}[/latex]
B. 350 [latex]{cm}^{2}[/latex]
C. 355 [latex]{cm}^{2}[/latex]
D. 348 [latex]{cm}^{2}[/latex]
- A. [latex]\frac {1}{2}[/latex]
B. 0
C. [latex]\frac {1}{\sqrt {2}}[/latex]
D. 1
- A. 21 %
B. 20 %
C. 22 %
D. 23 %
- A. 23 years
B. 24 years
C. 18 years
D. 20 years
- A. 78
B. 75
C. 60
D. 55
- A. 1
B. 0
C. -1
D. -2
- A. 15.25 years
B. 14 years
C. 14 .75 years
D. Cannot be determined
- A. 120
B. 180
C. 100
D. 80
- A. 20 percent
B. 25 percent
C. 40 percent
D. 15 percent
1. The ratio of the length of the parallel sides of a trapezium is 3:2. The shortest distance between them is 15 cm. If the area of the trapezium is 450 [latex]{cm}^{2}[/latex] the sum of the lengths of the parallel sides is
- A. 15 cm
B. 36 cm
C. 42 cm
D. 60 cm
- A. 514
B. 544
C. 344
D. 444
- A. 27 cm
B. [latex] \frac {16}{3}[/latex] cm
C. 15 cm
D. [latex] \frac {28}{3}[/latex] cm
- A. 30
B. 37.5
C. 25
D. 20
- A. 76.80
B. 80
C. 86
D. 86.80
- A. 57 percent
B. 36.31 percent
C. 71.25 percent
D. 33.33 percent
- A. 1 year
B. 2 year
C. 3 years
D. 4 years
- A. 1350
B. 1250
C. 1000
D. 125
- A. 7 : 5
B. 4 : 3
C. 8 : 5
D. 7 : 6
- A. 4
B. 5
C. 3
D. 6
1. If x + [latex] \frac {1}{4x}[/latex], find the value of [latex]8{x}^{3} + \frac {1}{8 {x}^{3}}[/latex]
- A. 18
B. 36
C. 24
D. 16
- A. 5
B. 25
C. 100
D. 125
- A. one-fourth of the previous height
B. [latex]\frac {1}{\sqrt {2}}[/latex]times of the previous height
C. half of the previous height
D. one-third of the previous height
- A. 15 %
B. 20 %
C. 25 %
D. 40 %
- A. 2 cm
B. 0.33 cm
C. 0.5 cm
D. 1 cm
- A. 28.8 percent
B. 24 percent
C. 25 percent
D. 21 percent
- A. 430
B. 630
C. 1068
D. 1260
- A. 4
B. 2
C. 8
D. 10
- A. Cannot be determined
B. 750
C. 4,250
D. 3,000
- A. 5
B. 10
C. 15
D. 20
1. If x = a + [latex]\frac {1}{a}[/latex] and y = a - [latex]\frac {1}{a}[/latex], then the value of [latex]{x}^{4}[/latex] + [latex]{y}^{4}[/latex] - [latex]2{x}^{2}{y}^{2}[/latex] is
- A. 24
B. 18
C. 16
D. 12
- A. 14 %
B. 34 %
C. 24 %
D. 20 %
- A. 500
B. 450
C. 600
D. 400
- A. 13,000
B. 16,000
C. 12,000
D. 10,000
- A. 998999
B. 999899
C. 989999
D. 999989
- A. 125 [latex]{cm}^{3}[/latex]
B. 216 [latex]{cm}^{3}[/latex]
C. 343 [latex]{cm}^{3}[/latex]
D. None of these
- A. 7:2
B. 2:7
C. 7:4
D. 2:3
- A. [latex] \frac {3}{4} [/latex]
B. [latex] \frac {5}{6} [/latex]
C. [latex] \frac {1}{3} [/latex]
D. [latex] \frac {2}{7} [/latex]
- A. 10
B. 11
C. 9
D. 8
- A. 15%
B. 16%
C. 14%
D. 12%
1. The length of a road is one kilometer. The number of plants required for plantation at a gap of 20 meters in both sides of the road is
- A. 102
B. 100
C. 51
D. 50
- A. 8 days
B. 2 days
C. 4 days
D. 16 days
- A. [latex]\frac {4}{3}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {3}{4}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac {1}{4}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {1}{3}[/latex]
- A. 20%
B. 22.5%
C. 25%
D. 27.5%
- A. 80 cm
B. 84 cm
C. 76 cm
D. 72 cm
- A. 6
B. 5
C. 4
D. 0
- A. 2 cm
B. 3 cm
C. 4 cm
D. 6 cm
- A. 20
B. 21
C. 110
D. 121
- A. [latex]{cos}^{2}(\frac {A}{3})[/latex]
B. [latex]\sqrt {sin\frac {A}{2}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt {cos\frac {A}{2}}[/latex]
D. [latex]{sin}^{2}(\frac {A}{2})[/latex]
- A. 8 days
B. 16 days
C. 25 days
D. 15 days
1. If 3x + [latex]\frac {1}{2x}[/latex] = 5 then the value of is [latex]8 {x}^{3} + \frac {1}{27 {x}^{3}}[/latex] :
- A. [latex]118 \frac {1}{2} [/latex]
B. [latex]30 \frac {10}{27} [/latex]
C. 0
D. 1
- A. 2a - 3b
B. 2a + 3b
C. 2a
D. 3b
- A. 12
B. 3
C. 11
D. 1
- A. 11
B. 9
C. 10
D. 8
- A. 49 sq cm
B. 196 sq cm
C. 98 sq cm
D. 77 sq cm
- A. 9 [latex]\frac {1}{11}[/latex]
B. 11 [latex]\frac {1} {9}[/latex]
C. 33 [latex]\frac {1}{3}[/latex]
D. 36 [latex]\frac {2} {3}[/latex]
- A. 400
B. 450
C. 200
D. 150
- A. 6,500
B. 6,000
C. 6,423.90
D. 6,500.50
- A. Rs. 1260
B. Rs. 1320
C. Rs. 1180
D. Rs. 1250
- A. [latex]\frac {-7} {3}[/latex],[latex]\frac {4} {7}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {3} {7}[/latex],[latex]\frac {-7} {4}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac {7} {3}[/latex],[latex]\frac {-4} {7}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {-3} {7}[/latex],[latex]\frac {7} {4}[/latex]
1. Successive discounts of 20% and 10% are equivalent to a single discount of :
- A. 28%
B. 25%
C. 30%
D. 15 %
- A. 10 units
B. 13 units
C. 5 units
D. 11 units
- A. 84000
B. 24000
C. 36000
D. 42000
- A. 2 years
B. 3 years
C. 4years
D. 6 years
- A. [latex] \frac {3}{8}[/latex]
B. [latex] \frac {24}{97}[/latex]
C. [latex] \frac {3}{9}[/latex]
D. [latex] \frac {9}{8}[/latex]
- A. 10
B. 18
C. 7
D. 16
- A. 900
B. 1200
C. 1800
D. 1500
- A. 34
B. 35
C. 36
D. 37
- A. 30
B. 3
C. 5
D. 32
- A. Rs. 10,000
B. Rs. 12,500
C. Rs. 10,250
D. Rs. 14,000
1. Parallel sides of a trapezium are 26 cm and 40 cm and the area is 792 [latex]{cm}^{2}[/latex]. What is the value of the distance (in cm) between parallel sides?
- A. 24
B. 48
C. 12
D. 36
- A. 5
B. 12
C. 5 [latex]\sqrt {2}[/latex]
D. 6 [latex]\sqrt {2}[/latex]
- A. 10
B. 12
C. 14
D. 16
- A. [latex]\sqrt [3]{6}[/latex]
B. [latex]\sqrt [2]{5}[/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt [6]{12}[/latex]
D. All are equal
- A. 0.0025
B. 0.0005
C. 0.25
D. 0.50
- A. 500
B. 510
C. 550
D. 560
- A. 4
B. 8
C. 10
D. 6
- A. 30
B. 36
C. 40
D. 20
- A. 3
B. 2
C. 7
D. 8
- A. 3.5
B. 7
C. 10.5
D. 14
1. The ratio of two numbers is 4 : 5. If both numbers are increased by 4, the ratio becomes 5 : 6. What is the sum of the two numbers?
- A. 9
B. 18
C. 27
D. 36
- A. 9
B. 16
C. 17
D. 17.5
- A. 252[latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
B. 156 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
C. 96 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
D. 1152 [latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
- A. 10 units
B. 13 units
C. 5 units
D. 11 units
- A. 84000
B. 24000
C. 36000
D. 42000
- A. 2 years
B. 3 years
C. 4years
D. 6 years
- A. [latex] \frac {3}{8}[/latex]
B. [latex] \frac {24}{97}[/latex]
C. [latex] \frac {3}{9}[/latex]
D. [latex] \frac {9}{8}[/latex]
- A. 10
B. 18
C. 7
D. 16
- A. 900
B. 1200
C. 1800
D. 1500
- A. 34
B. 35
C. 36
D. 37
1.Find the missing number in the following series:
4320, 720, ?, 36, 12, 6
- A. 144
B. 24
C. 72
D. 48
- A. 98
B. 96
C. 104
D. 88
- A. 60 sec
B. 80 sec
C. 70 sec
D. None of these
- A. 25 min
B. 30 min
C. 40 min
D. 20 min
- A. 200 mtr
B. 180 mtr
C. 90 mtr
D. 210 mtr
- A. 1 m/s
B. 1.33 m/s
C. 1.25 m/s
D. 1.66 m/s
- A. 85 min
B. 96 min
C. 100 min
D. 120 min
- A. 15 km
B. 22 km
C. 20 km
D. 25 km
- A. 50 kg
B. 66 kg
C. 67 kg
D. 47 kg
- A. -1
B. 0
C. 1
D. 2
1. If [latex]x= \frac {4 \sqrt {15}}{\sqrt {5} + \sqrt {3}}[/latex], the value of [latex]\frac {x + \sqrt {20}}{x - \sqrt {20}} + \frac {x + \sqrt {12}}{x - \sqrt {12}}[/latex] is
- A. 1
B. 2
C. [latex]\sqrt{3}[/latex]
D. [latex]\sqrt{5}[/latex]
- A. 8
B. 9
C. 10
D. 11
- A. 1
B. 9
C. [latex]\sqrt{99}[/latex]
D. [latex]\sqrt{99} - 1[/latex]
- A. [latex]\frac {18}{30}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {19}{30}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac {20}{30}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {21}{30}[/latex]
- A. 1, 518
B. 1, 581
C. 1,510
D. 1,508
- A. 4.5 km/h and 3 km/h
B. 4.5 km/h and 0.5 km/h
C. 4 km/h and 2 km/h
D. 5 km/h and 2 km/h
- A. 25 hours
B. 22 hours
C. 20 hours
D. 15 hours
- A. 3,500
B. 4,000
C. 4,500
D. 5,000
- A. 20 %
B. 18 %
C. 10 %
D. 16 [latex]\frac {2}{3}[/latex] %
- A. 56 cm
B. 36 cm
C. 42 cm
D. 48 cm
1. The average of nine consecutive numbers is n. If the next two numbers are also included the new average will
- A. increase by 2
B. remain the same
C. increase by 1.5
D. increase by 1
- A. 360
B. 720
C. 20
D. 120
- A. 24
B. 84
C. 60
D. 36
- A. 1
B. [latex] \frac {1}{2}[/latex]
C. 2
D. [latex] \frac {1}{3}[/latex]
- A. -2
B. 2
C. 0
D. 1
- A. 7
B. 8
C. 10
D. 12
- A. [latex] \frac {3b}{2}[/latex]
B. b
C. [latex] \frac {b}{2}[/latex]
D. [latex] \frac {2b}{3}[/latex]
- A. 20
B. 17
C. 13
D. 11
- A. [latex] \frac {1}{16}[/latex]
B. [latex] \frac {1}{4}[/latex]
C. 16
D. 2
- A. 240 [latex]\pi[/latex] cu.cm
B. 5280 cu.cm
C. 620 [latex]\pi[/latex] cu. cm
D. 360 [latex]\pi[/latex] cu. cm
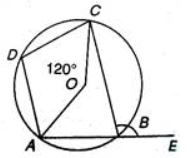
1. ABCD is a cyclic trapezium whose sides AD and BC are parallel to each other. If ?ABC = 72 °, then the measure of the ?BCD is
- A. 162 °
B. 18 °
C. 108 °
D. 72
- A. 44 cm
B. 16.5 cm
C. 12 cm
D. 10.56 cm
- A. 20 %
B. 18 %
C. 10 %
D. 8 %
- A. 50
B. 60
C. 80
D. 100
- A. 294
B. 343
C. 125
D. 216
- A. 4 % loss
B. 2 % loss
C. no loss no gain
D. 4 % gain
- A. 130 °
B. 80 °
C. 100 °
D. 120 °
- A. 2 cm
B. 5 cm
C. 6 [latex]\frac {2}{3} [/latex] cm
D. 6 cm
- A. 180
B. 150
C. 120
D. 110
- A. 20
B. 24
C. 30
D. 34
1. A man invests a certain sum of money at 6% p.a. simple interest and another sun at 7% p.a. simple interest. His income from interest after 2 years was Rs.354. One-fourth of the first sum is equal to one-fifth of the second sum. The total sum invested was:
- A. 2600
B. 2700
C. 2800
D. 2900
- A. 3000
B. 3060
C. 3120
D. 3250
- A. 56 loss
B. 78 profit
C. 80 profit
D. 70 loss
- A. 5 cm
B. 6 cm
C. 4 cm
D. 3 cm
- A. 2 : 1
B. 1 : 2
C. 4 : 5
D. 1 : 1
- A. 0
B. a + b + c
C. a - b + c
D. a + b - c
- A. 57.5 years
B. 50 years
C. 47.5 years
D. 55.5 years
- A. 12[latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex] cm
B. 6 cm
C. 12 cm
D. 3 [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex] cm
- A. 4
B. 2
C. 6
D. 3
- A. 6 cm
B. 6 [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex] cm
C. 3 [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex] cm
D. 9 cm
1. What length of the side of an equilateral triangle. If its area is 64[latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex] sq cm ?
- A. 8 cm
B. 16 cm
C. 16[latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex] cm
D. 8[latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex] cm
- A. 72°
B. 108 °
C. 54 °
D. 36°
- A. x + y = 4
B. x + y = 2
C. x - y = 4
D. x - y = 2
- A. 80
B. 169
C. 258
D. 40
- A. (3, 6)
B. (3,-6)
C. (-3,-6)
D. (-3, 6)
- A. Diagonals are congruent
B. Opposite sides are parallel
C. Diagonals are bisectors of each other
D. Diagonals bisect opposite angles
- A. 66 percent
B. 44.93 percent
C. 39.76 percent
D. 82.5 percent
- A. 66 percent
B. 44.93 percent
C. 39.76 percent
D. 82.5 percent
- A. 5
B. 6
C. 7
D. 4
- A. tanA
B. sinA
C. cosA
D. cotA
1. Rajat sells a machine for Rs 53 lakhs at a loss. Had he sold it for Rs 64 lakh, his gain would have been 10 times the former loss. Find the cost price of the machine.
- A. Rs 63 lakhs
B. Rs 69.3 lakhs
C. Rs 45 lakhs
D. Rs 54 lakhs
- A. a = 3; b = -3
B. a = -3; b = -3
C. a = 3; b = 3
D. a = -3; b = 3
- A. [latex]\frac {-4}{3}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {4}{3}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac {-3}{4}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {3}{4}[/latex]
- A. 18 [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]sq cm
B. 36 [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]sq cm
C. 27 [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]sq cm
D. 9[latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]sq cm
- A. [latex]\frac {22}{3}[/latex] cm
B. [latex]\frac {44}{3}[/latex]cm
C. 44 cm
D. 22 cm
- A. 12, 13
B. 25, 1
C. 9, 16
D. 31, 6
- A. 2 %
B. 8 %
C. 6 %
D. 4%
- A. (2, 0)
B. (-2, 0)
C. (0, -6)
D. (0, 6)
- A. 10 : 81
B. 81 : 10
C. 5 : 2
D. 2 : 2
- A. 2cosAsinB
B. 2sinAcosB
C. 2cosAcosB
D. 2sinAsinB
1. Between 200 and 400 how many numbers are divisible by 7?
- A. 25
B. 29
C. 30
D. 31
- A. 17 [latex]{a}^{2}[/latex]
B. 17 [latex]{b}^{2}[/latex]
C. 12[latex]{a}^{2}{b}^{2}[/latex]
D. 13
- A. x = 4; y = -8
B. x = -3; y = -8
C. x = 3; y = 8
D. x = -3; y = 8
- A. 5
B. 3
C. 9
D. 2
- A. 6x - 14y
B. 14y + 6x
C. 14y - 6x
D. 6xy
- A. cosecA + cotA
B. secA - cotA
C. cosecA - cotA
D. secA + cotA
- A. 288 km
B. 360 kmC. 240 km
D. 192 km
- A. 3, 2
B. 2, 3
C. 4, 2
D. 5, 6
- A. 25
B. 45
C. 20
D. 10
- A. 169
B. 37
C. 73
D. 48
1. Shopkeeper, sold cashew nuts at the rate Rs 1,260 a kg and bears a loss of 8%. Now if he decides to sell it at Rs 1,386 per kg, what will be the result?
- A. 1.2 percent gain
B. 2.4 percent gain
C. 1.2 percent loss
D. 2.4 percent loss
- A. 16 cm
B. 32 cm
C. 5.33 cm
D. 8 cm
- A. 71 percent
B. 113.3 percent
C. 13.6 percent
D. 28.7 percent
- A. x + y = 3
B. x + y = 1
C. x - y = 1
D. x - y = -3
- A. 2520 °
B. 2160 °
C. 2880 °
D. 3240 °
- A. [latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt {3}} [/latex]
B. -[latex]\frac{1}{\sqrt {3}} [/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]
D. -[latex]\sqrt {3}[/latex]
- A. 216
B. -4
C. -92
D. 108
- A. 16 cm
B. 4 cm
C. 8 cm
D. 12 cm
- A. 30
B. 3
C. 5
D. 32