Description
Description
Datatypes are playing crucial role in programming language and data types are used to store the data of a particular variable but the way of declaring the syntax of data types are different to every language likewise in Dot Net datatype declaration syntax will be as follows.
[vbnet]Dim Variable Name as Datatype[/vbnet]
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
Following conceptual figure describes about what are data types are available in programming languages.
Following are the datatypes and their sizes.
| DataType | Size |
|---|---|
| Integer | 4 bytes |
| Long | 8 bytes |
| Byte | 1 byte |
| Char | 2 bytes |
| Decimal | 16 bytes |
| Double | 8 bytes |
| Short | 2 bytes |
| Single | 4 bytes |
| String | Depends on the platform |
 Example
Example
This example describes about how to declare the data types in VB.Net code and how functionally it works.
[vbnet]
Module Module1
Sub Main()
Dim b As Byte
Dim n As Integer
Dim si As Single
Dim d As Double
Dim da As Date
Dim c As Char
Dim s As String
Dim bl As Boolean
b = 1
n = 1234567
si = 0.12345678901234566
d = 0.12345678901234566
da = Today
c = "U"c
s = "Me"
If ScriptEngine = "VB" Then
bl = True
Else
bl = False
End If
If bl Then
'the oath taking
Console.Write(c & " and," & s & vbCrLf)
Console.WriteLine("declaring on the day of: {0}", da)
Console.WriteLine("We will learn VB.Net seriously")
Console.WriteLine("Lets see what happens to the floating point variables:")
Console.WriteLine("The Single: {0}, The Double: {1}", si, d)
End If
Console.ReadKey()
End Sub
End Module
[/vbnet]
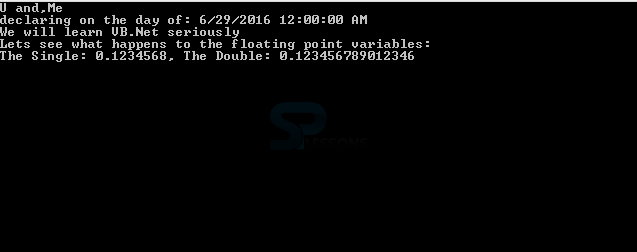
Output:
After compiling the code output will be as follows in console.
 Points
Points
- Dim Variable Name as Datatype is the way of declaring the syntax in VB.Net.
- Datatype stores the data of a particular variable.
- A string datatype works depends on the platform.