Description
Description
Servlet Exception Handling, An Servlet Exception Handling can be defined as an event which will be occurring while the program executes. When servlets gives the exception web container strives for the required configuration files. Exception is a common problem while executing the programs so where developer will use to try and catch blocks to resolve the error. Following example describes about how exception will be occurring and how to resolve that. The concept of exception handling already explained in core java.
 Example
Example
Servlet Exception Handling - Following is the example to describe an exception handling so first this example tells what is the result with out exception handling.
exception.java
[java]package exception;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/MyExceptionServlet")
public class exception extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
throw new ServletException("GET method is not supported.");
}
}[/java]
In doGet(), the parameters are appended to the URL and sent along with the header information. The purpose of serialVersionUID is to give the software engineer control over which forms of a class are viewed as contradictory as to serialization. For whatever length of time that the serialVersionUID sticks with it, the serialization system will attempt to decipher serialized cases, which may not be what you need.
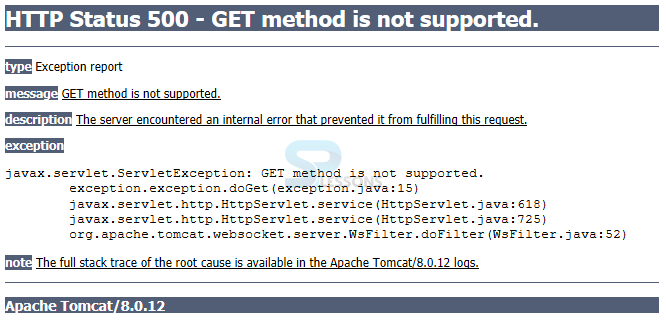
Output
When compile the program following is the output generated.
Following is the Servlet Exception Handling class to debug the exception.
AppExceptionHandler.java
[java]package exception;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
@WebServlet("/AppExceptionHandler")
public class AppExceptionHandler extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
processError(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
processError(request, response);
}
private void processError(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
// Analyze the servlet exception
Throwable throwable = (Throwable) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.exception");
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
String servletName = (String) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.servlet_name");
if (servletName == null) {
servletName = "Unknown";
}
String requestUri = (String) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.request_uri");
if (requestUri == null) {
requestUri = "Unknown";
}
// Set response content type
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.write("<html><head><title>Exception/Error Details</title></head><body>");
if(statusCode != 500){
out.write("<h3>Error Details</h3>");
out.write("<strong>Status Code</strong>:"+statusCode+"<br>");
out.write("<strong>Requested URI</strong>:"+requestUri);
}else{
out.write("<h3>Exception Details</h3>");
out.write("<ul><li>Servlet Name:"+servletName+"</li>");
out.write("<li>Exception Name:"+throwable.getClass().getName()+"</li>");
out.write("<li>Requested URI:"+requestUri+"</li>");
out.write("<li>Exception Message:"+throwable.getMessage()+"</li>");
out.write("</ul>");
}
out.write("<br><br>");
out.write("<a href=\"index.html\">Home Page</a>");
out.write("</body></html>");
}
}
[/java]
The purpose of serialVersionUID is to give the software engineer control over which forms of a class are viewed as contradictory as to serialization. For whatever length of time that the serialVersionUID sticks with it, the serialization system will attempt to decipher serialized cases, which may not be what you need. In the event that user roll out a semantic improvement that renders more established forms contrary, user can change the serialVersionUID to make deserializing more established occurrences fizzle.
In doGet(), the parameters are appended to the URL and sent along with the header information. doPost() shall be used when comparatively large amount of sensitive data has to be sent. Examples are sending data after filling up a form or sending login id and password.
index.html
[java]<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="US-ASCII">
<title>Home Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h2>Welcome to Splessons</h2>
<img src="E:\splessons.png" alt="splessons" height="150" width="150">
<p>Visit <a href="http://www.splessons.com/">splessons.com</a></p></center>
<body style="background:#CEF6E3">
</body>
</html>[/java]
Output
By compiling the program the output below get generated.
 Points
Points
- Exception raised data will be placed in try block.
- In this program developer not used web.xml file where used annotations only.
- Annotations are used to reduce the code of an application.