Description
Description
URL Rewrite in Servlets - URL rewriting is another way to support anonymous session tracking. With URL rewriting, every local URL the user might click on is dynamically modified, or rewritten, to include extra information. The extra information can be in the form of extra path information, added parameters, or some custom, server-specific URL change. Due to the limited space available in rewriting a URL, the extra information is usually limited to a unique session ID.
URL Rewriting in Servlets, which doesn't use cookies to send and receive Session-Id from the web application, To overcome this problem the Session-Id is appended to a URL, that URL goes to the browser window from web application along with the response and again that URL comes back to the web application from browser window along with a request. Generally user append Session-Id to the action URL of the dynamic form page. Following are the uses of URL rewriting.
- This URL Rewriting technique is same as cookies technique, but this URL Rewriting also works even though cookies are restricted coming to a browser window.
- The URL rewriting is the browser independent.
 Example
Example
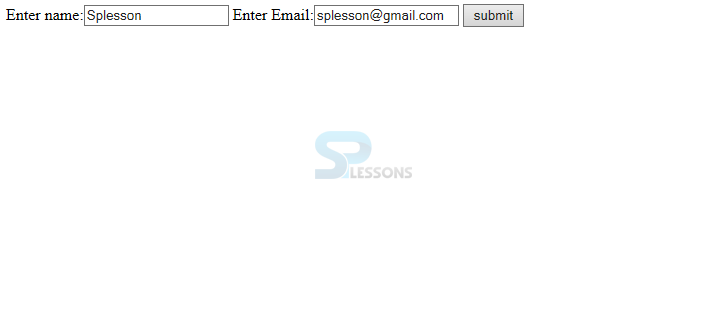
URL Rewrite in Servlets - Following is an example to understand the concept.index.Html
[html]
<html>
<form action="./welcome">
Enter name:<input type="text" name="username"/>
Enter Email:<input type="text" name="emailId"/>
<input type="submit" value="submit"/>
</form>
</html>
[/html]
Here the developer created two text boxes to Enter name and Enter Email.
web.xml
[xml]
<web-app >
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DemoURLRewriting</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>servleturlrewriting.DemoURLRewriting</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ShowURLRewriting</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>servleturlrewriting.ShowURLRewriting</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DemoURLRewriting</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/welcome</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ShowURLRewriting</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
[/xml]
Sample rule of WEB.XML file as follows.
Make sure that servlet name should be same and URL name also should be same. Here the developer used two classes they are DemoURLRewriting, ShowURLRewriting.
DemoURLRewriting.java
[java]
package servleturlrewriting;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class DemoURLRewriting extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String userName=request.getParameter("username");
String emailId=request.getParameter("emailId");
//appending the username in the query string
out.print("<h2><a href='servlet2?uname="+userName+"&email="+emailId+"'>click Here</a></h2>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
[/java]
Sets the content type of the response being sent to the client, if the response has not been committed yet. The given content type may include a character encoding specification. Sets the content type of the response being sent to the client, if the response has not been committed yet. The given content type may include a character encoding specification.
In doGet(), the parameters are appended to the URL and sent along with the header information. The doPost() shall be used when comparatively large amount of sensitive data has to be sent. Examples are sending data after filling up a form or sending login id and password. Flushes the output stream and forces any buffered output bytes to be written out. The general contract of flush is that calling it is an indication that, if any bytes previously written have been buffered by the implementation of the output stream, such bytes should immediately be written to their intended destination.
ShowURLRewriting.java
[java]
package servleturlrewriting;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ShowURLRewriting extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String userName = request.getParameter("uname");
String email = request.getParameter("email");
out.println("<h2>This is your name get from the URL pattern::"+userName+"</h2>");
out.println("<h2>This is your emailId get from the URL pattren::"+email+"</h2>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}
[/java]
Here the parameters will be called and the result will be displayed on the browser.
Output
URL Rewrite in Servlets - Following is the result where user has to enter the details.
Click on the link.
Result will be as follows.
 Description
Description
A Redirect is a client side request to have the web program go to another URL. This implies the URL that client find in the program will refresh to the new URL.
A Rewrite is a server-side revamp of the URL before it's completely prepared by IIS. This won't change what user find in the program in light of the fact that the progressions are avoided the client.
 Key Points
Key Points
- URL Rewrite in Servlets - The URL rewriting method is not secure because of parameters will display in the URL.
- URL Rewrite in Servlets - The URL rewriting is browser independent.
- The developer can not place huge data because the URL will have the limited length.