Introduction
Introduction
The process by which access to appropriate financial products and services is ensure is known as Financial Inclusion. Vulnerable groups need it like the weaker sections of society, lower income groups. It is equally essential that the financial products and services reach the target population at an affordable cost. Besides, it should reach in a fair and transparent manner through mainstream Institutional Players.
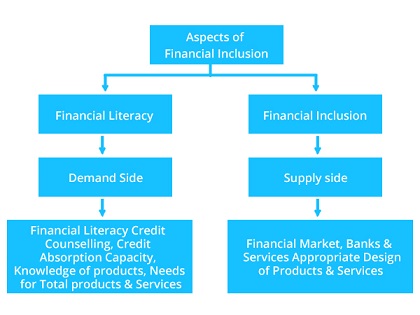
 Aspects
Aspects
 History
History
A large section of population in India still remains unbanked. This is the population from the lower income group who do not have access to financial products and services.
Here is a timeline to reveal how Financial Inclusions has been addressed in different policies even after 70 years of independence in India:
Financial inclusion can make significant changes in the Economy.
Since then this is expected to witness a revolution in the availability of financial instruments in rural areas, it is supposed to bring in specific changes in the rural economy as well.
 Importance
Importance
As the history reveals, the policymakers have been focusing on financial inclusion of rural and semi-rural areas in India.
This is mainly attributed to the importance it holds towards fulfilling the needs:
1.Financial inclusion promotes savings:
- The absence of savings has been the prime reason behind the lower income group category living under economic duress.
- Financial inclusions try to create a platform for inculcating the habit of saving money among all.
- Instruments like Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna have encouraged lower income group people, to have access to financial services like bank accounts, remittances, insurance, and pensions in an affordable way.
- Informal channels of credit continue to hold importance among the unbanked population who shall be vulnerably dependent upon them.
- These informal channels usually include family, friends, and moneylenders.
- Financial inclusion would mean greater availability of adequate and transparent credit from the formal banking channels.
- This shall allow the entrepreneurial spirit of the masses to bring in increased outputs and prosperity in the countryside.
- In the 70-year old history of economic independence of India, it has been witnessed that a considerable sum of money that is meant to reach the poorest of the poor, fails to reach them.
- India is known to have a large Bureaucratic System that provides a scope for money to leak. Such leakages do not allow the funds to reach the intended parties.
- Recent government efforts have replaced subsidizing products and making cash payments with direct cash transfers to beneficiaries through the bank accounts.
 Measures
Measures
The Central Bank or the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has taken several measures with the aim of achieving financial inclusions. The three main measures are:
1. No frills account: RBI has initiated no-frills account which provides the basic facilities of deposit and withdrawal to the account holders.
- These accounts make banking processes affordable by cutting down on extra frills that are not used by a lower section of society.
- RBI has also eased the Know Your Customer (KYC) norms for opening such accounts.
- The mechanism is a boon in areas where banks are unable to open branches due to cost considerations.
- The business correspondents shall provide affordability and easy accessibility to the unbanked population.
- With the help of suitable technology, the business correspondents take the banks to the doorsteps of the rural household population.
- The human-less transfer is expected to plug the leakages emerging due to various levels of bureaucracy.
- Relief to the beneficiaries is provided by reducing the government’s cost of transfer and monitoring.