Quiz
Quiz
1. Two adjacent members of a homologous series have :
(a) a difference of –CH2 in their structure
(b) a difference of 14 a.m.u. in molecular mass
(c) same general methods of preparation
(d) all of the above
Ans: D
2. Alkenes are characterized by
(a) C – C bonds
(b) C = C bonds
(c) C [latex]\equiv[/latex] C bonds
(d) cyclic structure
Ans: B
3. Which of the following contains carbonyl group?
(a) Ketones
(b) Aldehydes
(c) Esters
(d) All of these
Ans: D
4. The functional group present in CH3COOC2H5 is
(a) ketonic
(b) aldehydic
(c) ester
(d) carboxylic
Ans: C
5. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
Ans: C
6. Which of the following is incorrectly matched?
(a) Vinegar [latex]\rightarrow[/latex] carboxylic acid
(b) C2H6 [latex]\rightarrow[/latex] alkane
(c) Ethanol [latex]\rightarrow[/latex] alcohol
(d) Methanol [latex]\rightarrow[/latex] ketone
Ans: D
7. If a hydrocarbon has any double bond, it is
(a) alkyne
(b) alkane
(c) alkene
(d) All the above
Ans: C
8. Alkynes are characterized by –
(a) C – C bonds
(b) C = C bonds
(c) C [latex]\equiv[/latex] C bonds
(d) cyclic structure
Ans: C
9. How many different isomers are possible for a hydrocarbon
with the molecular formula C4H10?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 5
Ans: B
10. The general formula CnH2nO2 could be for open chain
(a) diketones
(b) carboxylic acids
(c) diols
(d) dialdehydes
Ans: B
11. The IUPAC name of CH3CH2COCl is
(a) propanoyl chloride
(b) ethanoyl chloride
(c) acetyl chloride
(d) chloroethane
Ans: A
12. General formula of alkenes and alkyl radicals are
respectively:
(a) CnH2n and CnH2n+1
(b) CnH2n and CnH2n+2
(c) CnH2n-1 and CnH2n
(d) CnH2n+1 and CnH2n+2
Ans: A
13. The IUPAC name of CH3COOC2H5 will be –
(a) ethyl acetate
(b) ethyl ethanoate
(c) methyl propanoate
(d) none of these
Ans: B
14. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely
Ans: B
15. Which is a general formula of alkenes?
(a) CnH2n+2
(b) CnH2n
(c) CnH2n–2
(a) None of these
Ans: A
16. Organic compounds will always contain
(a) carbon
(b) hydrogen
(c) nitrogen
(d) sulphur
Ans: A
17. Methane, ethane and propane are said to form a homologous
series because all are
(a) hydrocarbons
(b) saturated compounds
(c) aliphatic compounds
(d) differ from each other by a CH2 group
Ans: D
18. General formula of alkyne is
(a) CnH2n+2
(b) CnH2n
(c) CnH2n–2
(d) CnHn
Ans: C
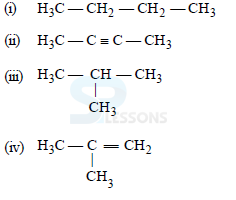
19. Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons?
(a) (i) and (iii) (b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv) (d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: C
20. Pentane has the molecular formula C5H12. It has
(a) 5 covalent bonds
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
Ans: C
21. The heteroatoms present in [latex]CH_{3} -- CH_{2} -- O — CH_{2} -- CH_{2}Cl[/latex] are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: D
22. Isomers of a substance must have the same
(a) structural formula
(b) physical properties
(c) chemical properties
(d) molecular formula
Ans: D