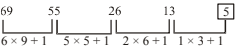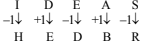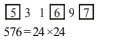Introduction
Introduction
Career in Banking is one of the most lucrative and most sought after careers. In India, Bank Recruitment Exams are primarily conducted for recruitment of Probationary Officers, Clerks & Specialist Officers. India currently[2019] has 93 commercial and 27 public sector banks out of which 19 are nationalized and 6 are SBI and its associate banks and rest two are IDBI Bank and Bharatiya Mahila Bank, which are categorized as other public sector banks. Recruitment for Bank Probationary Officers, Management Trainees, Clerks and for various other posts generally follow a 3 step recruitment process: Preliminary Exam + Mains Exam + Interview & Group Discussion. The article SBI PO Prelims Practice Set presents a practice set for the most sought after SBI PO recruitment. Until the year 2013, All Public Sector Banks used to conduct their own entrance test, GDs and Personal Interview for recruiting candidates. However, after 2014, IBPS started conducting recruitment Tests for 12 PSU Banks. SBI holds a separate entrance test for recruitment.
Prelims exams are very important to clear every government sector or bank related recruitment process in India. Prelims are also known as Screening Tests. Only those candidates who are selected in the prelims round are allowed to move further up in the recruitment process. The marks obtained in the preliminary exams are not considered for the final merit list. Preliminary Exams are only meant to be screening tests. Preliminary exams usually consist of 3 sections, with 100 questions with a time duration of 1 hour. Preliminary exams most certainly have negative marking.
 Model Test
Model Test
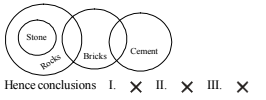
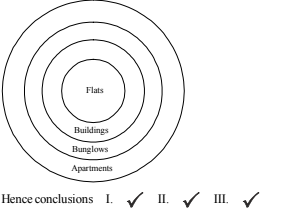
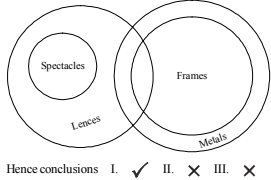
Directions Q (1 - 10): What will come in place of the question mark (?) in the following equations
1. [latex]\frac{117 × 117 × 117 - 98 × 98 × 98}{117 × 117 × 117 + 98 × 98 × 98}[/latex] = ?
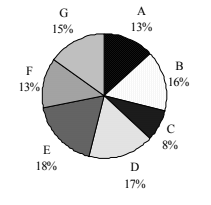
Proportion of population of seven villages in 1995.
11. In 1996, the population of villages A as well as B is increased by 10% from the year 1995. If the population of village A in 1995 was 5000 and the percentage of population below poverty line in 1996 remains same as in 1995, find approximately the population of village B below poverty line in 1996.
-
A. 215
B. 311
C. 19
D. 29
E. None of these
-
A. 6
B. 3
C. 5
D. -1
E. None of these
-
A. 18
B. 14
C. 324
D. 212
E. None of these
-
A. 120
B. 1.20
C. 12
D. 0.12
E. None of these
-
A. 4.485
B. 2.589
C. 4
D. 2
E. None of these
-
A. 0
B. 225
C. 300
D. 240
E. None of these
-
A. [latex]\frac{25}{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{4}{25}[/latex]
C. 4
D. 25
E. None of these
-
A. 8
B. 12
C. 16
D. 32
E. None of these
-
A. 825
B. 82.5
C. 3666.66
D. 2
E. None of these
-
A. 4 + [latex]\sqrt{15}[/latex]
B. 4 - [latex]\sqrt{15}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
D. 1
E. None of these
| Villages | % population below poverty line |
|---|---|
| A | 45 |
| B | 52 |
| C | 38 |
| D | 58 |
| E | 46 |
| F | 49 |
| G | 51 |
-
A. 4000
B. 45000
C. 2500
D. 3500
E. None of these
-
A. 19770
B. 19200
C. 18770
D. 19870
E. None of these
-
A. 3000
B. 2500
C. 4000
D. 3500
E. None of these
-
A. 4000
B. 6000
C. 6500
D. 4800
E. None of these
-
A. 207 : 76
B. 76 : 207
C. 152 : 207
D. Data inadequate
E. None of these
-
A. 5s
B. 7.5s
C. 10s
D. 15s
E. None of these
-
A. 75
B. 8
C. 9
D. 85
E. None of these
-
A. 15
B. 20
C. 10
D. 5
E. None of these
-
A. [latex]{a}^{2}[/latex]h/3[latex]{p}^{2}[/latex]cm
B. 3h[latex]{p}^{2}[/latex]/[latex]{a}^{2}[/latex]cm
C. [latex]{p}^{2}[/latex]/3[latex]{h}^{2}[/latex]cm
D. 3[latex]{a}^{2}[/latex]/h[latex]{p}^{2}[/latex]cm
E. None of these
-
A. ₹6000
B. ₹8230
C. ₹5000
D. ₹4600
E. None of these
-
A. 3
B. 9
C. 6
D. 12
E. None of these
-
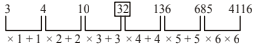
A. 136
B. 10
C. 4116
D. 32
E. None of these
-
A. 26
B. 13
C. 5
D. 55
E. None of these
-
A. 386
B. 6144
C. 96
D. 1536
E. None of these
-
A. 5
B. 20
C. 40
D. 26
E. None of these
-
A. 180
B. 415
C. 150
D. 210
E. 300
-
A. 3000
B. 300000
C. 3000000
D. 5000
E. 9000000
-
A. 2800
B. 6666
C. 4666
D. 2400
E. 2670
-
A. 1
B. [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
C. 2[latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{3}{4}[/latex]
E. [latex]\frac{9}{11}[/latex]
-
A. 27000000
B. 9000000000
C. 180000
D. 2.7 × [latex]{10}^{9}[/latex]
E. 2700000
-
A. Rs12
B. Rs20
C. Rs16
D. Rs18
E. None of these
-
A. 1 : 2
B. 2 : 1
C. 2 : 3
D. 3 : 4
E. None of these
-
A. Rs 40,000
B. Rs 40,500
C. Rs 45,500
D. Rs 50,000
E. None of these
-
A. Rs 45,000
B. Rs 18,000
C. Rs 15,500
D. Rs 28,000
E. None of these
-
A. 25 hours
B. 40 hours
C. 30 hours
D. 35 hours
E. None of these
36. Which is the third number to the left of the number which is exactly in the middle of the following sequence of numbers?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 4 6 8 9 7 5 3 9 8 7 6 4 3 2 1
-
A. 3
B. 2
C. 5
D. 6
E. None of these
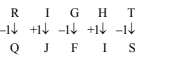
-
A. QJHIS
B. QJFGS
C. SHHGU
D. QJFIU
E. QJFIS
-
A. M
B. N
C. O
D. M or O
E. None of these
-
A. 25
B. 26
C. 27
D. Data inadequate
E. None of these
-
A. Ka
B. Bi
C. Ya
D. Pu
E. None of these
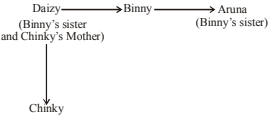
-
A. Niece
B. Sister
C. Cousin
D. Aunt
E. None of these
-
A. 24th
B. 23rd
C. 25th
D. 26th
E. None of these
-
A. 4
B. 2
C. 6
D. @
E. ©
-
A. CDLJMBD
B. CDWDBM
C. LDCJMBD
D. EFNJMBD
E. None of these
-
A. 19
B. 11
C. –31
D. 23
E. None of these
-
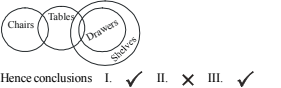
A. Only I and III follow
B. Only I and either II or III follow
C. Only II and either I or III follow
D. All I, II and III follow
E. None of these
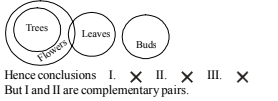
-
A. Only II and III follow
B. Only III follows
C. Only either I or II follows
D. Either I or II and III follow
E. None of these
-
A. Only I and either II or III follow
B. Only either II or III follows
C. Only I and II follow
D. All follow
E. None of these
-
A. None follows
B. Only I and II follow
C. Only II and III follow
D. Only I and III follow
E. All I, II and III follow
-
A. Only III follows
B. Only I follows
C. Only I and either II or III follow
D. Only I and II follow
E. None of these
-
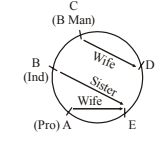
A. Brother
B. Uncle
C. Brother-in-law
D. Can’t be determined
E. None of these
-
A. the industrialist
B. his wife
C. D
D. Can’t be determined
E. None of these
-
A. D
B. A
C. B
D. Can’t be determined
E. None of these
-
A. Professor
B. Industrialist
C. Businessman
D. Can’t be determined
E. None of these
-
A. B
B. A
C. C
D. E
E. None of these
-
A. If only conclusion I is true
B. If only conclusion II is true
C. If either conclusion I or II is true
D. If neither conclusion I nor II is true
E. If both conclusions I and II are true
-
A. If only conclusion I is true
B. If only conclusion II is true
C. If either conclusion I or II is true
D. If neither conclusion I nor II is true
E. If both conclusions I and II are true
-
A. If only conclusion I is true
B. If only conclusion II is true
C. If either conclusion I or II is true
D. If neither conclusion I nor II is true
E. If both conclusions I and II are true
-
A. If only conclusion I is true
B. If only conclusion II is true
C. If either conclusion I or II is true
D. If neither conclusion I nor II is true
E. If both conclusions I and II are true
-
A. If only conclusion I is true
B. If only conclusion II is true
C. If either conclusion I or II is true
D. If neither conclusion I nor II is true
E. If both conclusions I and II are true
-
A. If only conclusion I is true
B. If only conclusion II is true
C. If either conclusion I or II is true
D. If neither conclusion I nor II is true
E. If both conclusions I and II are true
-
A. 2 8
B. 5 6 B
C. Q $ 9
D. 1 3 E
E. D R 7
-
A. 118
B. 46
C. 79
D. 107
E. None of these
-
A. 109
B. 41
C. 82
D. 27
E. None of these
-
A. • (13) 4
B. 4 • (13)
C. 1 £ D
D. • (13) £
E. None of these
-
A. RD
B. U •
C. KA
D. Q3
E. 6B
-
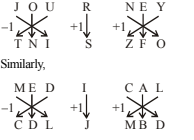
A. N, P, L
B. P, L, N
C. L, N, O
D. O, P, L
E. None of these
-
A. N
B. O
C. L
D. Can’t be determined
E. None of these
-
A. L
B. O
C. P
D. Can’t be determined
E. None of these
-
A. Architect
B. Pilot
C. Architect or pilot
D. Journalist
E. None of these
-
A. Father
B. Mother
C. Mother-in- law
D. Son - in - law
E. None of these
Directions Q (71 - 80): Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Long ago there was a poor Brahmin named Krishnan. He could not find enough work to do. Sometimes, he and his family had to go without food. At last Krishnan decided to leave his village in search of work. Early next morning, he left the house. He walked the whole day until he came to a thick jungle. He was tired, thirsty and hungry. While looking around for water to drink, he found a well. He went to the well and looked in. There he saw a jaguar, a monkey, a snake and a man. They had all fallen into the well. “O, noble Brahmin”, the jaguar called out to him, “Please help me out, so that I can go back to my family.”
“But you are a jaguar”, said Krishnan. “How do I know you will not kill me?” “Don’t be afraid of me, I promise I will not do you any harm”, replied the jaguar. Krishnan reached into the well and pulled out the jaguar. The jaguar thanked him and said, “I’m Shersingh. I live in a cave in the mountains. I shall be most delighted if I can repay my debt to you someday.” Krishnan then heard the monkey calling out to him from the well. The Brahmin at once pulled the monkey out. The monkey thanked the Brahmin. “If you are ever in need of food, just drop in at my place below that big mountain. Bali is my name.” Now the snake called out to him for help. “Help you!” exclaimed Krishnan. “You are a snake. What if you bite me?” “I shall never bite you”, said the snake. So Krishnan pulled the snake out of the well. The snake said, “Remember, if you are ever in any difficulty, just call out my name-Naagesh, and wherever you are, I shall find you.” The jaguar, the monkey and the snake took leave of the Brahmin. But before they left, they spoke to him about the man in the well. “Please do not help him,” said Shersingh. “If you do”, said Naagesh, “you will be in trouble yourself.” As soon as they left, the man in the well began to call out for help. Krishnan felt sorry for the man and pulled him out of the well. “Thank you for your kindness”, said the man. “I am Seth Ghanshyamdas. I am a goldsmith. If you ever need my help, don’t hesitate to visit my humble house near the city.” The goldsmith then left for home.
After some time, the Brahmin continued his journey. But he could not find any work. He then remembered Shersingh, Bali, Naagesh and Seth Ghanshyamdas. He thought it was time to seek their help. He first went to Bali. The monkey was overjoyed to see him. He gave him a warm welcome and offered him some really delicious fruits. The Brahmin told him how grateful he was. Now Krishnan went to see Shersingh, the jaguar. As soon as Shersingh saw Krishnan coming, he ran out to welcome him. He gave Krishnan a beautiful gold necklace and other precious jewellery. Krishnan thanked Shersingh for the jewellery and departed. His journey had at last brought him luck, he thought. He would be able to sell the ornaments for a good price. But who could help him to sell the ornaments? He then remembered Seth Ghanshyamdas. He went to him. The goldsmith was glad to see Krishnan. “I have come to ask for your help”, said Krishnan. “Here are some ornaments. Please give me a good price for them.” Seth Ghanshyamdas took the jewellery and examined it carefully. “I shall certainly help you”, he said. “But let me show them to another goldsmith. Please wait here, I will be right back.” He then went out with the ornaments. Seth at once rushed to the Palace of the King. He said, “A man brought these ornaments to me and asked me to sell them. But they are the ornaments I made for the Prince who is missing.” “Who is this man? Where is he?”, thundered the King. This rogue must have murdered my little Prince and robbed his jewels!” “He is a Brahmin named Krishnan, your Majesty”, replied the goldsmith, and he is there, in my house. The king called for his most dreaded soldiers. “Arrest the Brahmin who is in the goldsmith’s house and throw him into the darkest dungeons of the kingdom”, roared the King. The King’s guard stormed into the goldsmith’s house and seized Krishnan. Krishnan was thrown into a dark dungeon to await his execution. He then remembered the words of Naagesh, the snake. So he called out to him.
Suddenly, almost like magic, Naagesh slithered his way down a narrow window into the dingy cell. “O, Lord!” hissed Naagesh, “how did you manage to get yourself arrested?” Krishnan cried and then told the snake what had happened. “I have a plan”, hissed Naagesh. “I shall creep into the Queen’s room and bite her”, said Naagesh. “She will faint. No matter what they do, she will remain asleep. The poison will remain in her body until you place your hand on her forehead”, explained Naagesh. He then left Krishnan and went to the palace. He crept into the Queen’s room and bit her. The Queen fainted. The sad news that the Queen had been bitten by a snake spread all over the Kingdom. Vaidyas came from far and near, but their medicines had no effect. No one could revive the Queen. Finally, the King declared that anyone who could cure the Queen would be handsomely rewarded. Many people went to the palace but all of them failed. “I can cure the Queen”, Krishnan told the guards. At once they took him to the Queen. Krishnan sat beside the Queen and placed his hand on her forehead. Soon, she opened her eyes and sat up. The King was overjoyed and shed tears of happiness. He embraced Krishnan and thanked him. “Your Majesty”, said Krishnan. “I was sent to prison for a crime I did not commit.” Krishnan told the King the whole story. The King was fuming with rage when he heard what the goldsmith had done. He at once had the goldsmith arrested. The King then presented Krishnan with a large house and a thousand pieces of gold. Krishnan sent for his family and they all lived happily ever after.
71. Why did Krishnan decide to leave his village?
-
A. As he could not find much work in his own village and his family had to starve sometimes because of it.
B. As his family had requested him to do so.
C. As his village people had asked him to leave their village and look for work somewhere else.
D. As he wanted to search for food in a village different from his own.
E. None of the above
-
A. As the man in the well was a goldsmith
B. As the man in the well had cheated the snake, the monkey and the jaguar
C. As the man in the well was a thief
D. As the snake, the monkey and the jaguar hated the man as they had known him for a very long time
E. None of the above
-
A. As Naagesh had threatened him with dire consequences.
B. As he thought Naagesh would eat him.
C. As he thought Naagesh would bite him once he was out of the well.
D. As he thought that Naagesh would capture him as soon as he got out of the well.
E. None of the above.
-
A. As he thought that Seth Ghanshyamdas could help him in selling the ornaments gifted to him by Shersingh.
B. As he knew that Seth Ghanshyamdas had contact with the King which could prove to be beneficial.
C. As Seth Ghanshyamdas had requested krishnan to sell ornaments only to him
D. As Krishnan was extremely fond of Seth Ghanshyamdas
E. None of the above.
-
A. Only 1
B. Only 2
C. Only 3
D. Only 2 and 3
E. 1 and 3
-
A. That he would sneak Krishnan out of the dungeon without anyone noticing
B. That he would bite the King and make him unconscious
C. That he would bite Krishnan and make everyone believe that he was dead
D. That he would enter the Queen’s chamber and scare her
E. None of the above
-
A. That Krishnan had brought fake ornaments for selling
B. That krishnan was an honest Brahmin who had left his village
C. That Krishnan had killed the Prince
D. That Krishnan had brought those ornaments for selling which had been made for the missing Prince
E. None of the above
-
A. He put Krishnan back in the dungeon as he still held Krishnan responsible for the Prince’s death
B. He called for Krishnan’s wife and family
C. He presented gold to Krishnan and also a house to live in
D. He congratulated the snake on his efforts to save Krishnan
E. None of the above
-
A. He punished the snake for having harmed the Queen
B. He announced a reward to anyone who could cure the Queen
C. He immediately called for Krishnan to cure the Queen
D. He asked his guards to immediately look for someone who could cure the Queen
E. None of the above
-
A. Trust oneself before trusting overs
B. A good deed never goes in vain
C. You cannot change people but you can change yourself
D. Try and try until you succeed
E. One must be the change one wishes to see in this world
-
A. The whole
B. time she walked with her child in her arms, the only thing
C. the only thing
D. her was her son’s feature.
E. All correct
-
A. When the young artist returned
B. to his village, his family held a festive
C. dinner on its lawn to celebrate his triumphant
D. homecoming.
E. All correct
-
A. Had she not suppressed
B. all the details of her Company’s project
C. her Company would have bagged
D. the contract.
E. All correct
-
A. She trusted Mira with all her heart
B.and thus handled
C. over her life’s
D. savings to her instantly.
E. All correct
-
A. It is difficult
B. to see the picture
C. when you are inside
D. the frame.
E. All correct
-
A. took
B. beat
C. drag
D. mold
E. showed
-
A. presenting
B. requesting
C. tell
D. trusting
E. showing
-
A. two
B. couple
C. much
D. few
E. many
-
A. major
B. some
C. sorrow
D. very
E. astutely
-
A. lane
B. journey
C. leave
D. return
E. walking
-
A. reveal
B. think
C. saw
D. believe
E. learn
-
A. stands
B. reaches
C. swims
D. leak
E. watery
-
A. more
B. scene
C. whole
D. last
E. lucky
-
A. servants
B. mother
C. computers
D. relatives
E. man
-
A. minds
B. selves
C. property
D. pillars
E. country
-
A. which he liked
B. according to his convenience
C. voluntarily and willingly
D. according to his judgement
E. None of these
-
A. giving speeches
B. the object of admiration
C. the center of attraction
D. an object of public notice
E. None of these
-
A. exhausted my stock of
B. did not have enough
C. lost
D. carried a lot
E. None of these
-
A. someone has been murdered with some blue liquid
B. someone is being murdered and has become blue
C. suffer from persecution complex
D. make a great deal of noise and object vehemently
E. None of these
-
A. law of the mob
B. law of the underworld
C. law of the constitution
D. law of the parliament
E. None of these