Introduction
Introduction
Rural Banking is a form of service that provides solutions to the financial needs of the consumers in Rural areas. Rural banking had started since the establishment of Banking sector in India. Rural banks are mainly focused on Agro sector.Regional Rural Banks (also RRBs) are local level banking organizations primarily created with a view to serve the rural areas of India with basic banking financial services. However, RRBs may have branches set up for urban operations and their area of operation may include urban areas too.
The area of operation of Regional Rural Banks is limited to the area as notified by Government of India covering one or more districts in the State. RRBs also perform a variety of different functions. RRBs perform various functions in following heads. Providing banking facilities to rural and semi-urban areas. Carrying out government operations like disbursement of wages of MGNREGA workers, distribution of pensions etc. Providing Para-Banking facilities like locker facilities, debit and credit cards.
 History
History
Regional Rural Banks were established under the provisions of an Ordinance passed on September 1975 and the RRB Act. 1976 to provide sufficient banking and credit facility for agriculture and other rural sectors. These were set up on the recommendations of The M. Narasimham Working Group during the tenure of Indira Gandhi's government with a view to include rural areas into economic mainstream since that time about 70% of the Indian Population was of Rural Orientation.
The development process of RRBs started on 2 October 1975 with the forming of the first RRB, the Prathama Bank with authorised capital of Rs. 5 crore at its starting. Also on 2 October 1976 five regional rural banks were set up with a total authorised capital Rs. 100 crore ($10 Million) which later augmented to 500 crore ($50 Million).
 List of RRBs
List of RRBs
Regional Rural Banks - India
- Allahabad UP Gramin Bank
- Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas Bank
- Andhra Pragathi Grameena Bank
- Arunachal Pradesh Rural Bank
- Assam Gramin Vikash Bank
- Bangiya Gramin Vikash Bank
- Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank
- Baroda Rajasthan Ksethriya Gramin Bank
- Baroda UP Gramin Bank
- Bihar Gramin Bank
- Central Madhya Pradesh Gramin Bank
- Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank
- Chattisgarh Rajya Gramin Bank
- Dena Gujarat Gramin Bank
- Ellaquai Dehati Bank
- Gramin Bank Of Aryavrat
- Himachal Pradesh Gramin Bank
- Jammu And Kashmir Grameen Bank
- Jharkhand Gramin Bank
- Karnataka Vikas Grameena Bank
- Kashi Gomti Samyut Gramin Bank
- Kaveri Grameena Bank
- Kerala Gramin Bank
- Langpi Dehangi Rural Bank
- Madhya Bihar Gramin Bank
- Madhyanchal Gramin Bank
- Maharashtra Gramin Bank
- Malwa Gramin Bank
- Manipur Rural Bank
- Marudhara Rajasthan Gramin Bank
- Meghalaya Rural Bank
- Mizoram Rural Bank
- Nagaland Rural Bank
- Narmada Jhabua Gramin Bank
- Odisha Gramya Bank
- Pallavan Grama Bank
- Pandyan Grama Bank
- Paschim Banga Gramin Bank
- Pragathi Krishna Gramin Bank
- Prathama Bank
- Puduvai Bharathiar Grama Bank
- Punjab Gramin Bank
- Purvanchal Bank
- Saptagiri Grameena Bank
- Sarva Haryana Gramin Bank
- Sarva UP Gramin Bank
- Saurashtra Gramin Bank
- Sutlej Gramin Bank
- Telangana Grameena Bank
- Tripura Gramin Bank
- Utkal Grameen Bank
- Uttar Bihar Gramin Bank
- Uttarakhand Gramin Bank
- Uttarbanga Kshetriya Gramin Bank
- Vananchal Gramin Bank
- Vidharbha Konkan Gramin Bank
 Highlights
Highlights
In India there are 14,475 rural banks in the country of which 2126 are located in remote rural areas.
- SBI bank is the largest bank serving to rural banking
- Haryana state co-operative Apex bank limited, NABARD, Sindhanur Urban Souharda Co-operative bank, united bank of India are other banks operating in rural areas.
- Rural population of about 780 million with limited access to financial services.
- A high proportion of rural lending is from informal sources.
- About 500 – 600 million people
- Rural economy constitutes about 50% of GDP .
- Banks have woken up to the potential in the rural sector.
- Current demand for credit in rural India around Rs. 1, 33, 000 Crs.
- Commercial bank branches cover only 7% of rural sector and large market still untapped.
- 43% of households in middle and high income groups from rural India in 2005. Their number has grown by 79% from 1996-2005.
- One million self-help group linkage achieved in 2005.
- Committee on financial set-up in 2006.
- Rural banking faces two challenges they are Regulation, Distribution.
- Regulation with respect to banking has been designed for delivery in urban India.
- Distribution requires more manpower to be deployed in rural area.
- Rs. 1 crore business in micro finance required 30 people in terms of manpower, the same volume of business in other portfolios requires only one person.
- Public trusts
- Societies
- Section 25 companies
- Self help groups and federation
- Co-operative societies
- Non banking financial corporation
- Largest commercial bank in India.
- Bank with branch network – 9247.
- Rural and semi urban branches – 6473.
- SBI has 30 regional rural banks in India known as RRBs.
- The rural banks of SBI is spread in 13 states extending from Kashmir to Karnataka and Himachal Pradesh to North East.
- The total number of SBIs Regional Rural banks in India branches are 2349.
- The Bank is actively involved since 1973 in non-profit activity called community services Banking.
- Micro Finance deeply ingrained in SBI.
- Social obligation services like E-Ticketing.
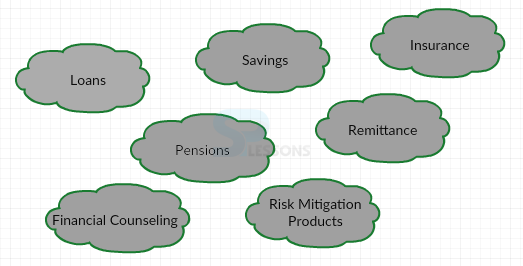
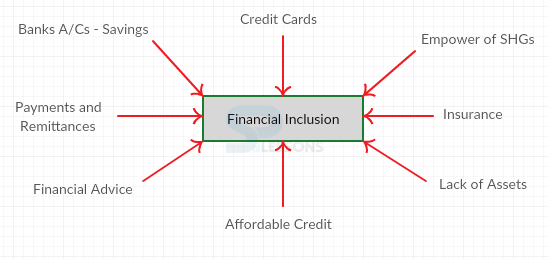
- Comprehensive financial services, viz, savings, credit, remittances, insurance and financial products through ICT.
- Opening of simple savings accounts for the villagers with zero balance.
- One of the villagers as SBI Mitra.
- Drop Box depositing cash at the SBI Mitra’s shop/house.
- Small emergency loan.
- SBI Mitra assists in opening account.
- Piloted in Bahirgaon village in Maharashtra.
- A smart card with photo and fingerprint.
- Card serves as the account.
- Can be used for govt disbursals, insurance and loan disbursals.
- This is medium limit of 20,000.
- Farmers can withdraw partial amount.
- 2.5% annual interest only on withdraw led amount.
- Credit linked 677 thousand SHGs as on December 2006 with total disbursement of US$660 million benefiting 9.48 million families.
- Market share of 43% of total SHGs financed by commercial banks in the Country.
- 734 thousand SHGs are having thrift account with total thrift of US$108 million in these accounts.
- 6400 thousand women beneficiaries.
- Increase in income.
- Increase in expenditure on education, clothes and health.
- Improvement in status of women and their confidence level.
- Improved health and hygiene.
- Better housing.
- Decline in social evils.
- Issue one crore IT enabled No Frill accounts through alternate channels.
- Open 15 lac No frill accounts through Banks Branch channel.
- Cover 1,00,000 unbanked villages through Business Correspondents /Business Facilities and opening new branches.
- Set up additional processing capacity of Rural and Semi Urban branches by setting up 300 rural credit processing centres.
- Open 870 new branches under second wave of branch expansion program.
- Open at least 250 rural household accounts at each rural and Semi urban branch every year as per GOI directives.
- Low cost ATM for Wage Disbursement with finger print authentication and local language interface.
- This ultra-low cost ATM costs just 1/10th that of the traditional ATM used in cities.
- Will enable transfer of funds from NREGA directly to the rural workers.
- It is just an ATM but an e-governance model that is People friendly and empower the Poorest labour to assert his/her rights.
- Smart Cards, Biometric scanning for signatures and Handled devices and other innovative technology needs to be explored.
- It will help bring down the cost per transaction as well as help improve the service delivery in Rural Areas.
- Banks currently have to invest 40% in priority sector lending (Agriculture, SME & Government Securities).
- MFI Lending provides 10-14% return as against 6-7% in Government instruments.
- Risks could be mitigated further by partnering with MFI in specific markets and while dealing with SHG directly in others.
- Thus entering the micro finance business makes a lot of commerce sense for SBI in the long run.
 Quiz
Quiz
1. Rural banks are mainly focused on?
- A. Agro Sector
B. Villages
C. Business
D. None of the Above
- A. RBI
B. SBI
C. Central bank
D. ICICI
- A. Regulation
B. Distribution
C. Both A and B
D. None of these
- A. Formal/Banks
B. Informal/Non-Banks
C. Both A and B
D. None of these
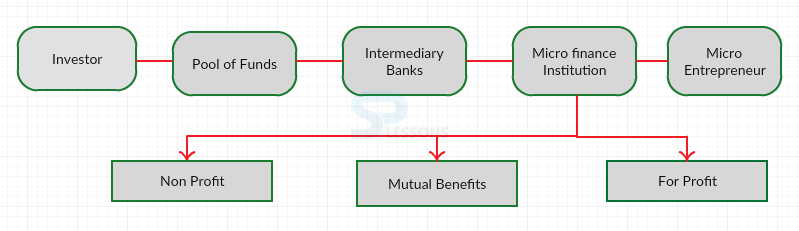
- A. Non Profit
B. Mutual Benefits
C. For Profit
D. All of these
- A. SBH
B. SBI
C. ICICI
D. None of these
- A. SBH
B. RBI
C. SBI
D. HDFC
- A. 25,000
B. 30,000
C. 35,000
D. 20,000
- A. 40%
B. 50%
C. 35%
D. 45%
- A. Micro finance institutions
B. community services Banking
C. Non profit banks
D. Informal Banks