Introduction
Introduction
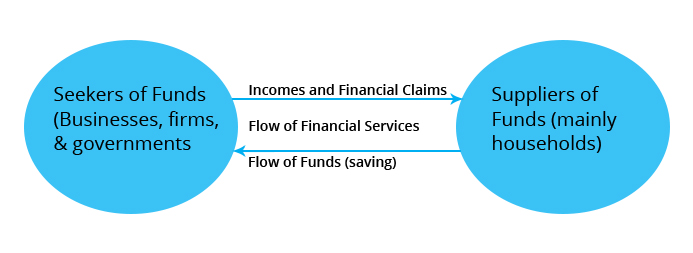
 Working
Working
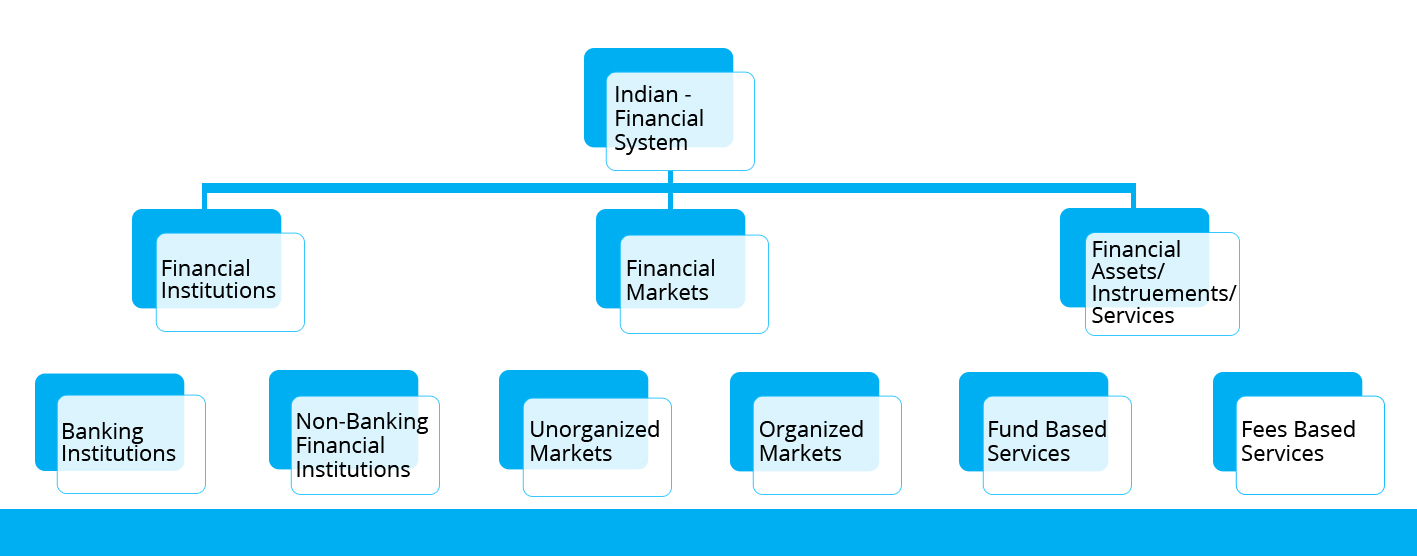
 Structure
Structure
The structure of Indian Financial System comprises of:
1. Financial Institutions: These institutions act as intermediaries of financial markets that will facilitate financial transactions occurring between individuals and financial customers. There are two types of financial institutions:
- Banking or depository institutions: These institutions are banks and credit unions that collect money from the public. In return, the public receives interest on money deposits. These can further be categorised as:
- Regulatory institutions like SEBI, RBI, IRDA
- Intermediaries that include commercial banks who provide short-term loans and other financial services.
- Non-intermediaries that provide long-term loans to corporate customers like NABARD, IDBI.
- Non-Banking or Non-depository institutions: These are firms and companies that deal in brokerage, insurance, and mutual funds to collect money deposits. They can also sell financial products.
- Capital Markets: These markets deal in long terms securities, i.e. securities that have a maturity period of more than one year.
- Money Market: These markets deal with short-term debt instruments that have a maturity period of less than one year.
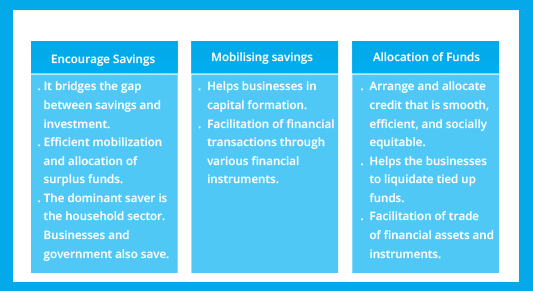
 Functions
Functions
 Importance
Importance
 Intermediary
Intermediary
Intermediaries Involved:
- The Indian financial system is equipped with proper channels to ensure that adequate information of the issue, issuer, and the security is passed on. These channels are referred to as financial intermediaries.
- These financial intermediaries ensure that the financial assets reach the ultimate investor to garner their requisite amount.
- Along with the development in the financial system, in India, financial intermediaries have also widened. It has now been conducted by various institutions but under the surveillance of the Reserve bank of India (RBI).
| Intermediaries | Type of Market | Example of institutions | Role Performed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Exchanges | Capital Market | NSE, BSE, Calcutta Stock Exchange, Cochin stock exchange etc. | Secondary markets to securities |
| Investment Bankers | Capital Market, Credit Market | Commercial banks, cooperative banks | Corporate advisory services, Issue of services |
| Underwriters | Capital Market, Money Market | Development banks, NBFC | Subscribe to unsubscribed portion of securities |
| Registrars, Depositories, Custodians | Capital Market | Insurance companies, mutual fund companies, and so on. | Issuance of securities to the investors on behalf of the company. Handle share transfer activity. |
| Primary Dealers Satellite Dealers | Money Market | Registered entities, commercial banks and their subsidiaries which have the license to purchase and sell government securities like SBI. | The market making in government securities. |
| Forex Dealers | Foreign Exchange Market | Western Union | Ensure exchange link currencies |