Introduction
Introduction
What is meant by Mutual Fund ?
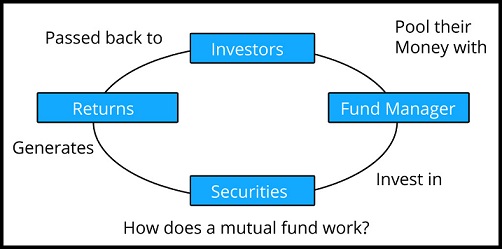
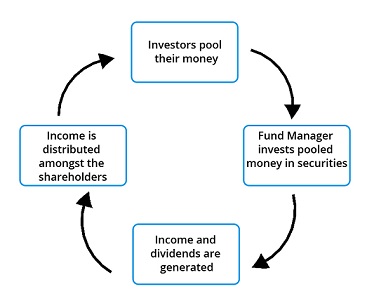
- A pool of money that is pooled together from various investors and invested in company shares, bonds, stocks, or other entity.
- In another way, a Mutual Fund is a professionally-managed trust that pools the savings of many investors and invests them in securities like stocks, bonds, short-term money.
- These collective funds (referred to as Assets Under Management or AUM) are then invested by an expert fund manager appointed by a mutual fund company (called Asset Management Company or AMC).
 Mutual Funds
Mutual Funds
History - Mutual Funds:
- The mutual fund industry in India began in 1963 with the formation of the Unit Trust of India (UTI) as an initiative of the Government of India and the Reserve Bank of India.
- In 1987, SBI Mutual Fund became the first non-UTI mutual fund in India.
- The year 1993 heralded a new era in the mutual fund industry.
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Act was passed in 1992
- The SEBI Mutual Fund Regulations came into being in 1996.
- The Association of Mutual Funds in India (AMFI), was established on 1995.
- SEBI has made AMFI certification mandatory for all those engaged in selling or marketing mutual fund products.
- Most suitable investment for the cautious investor.
- For these investors, high returns are less important than preserving their capital.
- Prefer more stable, lower risk investments, especially those which offer more liquidity.
- Opportunity to sell the products quickly if there is a downturn.
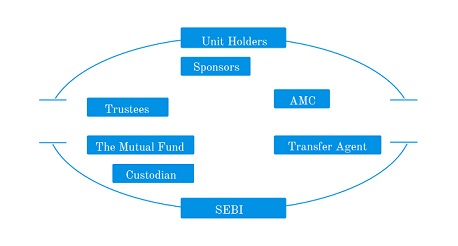
- Set up in the form of a trust that has a Sponsor, Trustees, Asset Management Company (AMC).
- The trust is established by a sponsor(s) who is like a promoter of a company.
- The trust is registered with Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) as a Mutual Fund.
- a. Buying a home
b. Building a retirement corpus
c. Child’s education and marriage
d. Legacy Planning
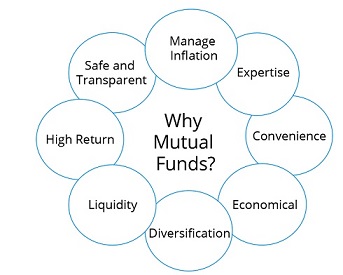
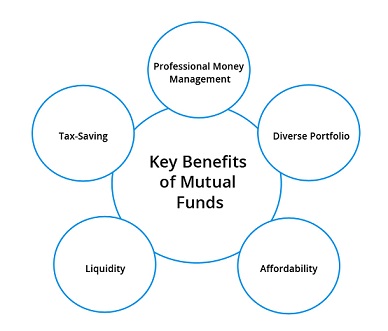
- MFs are managed by professional fund managers, responsible for making wise investments according to market movements and trend analysis.
- MFs allows to invest savings across a variety of securities and expand assets according to the objectives, and risk tolerance.
- MFs provide the freedom to earn on their(investors) personal savings.
- Investments can be as less as Rs. 500.
- MFs offer relatively high liquidity.
- Certain mutual fund investments are tax efficient.
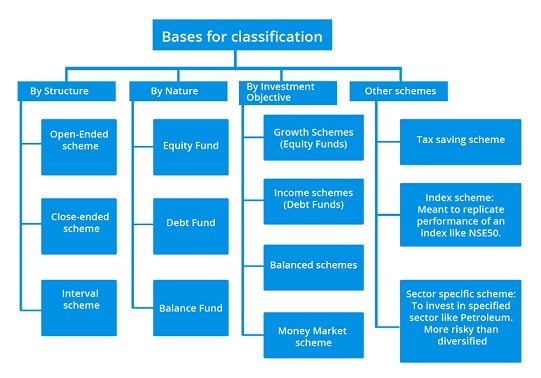
- Open-ended Scheme
- Close-ended Scheme
- Interval Scheme
- This scheme allows investors to buy or sell units at any point in time.
- This does not have a fixed maturity date.
- In India, this type of scheme has a stipulated maturity period and investors can invest only during the initial launch period known as the NFO (New Fund Offer) period.
- Operating as a combination of open and closed ended schemes, it allows investors to trade units at pre-defined intervals.
- Equity Fund
- Debt Fund
- Balance Fund
- Equities are a popular mutual fund category amongst retail investors.
- Although it could be a high-risk investment in the short term, investors can expect capital appreciation in the long run.
- If some one is at prime earning stage and looking for long-term benefits, growth(Equities) schemes could be an ideal investment.
- In a debt/income scheme, a major part of the investable fund are channelized towards debentures, government securities, and other debt instruments.
- This scheme allows investors to enjoy growth and income at regular intervals.
- Funds are invested in both equities and fixed income securities.
- Equity Fund
- Debt Fund
- Balance Fund
- Money Market Scheme
- Tax Saving Scheme
- Index Scheme
- Sector Specific Scheme
- This scheme offers tax benefits to its investors.
- The funds are invested in equities there by offering long-term growth opportunities.
- Tax saving mutual funds (called Equity Linked Savings Schemes) has a 3-year lock-in period.
- Index schemes is a widely popular concept in the west.
- These follow a passive investment strategy where your investments replicate the movements of benchmark indices like Nifty, Sensex, etc.
- Sectoral funds are invested in a specific sector like infrastructure, IT, pharmaceuticals, etc. or segments of the capital market like large caps, mid caps, etc.
- This scheme provides a relatively high risk-high return opportunity within the equity space.
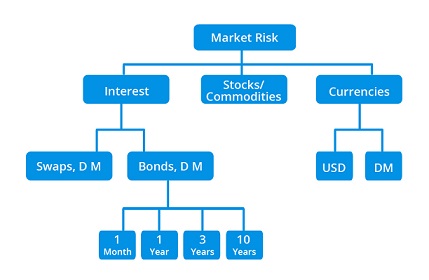
- Market risk is the inherent risk in all type of investments that result from fickle nature of market of gobal economy in general.
- Net Asset Value (NAV) is the amount which a unit holder would receive if the mutual fund were wound up.
- It is the net value of all assets less liabilities.
- NAV represents the market value of total assets of the Fund less total liabilities attributable to those assets.
- NAV changes daily.
- The value of assets and liabilities changes daily.
- NAV is computed as a value per unit of holding.
| Type of Fund | Typical Investment |
|---|---|
| Equity or Growth Fund | Equities like stocks |
| Fixed Income Fund | Fixed income securities like government and corporate bonds |
| Money Market Fund | Short-term fixed income securities like treasury bills |
| Balanced Fund | A mix of equities and fixed income securities |
| Sector-specific Fund | Sectors like IT, Pharma, Auto etc |
| Index Fund | Equities or Fixed income securities chosen to replicate a specific Index for example S&P CNX Nifty |
| Fund of funds | Other mutual funds |