Introduction
Introduction
PNB SO Online Test, will comprise of Objective Tests for 200 marks consisting of 4 Sections as follows. A composite time of 120 minutes will be given for answering the questions. The below sections gives the detailed information about PNB SO Quantitative Aptitude Section.
 Pattern
Pattern
| Sr.No. | Name of Tests | No. of Questions | Maximum Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reasoning | 50 | 50 | 120 mins |
| 2 | English Language | 50 | 25 | |
| 3 | Quantitative Aptitude | 50 | 50 | |
| 4 | Professional Knowledge (Relevant to the Post) | 50 | 75 | |
| Total | 200 | 200 | ||
 Syllabus
Syllabus
[Click Here] for PNB SO Online Test Syllabus
Note:
Penalty for Wrong Answers
There will be penalty for wrong answers marked in the Online Test. For each question for which a wrong answer has been given by the candidate one fourth or 0.25 of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as penalty to arrive at corrected score. If a question is left blank, i.e. no answer is marked by the candidate; there will be no penalty for that question.
 Samples
Samples
Average
1. The average weight of 3 person P, Q, R is 84 kg. Another person who is S joins the group and now the present average of the group becomes 80 kg. If another person T, whose weight is 3 kg more than that of S, replaces P then the average weight of Q, R, S, and T becomes 78 kg. Find the weight of P.
-
A. 70 kg
B. 72 kg
C. 79 kg
D. 78 kg
-
A. 35 years
B. 30 years
C. 40 years
D. 48 years
-
A. 15
B. 12
C. 18
D. 21
-
A. 7
B. 84
C. 9
D. 87
-
A. 55
B. 54
C. 52
D. 53.5
-
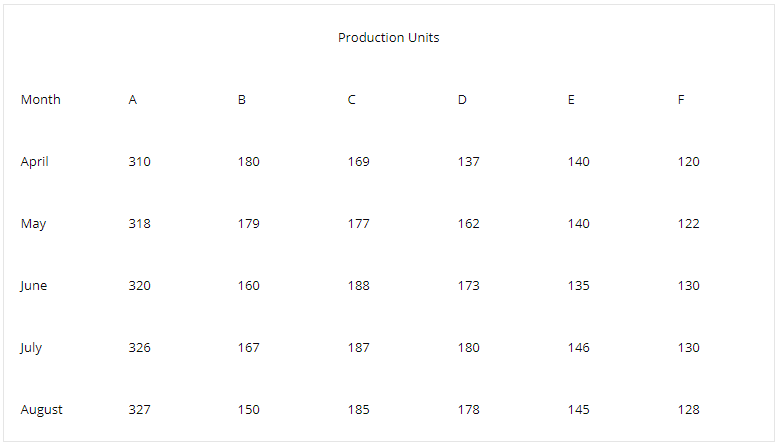
A. August
B. June
C. July
D. April
-
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
-
A. April & June
B. June & July
C. July & August
D. April & May
-
A. one
B. Three
C. Two
D. Four
-
A. 8 %
B. 10 %
C. 15 %
D. 18 %
-
A. 15
B. 30
C. 45
D. 60
-
A. 14/16
B. 15/19
C. 16/21
D. 17/23
-
A. 2/4
B. 25/29
C. 9/10
D. 17/24
-
A. 371.722
B. 391.622
C. 380.611
D. 463.94
-
A. 298.1057
B. 298.222
C. 298.946
D. 299.09
-
A. 3800
B. 4200
C. 4400
D. 3200
E. None of these
-
A. 193
B. 183
C. 223
D. 213
E. 233
-
A. 4/189
B. 6/63
C. 2/63
D. 20/21
E. None of these
-
A. 66, 77
B. 70, 84
C. 94, 108
D. 84, 96
E. 66, 106
-
A. 1,174
B. 74,100
C. 29, 154
D. 29, 145
E. None of these
-
A. 3: 7
B. 5: 7
C. 7: 3
D. 7: 5
E. None of these
-
A. 1: 3
B. 2: 3
C. 3: 4
D. 4: 5
E. None of these
-
A. 3 : 1
B. 3: 2
C. 4: 3
D. 5: 3
E. None of these
-
A. 1: 2
B. 2: 1
C. 2: 3
D. 3: 2
E. None of these
-
A. 18
B. 18.50
C. 19
D. 19.50
E. None of these
-
A. 2
B. 4
C. 5
D. 7
E. None of these
-
A. 210
B. 240
C. 320
D. 360
E. None of these
-
A. 107
B. 108
C. 109
D. 118
E. None of these
-
A. 620
B. 734
C. 862
D. 924
E. None of these
-
A. 205
B. 315
C. 405
D. 510
E. None of these
-
A. 4% of a
B. 5% of a
C. 20% of a
D. None of these
-
A. 72
B. 80
C. 120
D. 150
E. 100
-
A. 2 : 3
B. 1 : 1
C. 3 : 4
D. 4 : 3
-
A. 34%
B. 44%
C. 54%
D. 64%
-
A. 2700
B. 2900
C. 3000
D. 3100
Problems on Ages
1. Father is four times the age of his daughter. If after 5 years, he would be threee times of daughter’s age, then further after 5 years, how many times he would be of his daughter’s age?
-
A. 1.5 times
B. 2 times
C. 2.5 times
D. 3 times
-
A. 6.2 years
B. 7.7 years
C. 13.3 years
D. 10 years
-
A. 32.5 years
B. 27.5 years
C. 25 years
D. 24.9 years
-
A. 5 years
B. 25 years
C. 10 years
D. 15 years
-
A. 11 : 7
B. 9 : 5
C. 7 : 4
D. 7 : 3
-
A. 16
B. 18
C. 20
D. 22
-
A. No profit no loss
B. 5%
C. 8%
D. 10%
-
A. Rs 14.80
B. Rs 15.40
C. Rs 15.60
D. Rs 16.30
-
A. Rs 12.50
B. Rs 13.50
C. Rs 15.50
D. None of these
-
A. 8%
B. 9%
C. 10%
D. None of these
-
A. 270, 840, 1160
B. 341, 243, 245
C. 400, 800, 670
D. None of the above
-
A. 5:9
B. 5:7
C. 7:5
D. 9:5
-
A. Rs. 3000
B. Rs. 4000
C. Rs. 9000
D. Rs. 6000
-
A. 100
B. 10
C. 90
D. 150
-
A. 75
B. 125
C. 150
D. 300
-
A. Rs. 8500
B. Rs. 3200
C. Rs. 2100
D. Rs. 4300
-
A. Rs. 12000
B. Rs. 21000
C. Rs. 37000
D. Rs. 63000
-
A. Rs. 600
B. Rs. 666
C. Rs. 780
D. Rs. 800
-
A. Rs. 12000
B. Rs. 11000
C. Rs. 14000
D. Rs. 15000
-
A. Rs. 4000
B. Rs. 5000
C. Rs. 6000
D. Rs. 7000
-
A. Rs. 1.24 crores
B. Rs. 1.28 crores
C. Rs. 2.56 crores
D. Rs. None of these
-
A. 360
B. 375
C. 378
D. 384
-
A. 3
B. 4
C. 6
D. 9
-
A. Rs. 6500
B. Rs. 7500
C. Rs. 8000
D. Rs. 9000
-
A. 40
B. 75
C. 90
D. 100
-
A. 1000 mt
B. 120 mt
C. 1200 mt
D. 600 mt
-
A. 20 min
B. 50 min
C. 60 min
D. 40 min
-
A) 1333.33 mt
B) 1000 mt
C) 7500 mt
D) 1250 mt
-
A. 2.5 km
B. 3.6 km
C. 5.5 km
D. 12.5 km
-
A. 45 km/ph
B. 55 km/ph
C. 60 km/ph
D. 65 km/ph
-
A. 12 hrs
B. 18 hrs
C. 11½ hrs
D. 15 hrs
E. 22 hrs
-
A. 5 days
B. 10 days
C. 15 days
D. 20 days
E. 25 days
-
A. 2 days
B. 3 days
C. 4 days
D. 5 days
E. 1 days
-
A. 12 days
B. 4 days
C. 3 days
D. 2 days
E. None of these
-
A. 45 days
B. 22.5 days
C. 25 days
D. 18 days
E. 12 days