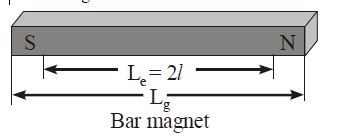Introduction
Introduction
Magnet is a material/object that has the property of attracting pieces of iron, cobalt and nickel and when freely suspended it points towards north and south. The attracting power of a magnet appears to be concentrated at definite regions called poles. When a magnet is broken into pieces, each piece becomes an independent magnet. The two poles of the magnet have equal strength. Like poles repel and unlike poles attract each other. The phenomenon of attracting magnetic substances like iron, cobalt, nickel etc. is called Magnetism. in simple words, An object/material with the property of magnetism is called a magnet.
A lodestone is a naturally magnetized piece of the mineral magnetite. The property of magnetism was first discovered lodestones. Earth is also a natural magnet. In magnetized substance all the atomic magnets are aligned in same direction and thus resultant magnetism is non-zero.
 Magnetism
Magnetism
Bar Magnet:
A bar magnet consists of two equal and opposite magnetic poles separated by a small distance. Poles are not exactly at the ends.
The shortest distance between two poles is called effective length.
[latex](L_c) [/latex] less than its geometric length [latex](L_g) [/latex] and is For bar magnet
[latex](L_c) [/latex]= 2l and [latex](L_c) [/latex] = (5/6) [latex](L_g) [/latex]
Types of Magnets :
Artificial magnets:
These magnets are created by artificial means.Iron ore which we know as magnetite has magnetic properties of attracting iron, cobalt an nickel. These are called lodestones.
Types of Magnetic Substances:
- Ferro-magnets: These are special substances which are strongly magnetized by relatively weak magnetic fields. Iron, nickel and cobalt are familiar examples of this class.
- Para magnetic substances: These magnetic substances when placed in a strong magnetic field get magnetized in the same sense as the external field. Aluminium, chromium, copper sulphate and liquid oxygen are familiar examples.
- Diamagnetic Substances: These substances when placed in a magnetic field get weakly magnetized in a sense opposite to the applied field. A few examples are bismuth, antimony, gold, water, alcohol and hydrogen.
(i) Attractive property : When a magnet is dipped into iron fillings it is found that the concentration of iron filings, i.e., attracting power of the magnet is maximum at two points near the ends and minimum at the centre. The places where its attracting power is maximum are called poles.
(ii) Directive property : When a magnet is suspended its length becomes parallel to N-S direction. The pole pointing north is called the north pole while the other pointing in the geographical south is called the south pole of the magnet. The line joining the two poles of a magnet is called magnetic axis and the vertical plane passing through the axis of a freely suspended or pivoted magnet is called magnetic meridian.
(iii) Poles of a magnet always exist in pairs : In a magnet the two poles are found to be equal in strength and opposite in nature. If a magnet is broken into number of pieces, each piece becomes a magnet with two equal and opposite poles. This shows that mono pole do not exist.
(iv) Repulsive property : A pole of a magnet attracts the opposite pole while repels similar pole.
Demagnetization of Magnet
A magnet gets demagnetized, i.e., loses its power of attraction if it is heated, hammered or alternating current is passed through a wire wound over it.
Permanent Magnets
The permanent artificial magnets are made of some metals and alloys like Carbon-steel, Alnico, Platinum-cobalt, Alcomax, Ticonal etc.
The permanent magnets are made of ferromagnetic substances with large coercivity and retentivity
Temporary Magnets
The temporary artificial magnets like electromagnets are prepared by passing current through coil wound on soft iron core. These cannot retain its strength for a long time. These are made from soft iron, non-metal and alloy. Electromagnets are stronger than permanent magnet.
Some Applications of Electromagnets
(i) Electric motors
(ii) Doorbells
(iii) In scrapyards to separate iron from other metals
If two magnetic poles of strengths m1 and m2 are kept at a distance r apart then force of attraction or repulsion between the two poles is directly proportional to the product of their pole strengths and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
F [latex]∝[/latex] [latex]\frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2}[/latex]
F =[latex]\frac{\mu_0}{4Π}[/latex] [latex]\frac{m_1 m_2}{r^2}[/latex]
where F =[latex]\frac{\mu_0}{4Π}[/latex]=[latex]10^{-7}Wb A^{-1} m^{-1} [/latex]= [latex]10^{-7}[/latex] henry/m
[latex]\mu_0[/latex] is permeability of free space or absolute permeability
The space around a magnet (or a current carrying conductor) in which its magnetic effect can be experienced is called the magnetic field. If a magnet is cut into two equal parts along the length then pole strength is reduced to half and length remains unchanged.
New magnetic dipole moment [latex]M^{\prime}[/latex]= [latex]m^{\prime}(2l)[/latex]= [latex]\frac{m}{2}× 2l[/latex]=[latex]\frac{M}{2}[/latex]
If a magnet is cut into two equal parts transverse to the length then pole strength remains unchanged and length is reduced to half.
New magnetic dipole moment [latex]M^{\prime}[/latex] = m[latex]\frac{2l}{2}[/latex]=[latex]\frac{M}{2}[/latex]
Magnetic Lines of Force
Magnetic line of force is an imaginary curve tangent to which at a point gives the direction of magnetic field at that point or the magnetic field line is the imaginary path along which an isolated north pole will tend to move if it is free to do so.Magnetic lines of force do not intersect each other. Because if they do, there will be two directions of magnetic field which is not possible.
Gauss’s Law in Magnetism
The surface integral of Magnetic field [latex]\vec B[/latex] over a closed surface S is always zero.
Mathematically
[latex]\oint_S\vec B[/latex].[latex]\vec {da}[/latex] = 0
The branch of Physics which deals with the study of earth's magnetic field is called terrestrial magnetism.
William Gilbert suggested that earth itself behaves like a huge magnet.
(a) A freely suspended magnet always comes to rest in N-S direction.
(b) A piece of soft iron buried in N-S direction inside the earth acquires magnetism.
Geographic meridian :
It is a vertical plane passing through geographic north and south pole of the earth.
Geographic equator :
A great circle on the surface of the earth in a plane perpendicular to geographical axis is called geographic equator. All places on geographic equator are at equal distances from geographical poles.
Magnetic meridian :
It is a vertical plane passing through the magnetic north and south pole of the earth.
Magnetic equator :
A great circle on the surface of the earth in a plane perpendicular to magnetic axis is called magnetic equator.
The physical quantities which determine the intensity of earth's total magnetic field completely both in magnitude and direction are called magnetic elements.
Angle of declination [latex](\phi)[/latex] :
The angle between the magnetic meridian and geographical meridian at a place is called angle
of declination.
Angle of dip or inclination[latex]( θ)[/latex] :
The angle through which the N pole dips down with reference to horizontal is called the angle
of dip. At magnetic north and south pole angle of dip is 90°. At magnetic equator the angle of dip is 0°.
Horizontal component of earth's magnetic field :
The total intensity of the earth's magnetic field makes an angle q with horizontal. It has
(i) component in horizontal plane called horizontal component BH.
(ii) component in vertical plane called vertical component
[latex]B_H[/latex] [latex]B_V[/latex]
[latex]B_V[/latex]= B[latex]\sin θ[/latex]
[latex]B_H[/latex]= B[latex]\cos θ[/latex]
so [latex]\frac{B_V}{B_H}[/latex]= [latex]\tan θ[/latex]
B=[latex]\sqrt{B_{H^2} + B_{V^2}}[/latex]
It is defined as the magnetic dipole moment developed per unit volume when a magnetic material is subjected to magnetising field.
[latex]\frac{Magnetic dipole moment}{Volume}[/latex]= [latex]\frac{M}{V}[/latex]
Magnetic Susceptibility
The magnetic susceptibility of a magnetic substance is defined as the ratio of the intensity of magnetization to magnetic intensity.
Magnetic susceptibility [latex]x_m[/latex]= [latex]\frac{I}{H}[/latex]
Magnetic Permeability
The magnetic permeability of a magnetic substance is defined as the ratio of the magnetic induction to the magnetic intensity
Magnetic Permeability [latex]μ[/latex]= [latex]\frac{B}{H}[/latex]
The lagging of intensity of magnetization (I) or magnetic induction (B) behind the magnetizing field (H) during the process of magnetization and demagnetization of a ferromagnetic material is called hysteresis.
Retentivity :
The value of I (or B) of a material when the magnetizing field is reduced to zero is called retentivity or
residual magnetism of the material.
Coercivity :
The value of reverse magnetising field required to reduce residual magnetism to zero is called coercivity of the
material.
Comparison of properties of soft iron and steel :
(1) The area of hysteresis loop for soft iron is much smaller than for steel, so energy loss per unit volume per cycle for soft iron is smaller than steel.
(2) The retentivity of soft iron is greater than that of steel.
(3) The coercivity of steel is much larger than that of soft iron.
(4) The magnetisation and demagnetisation is easier in soft iron than steel.
(5) Soft iron acquires saturation magnetisation for quite low value of magnetizing field than in case of steel or soft iron is much strongly magnetized than steel.
Diamagnetic Substances :
The substances which when placed in a magnetic field are feebly magnetised in a direction
opposite to that of the magnetising field are called diamagnetic substances.
Some diamagnetic substances are Cu, Zn, Bi, Ag, Au, Pb, He, Ar, NaCl, [latex]H_2O[/latex], marble, glass, etc.
Paramagnetic Substances :
The substances which when placed in a magnetic field are feebly magnetized in the direction of magnetizing field are called para magnetic substances.
Some paramagnetic substances are Al, Na, Sb, Pt, [latex]CuCl_2[/latex], Mn, Cr, liquid oxygen, etc.
Ferromagnetic Substances :
The substances which when placed in a magnetic field are strongly magnetized in the direction of the magnetizing field are called ferromagnetic substances.
Iron, cobalt, nickel, etc. are some examples of ferromagnetic substance.
 Quiz
Quiz
1. ____ is a substance which has the property of attracting pieces of iron, cobalt, nickel and when freely suspended it points towards north and south?
- A. Magnets
B. Magnetic induction
C. Magnetic substance
D. Magnetic field of the earth
- A. Ferro-magnets
B. Para magnetic substances
C. Diamagnetic substances
D. Artificial magnets
- A. Ferro-magnets
B. Para magnetic substances
C. Diamagnetic substances
D. Artificial magnets
- A. Ferro-magnets
B. Para magnetic substances
C. Diamagnetic substances
D. Artificial magnets
- A. Magnetic induction
B. Voltmeter
C. Galvanometer
D. An ammeter