Introduction
Introduction
Before learning about Maven Pom XML files, Maven Archetype has is to be known. Maven Pom XML chapter explains about the File Structure and POM files.
 Description
Description
Basically, Maven creates two things:
Initially, run Maven Archetype colon generate command to get the output.
- Project template
- Build
- File Structure
- Pom.xml
 Description
Description
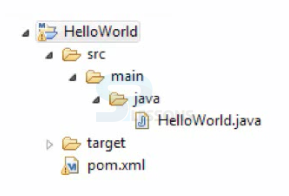
Initially, Maven finds source/main/Java directory in the project and then compiles the code to a target directory by referencing the default and the code is written in
pom.xml file.  Structure
Structure
 Description
Description
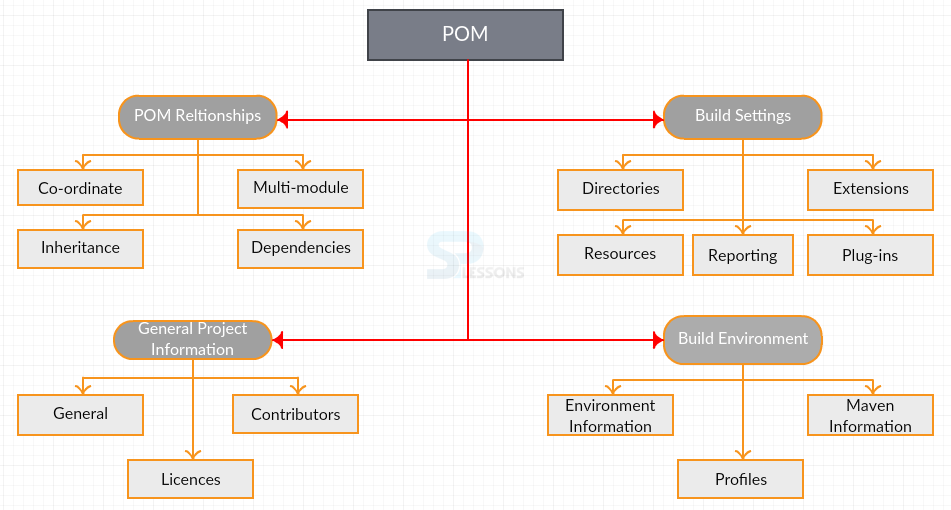
POM stands for Project Object Model, in which the structure and identity of a project is declared and the builds are configured. POM will relate various projects.
POM gives detailed information about the project and helps in generating source output by modifying the default behavior. It is similar to Java’s
web.xml or ANT’s build.xml. The description and configuration is established in four different categories.
 Description
Description
Super POM is the extension of POM in a project and defines the default configuration variables being shared by the projects.
- The default super POM has a remote repository called central.
- Central repository has plug-ins.
- Default values for directories can be set using build element in the Standard Directory layout.
- Default versions of core plug-ins are defined in Super POM.
 Examples
Examples
The following is an example of super POM:
[xml]
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>my-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
<relativePath>../my-parent</relativePath>
</parent>
<artifactId>my-project</artifactId>
...
</project>[/xml]
 Key Points
Key Points
- POM is the Project Object Model.
- It defines the relationship between the projects.
- All POM files will be inherited from Super POM.