Description
Description
PHP Variables are nothing but a named storage locations in the memory.
There is no need to declare the variable type in advance.In other programming languages, the variable name, data type has to be declared before using it.But in PHP, types are associated with the values so declaration is not necessary.The initial step while using a variable is value assignment.
Assigning a variable is easy.Write the name and add a single equal sign = and then the expression that has to be assigned a variable.For example, Eg: $pi=3+0.1489.
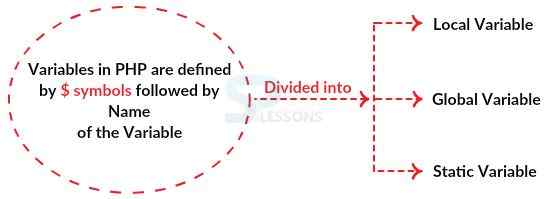
Generally Variables in PHP are defined by " $" symbol followed by
name of the Variable. Variables in PHP are case sensitive.
 Syntax
Syntax
$x , $y, $Name .. etc.,
 Example
Example
 Description
Description
- Variables starts with $ sign and next with the variable name.
- Variable names start with the Letter or Underscore sign, followed by underscores, numbers, or characters.
- Variables are case sensitive( $splessons and $sPLessoNs are different variables).
- Variables never start with Numbers.
- Variables can be defined by using alpha-numeric characters and underscores only.
 Description
Description
Scope is nothing but the rules when a name in two different places has the same meaning. PHP has four different variable scopes depending on the variable defined location.
- Local
- Global
- Static
 Description
Description
Local variables are defined and accessed within the function. They are not accessible outside the function.
 Example
Example
[php]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<?php
function myVariables()
{
$age = 25; // local scope
echo "The Variable age defined inside the function and the value is: ".$age." <br><br>";
}
myVariables(); // if you call the age variable outside function, will give an error
echo "The Variable age outside function is: ".$age."";
?>
</body>
</html>
[/php]
Output:
Output:
[php]
The Variable age defined inside the function and the value is: 25
[/php]
 Description
Description
Global variables are defined outside of the function.One can access the global variables anywhere in the script, outside the function.
But, global variables can also be accessed inside the function also, by using the keyword
global before the variable declaration.  Example
Example
 Description
Description
Generally, after the execution of function is completed, the variables and the values in the variable will be deleted.But some times, local variable should not be deleted and should work in further execution also.For that, use the keyword
static. Static is kept before the variable, at the first time of declaration.  Example
Example
 Key Points
Key Points
- PHP Variables are defined by ” $” symbol.
- Local variables are not accessible outside the function.
- Global variables are accessed anywhere inside the script.
- Static variables does not delete the local functionality of a variable and works even after execution.