Description
Description
Decision Making means the controller will decide whether the set of operations going to be executed or not.The controller will make the decision based on the condition. If the condition is True then only the statements going to execute. Otherwise, the statements are not going to execute.Following are the different types of Decision-Making Statements.
- If..Then Statement
- If..Then..Else Statement
- Nested If Statement
- Select Statement
 Description
Description
The frequently used condition is if then statement , it is utilized to say that true condition.Following is an example which describes about this statement.
[vbnet]Module Module1
Sub Main()
'local variable definition
Dim a As Integer = 10
' check the boolean condition using if statement
If (a < 20) Then
' if condition is true then print the following
Console.WriteLine("a is less than 20")
End If
Console.WriteLine("value of a is : {0}", a)
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module[/vbnet]
Output:
 Description
Description
This statement describes two conditions that are true and false.Following is an example which describes this statement.
[vbnet]Module Module1
Sub Main()
'local variable definition '
Dim a As Integer = 100
' check the boolean condition using if statement
If (a < 20) Then
' if condition is true then print the following
Console.WriteLine("a is less than 20")
Else
' if condition is false then print the following
Console.WriteLine("a is not less than 20")
End If
Console.WriteLine("value of a is : {0}", a)
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module[/vbnet]
Output:
 Description
Description
If a developer writes one if statement inside another if statement, then it's called Nested If Statement.Following is an example.
[vbnet]Module Module1
Sub Main()
'local variable definition
Dim a As Integer = 100
Dim b As Integer = 200
' check the boolean condition
If (a = 100) Then
' if condition is true then check the following
If (b = 200) Then
' if condition is true then print the following
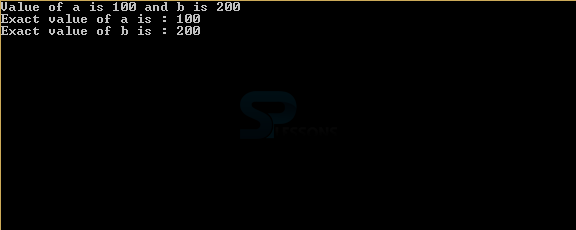
Console.WriteLine("Value of a is 100 and b is 200")
End If
End If
Console.WriteLine("Exact value of a is : {0}", a)
Console.WriteLine("Exact value of b is : {0}", b)
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module[/vbnet]
Output:
 Description
Description
This statement is like a switch case statement like as in other languages, here each value will be represented by case.Following is an example.
[vbnet]Module Module1
Sub Main()
'local variable definition
Dim grade As Char
grade = "B"
Select Case grade
Case "A"
Console.WriteLine("Excellent!")
Case "B", "C"
Console.WriteLine("Well done")
Case "D"
Console.WriteLine("You passed")
Case "F"
Console.WriteLine("Better try again")
Case Else
Console.WriteLine("Invalid grade")
End Select
Console.WriteLine("Your grade is {0}", grade)
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module[/vbnet]
Output:
 Points
Points
- If select case placed inside another select case then it is called as nested select case statement.
- The functionality of above all statements are same in every language.