Description
Description
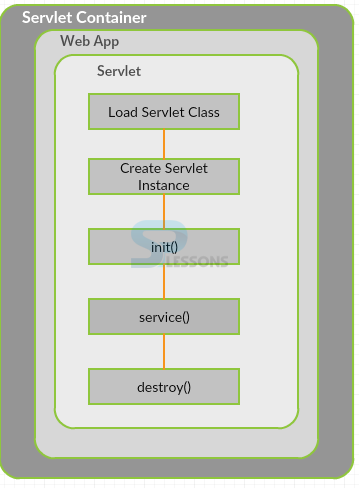
Servlet Interface, When the Servlet is deployed in the server the Servlet container creates life cycle of the Servlet. The central abstraction in the Servlet API is the Servlet interface, all the Servlets have to implement this interface either directly or by extending a class such as GenericServlet, HttpServlet. Following are the different methods of servlet interface.
The following steps show the different methods used in Servlet Life Cycle.
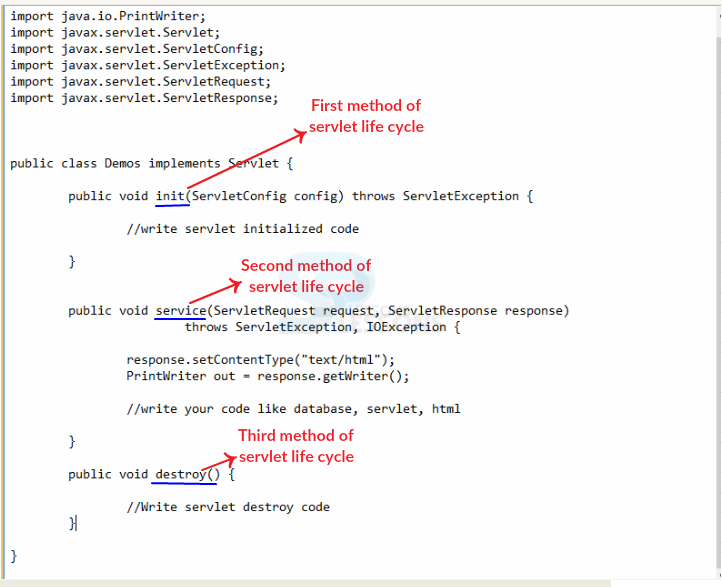
- public void init(ServletConfig config)
- public void service(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response)
- public void destroy()
- public ServletConfig getServletConfig()
- public String getServletInfo()
- Loading the servlet class
- Creating servlet instance
- init method
- service method
- destroy method
 Methods
Methods
Loading the servlet class: When the web container gets the request from the browser for servlet then servlet class will be loaded.
Creating servlet instance: The web container creates an object for the servlet when servlet class is loaded, here the important point is an object will be created in life cycle only once.
init method: This method will be called by the web container after an object was created to the servlet. The functionality of the init() method is to initialize the servlet, following is the regular syntax to declare the init() method.
[java]public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException [/java]
service method: The service() method will be called by web container when servlet will have the request, in case servlet is not initialized then above methods will be utilized. In the life cycle of servlet this method will be utilized only once. Following is a syntax to declare the service() method.
[java]public void service(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException [/java]
destroy method: Web container is the responsibility to call this method utilized while vanishing an object of the Servlet from the service, it provides the chance for servlet to clean up the memory or junk data. Following is the Syntax for the destroy method.
[java]public void destroy()[/java]
Following is the code structure of life cycle methods.
 Example
Example
First.java
[java]package servletinterface;
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
public class First implements Servlet{
ServletConfig config=null;
public void init(ServletConfig config){
this.config=config;
System.out.println("servlet is initialized");
}
public void service(ServletRequest req,ServletResponse res)
throws IOException,ServletException{
res.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out=res.getWriter();
out.print("<html><body>");
out.print("<b>Hey man, welcome to SPLesons.</b>");
out.print("</body></html>");
}
public void destroy(){System.out.println("servlet is destroyed");}
public ServletConfig getServletConfig(){return config;}
public String getServletInfo(){return "copyright 2007-1010";}
}[/java]
web.xml
Sample rule of WEB.XML file as follows.
[xml]<web-app>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>s1</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>servletinterface.First</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>s1</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>[/xml]
index.html
[html]
<center><a href="./hello">Invoke Generic Servlet</a></center>[/html]
Output
By compiling the program the follolwing output get generated.
By clicking on the link following output will be generated.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Servlet Interface - The init() will be called by web container only once.
- The destroy() cleans the junk files to free up the memory.
- The destroy() will be called only if the servlet is unloaded.