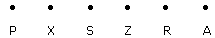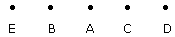Introduction
Introduction
NABARD Office Attendant Mains Examination, conducted in online Mode, duration of 120 minutes, a total of 155 Questions, a maximum score of 155 marks, and, consists of 4 sections, namely – English Language, Test of Reasoning, Quantitative Aptitude, General Awareness. The article NABARD Office Attendant Mains Reasoning provides Test of Reasoning (Mcq’s) useful to the candidates while preparing NABARD Office Attendant 2020
 Imp Dates
Imp Dates
NABARD Office Attendant Important Dates
| Event | Date |
|---|---|
| Application Start Date | 25.12.2019 |
| Application Last Date | 12.01.2020 |
| Last Date to pay the Application Fee | 12.01.2020 |
| Download of call letters for Online examination – Preliminary | Preliminary Exam Hall Ticket |
| Preliminary Exam Date | 04th Feb |
| Prelims Result Date | 26-02-2020 |
| Mains Exam Date | March 14 2020 |
| Prelims Result Date | 27-02-2020 |
| Mains Admit Card Release Date | Will Update Soon!!! |
| Mains Result Date | Will Update Soon!!! |
 Pattern
Pattern
| S. No. | Name of test (objective) | No. of questions | Maximum Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Test of Reasoning | 35 | 35 | Composite time of 120 minutes |
| 2. | Quantitative Aptitude | 35 | 35 | |
| 3. | General Awareness | 50 | 50 | |
| 4. | English Language | 35 | 35 | |
| Total | 155 Questions | 155 Marks |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
| S.No | Name of Test | Syllabus |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Test of Reasoning | |
| 2 | English Language | |
| 3. | General Awareness |
|
| 4. | Numerical Ability |
|
 Samples
Samples
1. 5 20 320 1280 20480 ?
- A. 71960
B. 42480
C. 32340
D. 81920
- A. 90
B. 85
C. 65
D. None of these
- A. 116
B. 220
C. 312
D. 224
- A. 13
B. 26
C. 39
D. 52
- A. 195
B. 210
C. 203
D. 205
1. Pointing to a photograph of a boy Suresh said, "He is the son of the only son of my mother." How is Suresh related to that boy?
- A. Cousin
B. Brother
C. Uncle
D. Father
- A. Q - N + M x P
B. P + S x N - Q
C. P - M + N x Q
D. Q - S % P
1. What is the code of the word ‘Wisdom’?
- A. %N9
B. $L19
C. $O19
D. %D19
- A. Reach
B. Your
C. Own
D. Star
1. Chug : Train : : Bang : ?
- A. House
B. Animal
C. Door
D. Man
- A. UVWX
B. UWVX
C. UXWV
D. UWXV
1. Find the one which does not belong to that group ?
- A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 9
- A. 27
B. 37
C. 47
D. 67
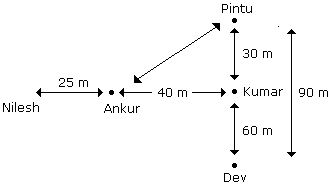
1. Which one is in the North-East of the person who is to the left of Kumar?
- A.Dev
B.Nilesh
C.Ankur
D.Pintu
- A. 215 m
B. 155 m
C. 245 m
D. 185 m
1. A, P, R, X, S and Z are sitting in a row. S and Z are in the centre. A and P are at the ends. R is sitting to the left of A. Who is to the right of P ?
- A. A
B. X
C. A
D. Z
- A. Between B and D
B. Between B and C
C. Between E and D
D. Between C and E
1. SCD, TEF, UGH, ____, WKL
- A. CMN
B. UJI
C. VIJ
D. IJT
- A. B2C2D
B. BC3D
C. B2C3D
D. BCD7
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
1. Statement: Should India encourage exports, when most things are insufficient for internal use itself?
Arguments:
1. Yes. We have to earn foreign exchange to pay for our imports.
2. No. Even selective encouragement would lead to shortages.
- A. Only argument I is strong
B. Only argument II is strong
C. Either I or II is strong
D. Neither I nor II is strong
- A. Only argument I is strong
B. Only argument II is strong
C. Either I or II is strong
D. Neither I nor II is strong