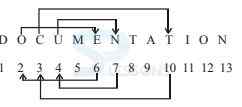
Introduction
Introduction
Career in Banking is one of the most lucrative and most sought after careers. In India, Bank Recruitment Exams are primarily conducted for recruitment of Probationary Officers, Clerks & Specialist Officers. India currently[2019] has 93 commercial and 27 public sector banks out of which 19 are nationalized and 6 are SBI and its associate banks and rest two are IDBI Bank and Bharatiya Mahila Bank, which are categorized as other public sector banks. Recruitment for Bank Probationary Officers, Management Trainees, Clerks and for various other posts generally follow a 3 step recruitment process: Preliminary Exam + Mains Exam + Interview & Group Discussion. The article SBI PO Prelims Practice Quiz presents a practice set for the most sought after SBI PO recruitment. Until the year 2013, All Public Sector Banks used to conduct their own entrance test, GDs and Personal Interview for recruiting candidates. However, after 2014, IBPS started conducting recruitment Tests for 12 PSU Banks. SBI holds a separate entrance test for recruitment.
Prelims exams are very important to clear every government sector or bank related recruitment process in India. Prelims are also known as Screening Tests. Only those candidates who are selected in the prelims round are allowed to move further up in the recruitment process. The marks obtained in the preliminary exams are not considered for the final merit list. Preliminary Exams are only meant to be screening tests. Preliminary exams usually consist of 3 sections, with 100 questions with a time duration of 1 hour. Preliminary exams most certainly have negative marking.
 Quiz
Quiz
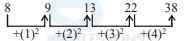
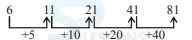
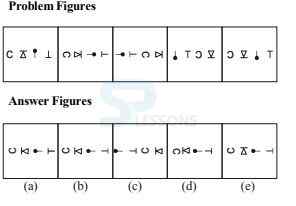
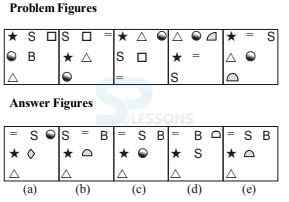
Directions Q (1 - 10): What will come in place of question mark (?) in the following questions
1. 48% of 525 + ? % of 350 = 399
-
A. 42
B. 46
C. 28
D. 26
E. None of these
-
A. 2[latex]\frac{13}{45}[/latex]
B. 2[latex]\frac{4}{5}[/latex]
C. 3[latex]\frac{22}{45}[/latex]
D. 3[latex]\frac{5}{9}[/latex]
E. None of these
-
A. 46
B. 42
C. 1764
D. 2116
E. None of these
-
A. [latex]\frac{27}{115}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{22}{117}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{25}{117}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{22}{115}[/latex]
E. None of these
-
A. 25[latex]\frac{11}{14}[/latex]
B. 25[latex]\frac{3}{7}[/latex]
C. 26[latex]\frac{3}{7}[/latex]
D. 26[latex]\frac{5}{14}[/latex]
E. None of these
-
A. 49
B. 14
C. 21
D. 7
E. None of these
-
A. 448
B. 476
C. 480
D. 464
E. None of these
-
A. 411.2
B. 41.12
C. 64.25
D. 421.25
E. None of these
-
A. 37.50
B. 37.25
C. 370.25
D. 372.50
E. None of these
-
A. 6575
B. 6475
C. 6455
D. 6745
E. None of these
-
A. 1550
B. 1510
C. 1540
D. 1580
E. None of these
-
A. 3 :17
B. 4 : 15
C. 2 : 15
D. 2 : 13
E. None of these
-
A. 26
B. 36
C. 6
D. 46
E. None of these
-
A. 9 : 4
B. 8 : 3
C. 7 : 2
D. 8 : 5
E. None of these
-
A. 90
B. 70
C. 80
D. 60
E. None of these
-
A. 22
B. 19
C. 20
D. 21
E. None of these
-
A. 36
B. 28
C. 24
D. 32
E. None of these
-
A. 183
B. 185
C. 138
D. 139
E. None of these
-
A. 30
B. 31
C. 34
D. 36
E. None of these
-
A. 81
B. 61
C. 71
D. 91
E. None of these
-
A. 450
B. 500
C. 400
D. 600
E. None of these
-
A. Rs 2890
B. Rs 2980
C. Rs 2780
D. Rs 2870
E. None of these
-
A. 3 : 4
B. 4 : 3
C. 4 : 5
D. 5 : 4
E. None of these
-
A. Rs 2450
B. Rs 2245
C. Rs 2405
D. Rs 2425
E. None of these
-
A. Rs 1875
B. Rs 1885
C. Rs 1775
D. Rs 1765
E. None of these
-
A. 250 m
B. 200 m
C. 240 m
D. 450 m
E. None of these
-
A. [latex]\frac{5}{11}[/latex], [latex]\frac{3}{8}[/latex], [latex]\frac{4}{9}[/latex], [latex]\frac{2}{7}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{5}{11}[/latex], [latex]\frac{4}{9}[/latex], [latex]\frac{3}{8}[/latex], [latex]\frac{2}{7}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{2}{7}[/latex], [latex]\frac{3}{8}[/latex], [latex]\frac{4}{9}[/latex], [latex]\frac{5}{11}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{2}{7}[/latex], [latex]\frac{4}{9}[/latex], [latex]\frac{3}{8}[/latex], [latex]\frac{5}{11}[/latex]
E. None of these
-
A. 26
B. 36
C. 71
D. 62
E. None of these
-
A. 4 days
B. 5 days
C. 6 days
D. 3 days
E. None of these
-
A. 160
B. 150
C. 140
D. 148
E. None of these
-
A. 91
B. 95
C. 99
D. 97
E. None of these
-
A. Rs. 16000
B. Rs. 18000
C. Rs. 16500
D. Rs. 18500
E. None of these
-
A. 10.5
B. 12.5
C. 11
D. 12
E. None of these
-
A. Rs. 100000
B. Rs. 60000
C. Rs. 80000
D. Rs. 110000
E. None of these
-
A. 11 years
B. 11.275 years
C. 11.50 years
D. 11.975 years
E. None of these
36. Bihar is related to India in the same as Florida is related to?
-
A. Canada
B. Mexico
C. North America
D. USA
E. None of these
-
A. UMRSME
B. EIWNTR
C. PIGRSN
D. LCUOD
E. None of these
-
A. R
B. O
C. S
D. P
E. None of these
-
A. C
B. I
C. T
D. U
E. None of these
-
A. 18
B. 24
C. 21
D. 27
E. None of these
-
A. if only conclusion I follows.
B. if only conclusion II follows.
C. if neither I nor II follows.
D. if both I and II follow.
E. None of these
-
A. if only conclusion I follows.
B. if only conclusion II follows.
C. if neither I nor II follows.
D. if both I and II follow.
E. None of these
-
A. if only conclusion I follows.
B. if only conclusion II follows.
C. if neither I nor II follows.
D. if both I and II follow.
E. None of these
-
A. if only conclusion I follows.
B. if only conclusion II follows.
C. if neither I nor II follows.
D. if both I and II follow.
E. None of these
-
A. if only conclusion I follows.
B. if only conclusion II follows.
C. if neither I nor II follows.
D. if both I and II follow.
E. None of these
-
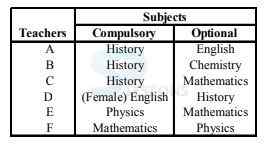
A. History
B. Physics
C. Chemistry
D. English
E. None of these
-
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. None of these
-
A. D
B. B
C. A
D. C
E. None of these
-
A. A
B. B
C. E
D. D
E. None of these
-
A. A, C and D
B. B, C and D
C. C and D
D. A, B and C
E. None of these
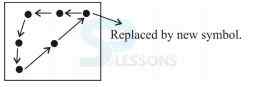
-
A. $D$D$
B. $$D$D
C. $DD$$
D. $DD$$
E. None of these
-
A. D$$$
B. $D$D
C. $DD$
D. $$DD
E. None of these
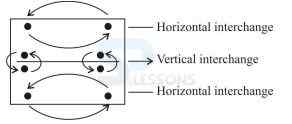
-
A. 18
B. 25
C. 17
D. 16
E. None of these
-
A. 28
B. 48
C. 26
D. 50
E. None of these
-
A. $DD$D
B. $$DDD
C. $$$DD
D. $DD$$
E. None of these
-
A. if only conclusion I is true;
B. if only conclusion II is true;
C. if either conclusion I or II is true;
D. if neither I nor II is true and
E. if both conclusions I and II are true.
-
A. if only conclusion I is true;
B. if only conclusion II is true;
C. if either conclusion I or II is true;
D. if neither I nor II is true and
E. if both conclusions I and II are true.
-
A. if only conclusion I is true;
B. if only conclusion II is true;
C. if either conclusion I or II is true;
D. if neither I nor II is true and
E. if both conclusions I and II are true.
-
A. if only conclusion I is true;
B. if only conclusion II is true;
C. if either conclusion I or II is true;
D. if neither I nor II is true and
E. if both conclusions I and II are true.
-
A. if only conclusion I is true;
B. if only conclusion II is true;
C. if either conclusion I or II is true;
D. if neither I nor II is true and
E. if both conclusions I and II are true.
-
A. Z
B. G
C. I
D. L
E. None of these
-
A. SVJ
B. AFS
C. IVS
D. SFA
E. None of these
-
A. T
B. J
C. S
D. Z
E. None of these
-
A. 15
B. L
C. K
D. I
E. None of these
-
A. M
B. T
C. X
D. E
E. P
Directions Q (71 - 80): Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions given below it.
Once upon a time a dishonest king had a man called the Valuer in his court. The Valuer set the price which ought to be paid for horses and elephants and the other animals. He also set the price on jewelry and gold, and things of that kind. This man was honest and just and set the proper price to be paid to the owners of the goods. The king, however, was not pleased with this Valuer, because he was honest. "If I had another sort of a man as Valuer, I might gain more riches," he thought.
One day the king saw a stupid, miserly peasant come into the palace yard. The king sent for the fellow and asked him if he would like to be the Valuer. The peasant said he would like the
position. So the king had him made Valuer. He sent the honest Valuer away from the palace.
Then the peasant began to set the prices on horses and elephants, upon gold and jewels. He did not know their value, so he would say anything he chose. As the king had made him
Valuer, the people had to sell their goods for the price he set. By and by a horse-dealer brought five hundred horses to the court of this king. The Valuer came and said they were worth a mere measure of rice. So the king ordered the horse-dealer to be given the measure of rice, and the horses to be put in the palace stables.
The horse-dealer then went to see the honest man who had been the Valuer and told him what had happened. "What shall I do?" asked the horse-dealer. "I think you can give a present to the Valuer which will make him do and say what you want him to do and say," said the man. "Go to him and give him a fine present, then say to him: "You said the horses are worth a measure of rice but now tell what a measure of rice is worth! Can you value that standing in your place by the king?" If he says he can go with him to the king, and I will be there, too."
The horse-dealer thought this was a good idea. So he gave a fine present to the Valuer, and said what the other man had told him to say., The stupid Valuer took the present, and said: "Yes, I can go before the king with you and tell what a measure of rice is worth. I can value that now." Well, let us go at once," said the horse-dealer. So they went before the king and his ministers in the palace.
The horse-dealer bowed down before the king and said: "O King, I have learned that a measure of rice is the value of my five hundred horses. But will the king be pleased to ask the Valuer
what is the value of the measure of rice"? The king, not knowing what had happened, asked, "How now, Valuer, what are five hundred horses worth?" "A measure of rice, O King!" said he. "Very good, then! If five hundred horses are worth a measure of rice, what is the measure of rice worth?" "The measure of rice is worth your whole city," replied the foolish fellow.
The ministers clapped their hands, laughing, and saying, "What a foolish Valuer! How can such a man hold that office? We used to think this great city was beyond price, but this man
says it is worth only a measure of rice, "Then the king was ashamed, and drove out the foolish fellow. "I tried to please the king by setting a low price on the horses, and now see what has happened to me!" said the Valuer, as he ran away from the crowd.
71. Who did the king appoint as the new Valuer
-
A. A minister
B. A horse merchant
C. Himself
D. A stingy peasant
E. None of these
-
A. As the Valuer was not good at his work
B. As he had dishonored the king
C. As the Valuer had been dishonest with the king about the prices that he set for goods
D. As the king believed that he was not earning much because of the Valuer's honesty
E. None of these
-
A. Only (1)
B. Only (2)
C. Only (2) and (3)
D. Only (1) and (3)
E. All the three (1), (2) and (3)
-
A. Slow and steady wins the race
B. Change is the only permanent thing in life
C. An honest answer is a sign of true friendship
D. Haste makes waste
E. No legacy is so rich as honesty
-
A. As he had sold the king's city at a very low price
B. As he had displayed his stupidity by quoting an abysmally low price on the king's city
C. As he had cheated the horse dealer
D. As he had not calculated the price of the five hundred horses correctly
E. None of these
-
A. He accepted the present and resigned from his post as was requested by the horse-dealer
B. He accepted the present and agreed to state the worth of a measure of rice in the presence of the King
C. He accepted the present and immediately returned the horse-dealer's horses
D. He refused to accept the present from the horse-dealer and asked him to leave the premises
E None of these
-
A. Only (1)
B. Only (3)
C. Only (1) and (2)
D. Only (1) and (3)
E. All the three (1), (2) and (3)
-
A. The king's entire city
B. The king's life
C. Two horses
D. Not mentioned in the passage
E. None of these
-
A. As the new Valuer had set a very inappropriate price for his five hundred horses
B. As his five hundred horses were stolen from him by the king
C. As he was a very good friend of the old Valuer
D. As the king had requested him to do so
E. None of these
-
A. He asked the horse-dealer to inquire with the king about the worth of a measure of rice
B. He asked the horse-dealer to bribe the new Valuer and get his horses back
C. He asked the horse-dealer to forget about his horses and go on with his life
D. He asked the horse-dealer to publicize his plight and thus get his horses back
E. None of these
-
A. for checking out
B. to checking out
C. to check outing
D. to checked out
E. No correction required
-
A. who ignored an
B. those ignoring an
C. who ignores a
D. that ignored a
E. No correction required
-
A. no ending to herself
B. no ends of herself
C. no end of herself
D. no end with herself
E. No correction required
-
A. to walks on
B. walking down
C. walking with
D. walks to
E. No correction required
-
A. making heads turn
B. make head turnings
C. making heads turning
D. makes heads turn
E. No correction required
-
A. The city's fashion-conscious ladies
B. came together at a city hotel to check out an exibition (b)
C. by various
D. designers and labels.
E. All correct
-
A. The ministry's proposal
B. for an autonomous
C. overarching authority
D. for higher education and research was finally approval.
E. All correct
-
A. Silense
B. is to retreat
C. in wordless prayer, gazing
D. out the window of your heart, and going for slow meandering walks in a garden.
E. All correct
-
A. A majority of Army tanks continue to grope
B. in the dark, stricken
C. as they are with an ecute (c)
D. case of night blindness.
E. All correct
-
A. Back home, the ever affable (a)
B. Bollywood singer shares the excitement (b) of having
C. performed
D. at the Royal Hall in London.
E. All correct
-
A. took
B. was
C. great
D. handle
E. mended
-
A. try
B. told
C. were
D. bent
E. learnt
-
A. main
B. exactly
C. many
D. because
E. too
-
A. call
B. make
C. stall
D. go
E. visit
-
A. forcefully
B. hardly
C. usually
D. costly
E. truly
-
A. ask
B. bring
C. got
D. throw
E. create
-
A. party
B. time
C. answer
D. doubt
E. water
-
A. body
B. many
C. lots
D. weight
E. quantity
-
A. thrashed
B. saw
C. stick
D. pulled
E. splashed
-
A. withered
B. crushed
C. killed
D. grew
E. smiled