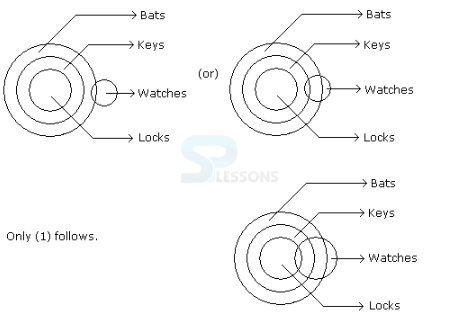
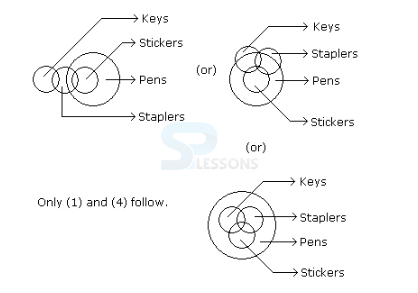
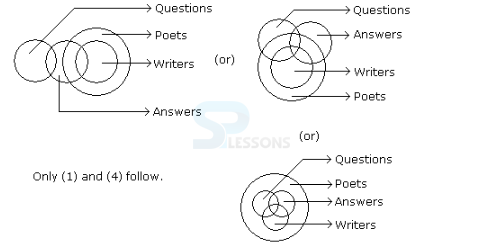
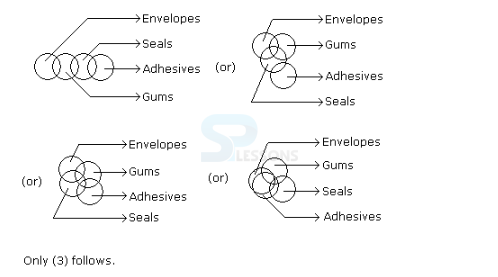
Introduction
Introduction
NHB Assistant Manager (AM) Online Test, will comprise of Objective Tests for 200 marks consisting of 4 Sections and Descriptive Test for 25 marks as follows. A composite time of 3 Hours will be given for answering the questions for the Objective tests and 30 minutes for Descriptive test. The below sections gives the detailed information about NHB AM Reasoning and Computer Aptitude Section.
 Pattern
Pattern
| Sr.No. | Name of Tests | No. of Questions | Maximum Marks | Medium of Exam | Time allotted for each test (Separately timed) | Type of Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reasoning and Computer Aptitude | 45 | 60 | English & Hindi | 60 Minutes | Objective |
| 2 | General Awareness (with special focus on Economy & Banking) and Computer Knowledge | 50 | 50 | English & Hindi | 40 Minutes | |
| 3 | English Language | 25 | 30 | English | 35 Minutes | |
| 4 | Quantitative Aptitude (with special emphasis on Data analysis and interpretation) | 35 | 60 | English & Hindi | 45 Minutes | |
| Total | 155 | 200 | 03 Hours | |||
| English Language* (Letter Writing and Essay) | 02 | 25 | English | 30 minutes | Descriptive | |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
[Click Here] for NHB Assistant Manager Online Exam Syllabus
Note:
Each question in Objective Tests will have five alternative choices, out of which one will be the correct answer. There will be a penalty for wrong answers marked in the Objective Tests. For every wrong answer marked, one fourth of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as penalty to arrive at corrected score. If a question is left blank, i.e. no answer is marked by the candidate, there will be no penalty for that question.
 Samples
Samples
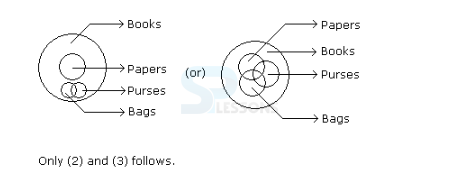
Puzzles & Seating Arrangements
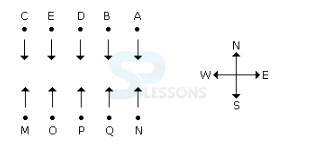
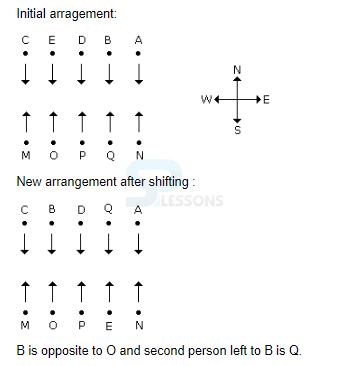
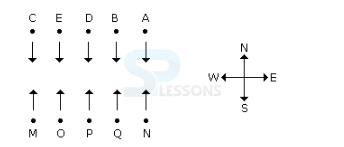
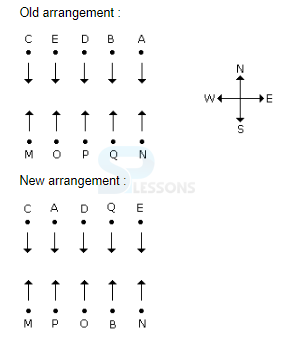
Each of these questions is based on the information given below:
1. A, B, C, D, and E are five men sitting in a line facing to the south - while M, N, O, P and Q are five ladies sitting in a second line parallel to the first line and are facing to North.
2. B who is just next to the left of D is opposite to Q.
3. C and N are diagonally opposite to each other.
4. E is opposite to O who is just next right of M.
5. P who is just to the left of Q is opposite to D.
6. M is at one end of the line.
1. Who is sitting third to the right of O?
- A. Q
B. N
C. M
D. Data inadequate
- A. Q
B. P
C. E
D. D
- A. EQ
B. BO
C. AN
D. AM
- A. D
B. A
C. E
D. O
- A. B
B. A
C. C
D. D
- A. Husband
B. Wife
C. Daughter
D. Son
E. None of these
- A. Sister
B. Mother
C. Niece
D. Data Inadequate
E. None of these
- A. Grandson
B. Son
C. Data Inadequate
D. None of these
- A. Son
B. Grandson
C. Daughter
D. Granddaughter
E. None of these
- A. Mother
B. Sister
C. Aunt
D. Grandmother
- A. B
B. F
C. K
D. W
E. None of these
- A. 60
B. 61
C. 62
D. 58
E. None of these
- A. 29
B. 36
C. 27
D. 35
E. None of these
- A. A
B. C
C. B
D. D
E. None of these
- A. 36
B. 35
C. 33
D. 34
E. None of these
- A. Three
B. Four
C. Five
D. Six
E. None of these.
- A. 91 are 31 trees 18 27 desks hour zero 16 chairs
B. 91 trees 18 27 desk are hour zero 31 16 chairs
C. 91 are 31 chairs trees 18 27 desk hour zero 16
D. 91 are 31 chairs 27 desks 18 trees hour zero 16
E. None of these.
- A. Step 4
B. Step 5
C. Step 6
D. Step 7
E. None Of these.
- A. 94 car window 86 shut 52 31 house
B. 86 window 94 car shut 52 31 house
C. car shut window 86 52 31 house 94
D. cannot be determined
E. None of these.
- A. Step 7
B. Step 8
C. Step 6
D. Step 5
E. None of these.
- A. 17M12
B. 13J17
C. 20I19
D. 21J23
- A. *
B. $
C. %
D. ^
- A. I
B. 5
C. Q
D. B
- A. Z
B. U
C. +
D. 7
- A. K25P
B. L25P
C. L25O
D. L27P
- A. Only I and II are implicit
B. Only II and III are implicit
C. Only III is implicit
D. All are implicit
E. None of these
- A. Only I and III are implicit
B. Only II is implicit
C. Only II and III are implicit
D. All I, II and III are implicit
E. None of these
- A. Only I and II are implicit
B. Only II and III are implicit
C. Only I and III are implicit
D. Only II is implicit
E. None of these
- A. Only I is implicit
B. Only II and III are implicit
C. Only I and III are implicit
D. All are implicit
E. None of these
- A. None is implicit
B. All are implicit
C. Only I and II are implicit
D. Only II and III are implicit
E. Only I and III are implicit
Direction Sense
1. A horse is facing north. It turns 90 degrees in the clockwise direction, then 180 degrees in the anti-clockwise and then another 90 degrees in the same direction. Which direction is the horse facing now?
- A. East
B. South
C. Southwest
D. Southeast
- A. North-East
B. West
C. South-East
D. South
- A. West
B. North-East
C. East
D. South-West
- A. South-East
B. North-West
C. East
D. West
- A. North
B. North-West
C. North-East
D. East
- A. Only (1) and (2)
B. Only (1)
C. Only (2)
D. Only (1) and (3)
- A. Only (1) and (2)
B. Only (2) and (4)
C. Only (2) and (3)
D. Only (1) and (4) and either (2) or (3)
- A. Only (1) and (2)
B. Only (1) and (4)
C. Only (1) and (3)
D. Only (2) and (4)
- A. Only (3)
B. Only (1)
C. Only (2)
D. Only (4)
- A. Only (1)
B. Only (2) and (3)
C. Only (1) and (2)
D. Only (1) and (3)
- A. 81
B. 88
C. 64
D. 121
E. 100
- A. 90
B. 100
C. 110
D. 120
E. 132
- A. 74
B. 89
C. 91
D. 87
E. 81
- A. Red
B. Blue
C. Green
D. Violet
E. Brown
- A. 31313113
B. 31113131
C. 13331313
D. 31131131
E. 13113313
- A. x gt; 40
B. x gt; 50
C. x gt; 60
D. x gt; 70
- A. x > -1/5
B. x > -1/7
C. x > -2/5
D. x > -2/9
- A. $215
B. $165
C. $200
D. $170
- A. x 22
C. x < 22
D. x < 18
- A. distributive property of inequality
B. multiplicative property of inequality
C. additive property of inequality
D. transitive property of inequality
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
- A. If the data in statement I alone are sufficient.
B. If the data in statement II alone are sufficient.
C. If the data either in statement I alone or in statement II alone are sufficient.
D. If the data given in both the statements I and II together are not sufficient.
E. If the data in both the statements I and II together are necessary.
History and Generation of Computers
1. Who founded IBM Company and was also responsible for completing tabulating the US Census with his punch-card tabulator in only six weeks.
- A. Hollerith
B. Jacquard
C. Babbage
D. Pascal
- A. Abacus
B. Stepped Reckoner
C. Pascaline
D. None of the above
- A. Augusta Ada Byron
B. Claude E. Shannon
C. George Moore
D. Peter Norton
- A. Exponential Decrease in number of Transistors in Integrated Circuit.
B. Exponential Decrease of Transistor Size in Integrated Circuit
C. Exponential Increase in Transistor Switching in Integrated Circuit
D. Exponential Increase in number of Transistors in Integrated Circuit.
- A. Computer Engine
B. Diesel Engine
C. Difference Engine
D. Petrol Engine
- A. Volatile storage
B. Non-volatile storage
C. Sequential storage
D. Direct storage
E. None of these
- A. Network interface card
B. CPU
C. RAM
D. ROM
E. None of these
- A. Character, File, Record, Field, Database, File
B. Character, Record, Field, Database, File
C. Character, Field, Record, File, Database
D. Bit, Byte, Character, Record, Field, File, Database
E. None of these
- A. ROM
B. EPROM
C. EEPROM
D. All of the above
E. none of these
- A. external
B. auxiliary
C. internal
D. main
E. none of these
- A. that does not change during the execution of the program
B. that can change during the execution of the program
C. that can vary during the execution of the program
D. none of these
- A. DOS
B. The operating system which contains the disk-oriented commands and uses disk devices for permanent storage
C. Both A & B
D. None of these
- A. Unbundled
B. Bundled
C. Utility
D. None of these
- A. An optical input device used to read documents
B. A device that arranges the documents
C. A device that is used to edit the document
D. None of these
- A. Permits one computer to execute the machine-language instructions of another computer of a different make
B. Is not broken down into smaller units
C. Permits one computer to execute the machine-language instructions of another computer of the same make.
D. None of these
- A. the amount of available physical memory
B. operating System
C. instruction set architecture
D. none of the mentioned
- A. the instruction must be restarted
B. the instruction must be ignored
C. the instruction must be completed ignoring the page fault
D. none of the mentioned
- A. one
B. two
C. three
D. none of the mentioned
- A. the amount of available physical memory
B. operating System
C. instruction set architecture
D. none of the mentioned
- A. proportional allocation algorithm
B. equal allocation algorithm
C. split allocation algorithm
D. none of the mentioned
- A. leased line
B. digital subscriber line
C. digital signal line
D. none of the mentioned
- A. internet exchange point
B. subscriber endpoint
C. isp endpoint
D. none of the mentioned
- A. HTTP
B. DHCP
C. DNS
D. None of the mentioned
- A. 32 bits
B. 64 bits
C. 128 bits
D. 265 bits
- A. packet switching
B. circuit switching
C. both packet switching and circuit switching
D. none of the mentioned
- A. Users
B. Clients
C. End Users
D. Stake Holders
- A. End Users
B. Data
C. Application Request
D. HTML
- A. System-centered
B. User-centered
C. Company-centered
D. Data-centered
- A. Relation
B. Attribute
C. Parameter
D. Constraint
- A. Relation
B. Attribute
C. Parameter
D. Constraint
- A. Padded
B. XORed
C. Concatenated
D. ANDed
- A. secret value
B. identifying label
C. initialization vector
D. secret value
- A. record_overflow
B. no_certificate
C. internal_error
D. decode_error
- A. Anonymous Diffie-Hellman
B. Fixed Diffie-Hellman
C. RSA
D. Fortezza
- A. client finished for the client
B. client finished for the client, server finished for the server
C. server finished for the server
D. client finished for the server, server finished for the client
Introduction to Computer Organisation
1. A low memory can be connected to microprocessor by using
- A. INTER
B. RESET IN
C. Both (a) and (b)
D. READY
- A. An operand and an address
B. A decoder and an accumulator
C. Sequence register and decoder
D. None of these
- A. Devices have 8-bit addresses
B. Devices are accessed using IN and OUT instructions
C. There can be a maximum of 256 input devices and 256 output devices
D. Arithmetic and logic operations can be directly performed with the I/O data.
- A. Direct memory access
B. Vectoring the interrupt
C. System Interrupt
D. Cycle stealing
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. None of these
- A. programmable interval timer
B. interrupt timer
C. programmable timer
D. none of the mentioned
- A. spool
B. output
C. status
D. magic
- A. Expansion bus
B. PCI bus
C. SCSI bus
D. None of the mentioned
- A. non-blocking I/O
B. blocking I/O
C. asynchronous I/O
D. synchronous I/O
- A. Read by the host to get input
B. Read by the controller to get input
C. Written by host to send output
D. Written by host to start a command
- A. brackets
B. back-slash
C. insecure data
D. punctuation marks
- A. beginners
B. student applications
C. commercial applications
D. household user interface
- A. fixed variable
B. default variables
C. default constants
D. called by other programs
- A. one-dimensional array
B. two-dimensional array
C. three-dimension array
D. multi-dimension array
- A. array in BASIC
B. array in PASCAL
C. array in COMAL
D. array in COBOL
- A. The use of discontinuous networks is not allowed
B. The use of variable length subnet masks is permitted
C. RIPv1 is a classless routing protocol
D. RIPv2 supports classless routing
- A. It sends back the protocol received from a router as a poison pill, which stops the regular updates. The use of variable length subnet masks is permitted
B. It is information received from a router that can’t be sent back to the originating router.RIPv2 supports classless routing
C. It prevents regular update messages from reinstating a route that has just come up
D. It describes when a router sets the metric for a downed link to infinity
- A. It has a lower administrative distance than RIPv1
B. It converges faster than RIPv1
C. It has the same timers as RIPv1
D. It is harder to configure than RIPv1
- A. When a new Layer 2-only switch is added to the network
B. When you are migrating from one routing protocol to another
C. When you are using routers from multiple vendors
D. When there are host-based routers from multiple vendors
- A. IP EIGRP and AppleTalk EIGRP
B. AppleTalk EIGRP and RIPv2
C. RIPv2 and IP EIGRP
D. IPX RIP & AppleTalk EIGRP
- A. CTRL+INSERT
B. CTRL+END
C. CTRL+HOME
D. CTRL+ALT
- A. CTRL+INSERT
B. CTRL+END
C. CTRL+HOME
D. CTRL+ALT
- A. PAGE UP
B. PAGE DOWN
C. HOME
D. INSERT
- A. Functional Keys
B. Home Key
C. Arrow Keys
D. None of these
- A. CTRL+SHIFT+_
B. CTRL+SHIFT+
D. CTRL+SHIFT+ =
- A. (35.68)8
B. (35.24)8
C. (34.34)8
D. (35.59)8
- A. It requires a very large string of 1’s and 0’s to represent a decimal number
B. It requires a sparingly small string of 1’s and 0’s to represent a decimal number
C. It requires a large string of 1’s and a small string of 0’s to represent a decimal number
D. None of the Mentioned
- A. Bit
B. Byte
C. Nibble
D. Word
- A. MSB
B. LSB
C. Bits
D. Nibble
- A. 450
B. 451
C. 421
D. 501