Introduction
Introduction
This chapter demonstrate the JUnit Test Classes. Which explore the some features of the test cases those features are use full to perform more test cases at a single time. JUnit have the several test classes below demonstrate some of the Junit Test Class.
- Creating Test class in JUnit.
- Parameterized test
 Description
Description
In order to create the Junit Test Class which has the several basic test methods based on the test requirement. JUnit runs the multiple test methods and some annotations at a time the below code demonstrates the creating a Junit Test Class.
[c]import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Ignore;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.AfterClass;
import com.simpleprogram.proteintracker.TrackingService;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class trackingServiceeTest {
private TrackingService service;
@BeforeClass
public static void before()
{
System.out.println("Before Class");
}
@AfterClass
public static void after()
{
System.out.println("After Class");
}
@Before
public void setUp()
{
System.out.println("Before");
service = new TrackingService();
}
@After
public void tearDown()
{
System.out.println("After");
}
@Test
public void NewTrackingServiceTotalIsZero()
{
assertEquals("Tracking service was not zero", 0, service.getTotal());
}
@Test
@Ignore
public void WhenAddingProteinTotalIncresesByThatAmount()
{
service.addProtein(10);
assertEquals("Protein amount was not correct", 10, service.getTotal());
}
@Test
public void WhenRemovingProteinTotalRemainsZero()
{
service.removeProtein(5);
assertEquals(0, service.getTotal());
}
}
[/c]
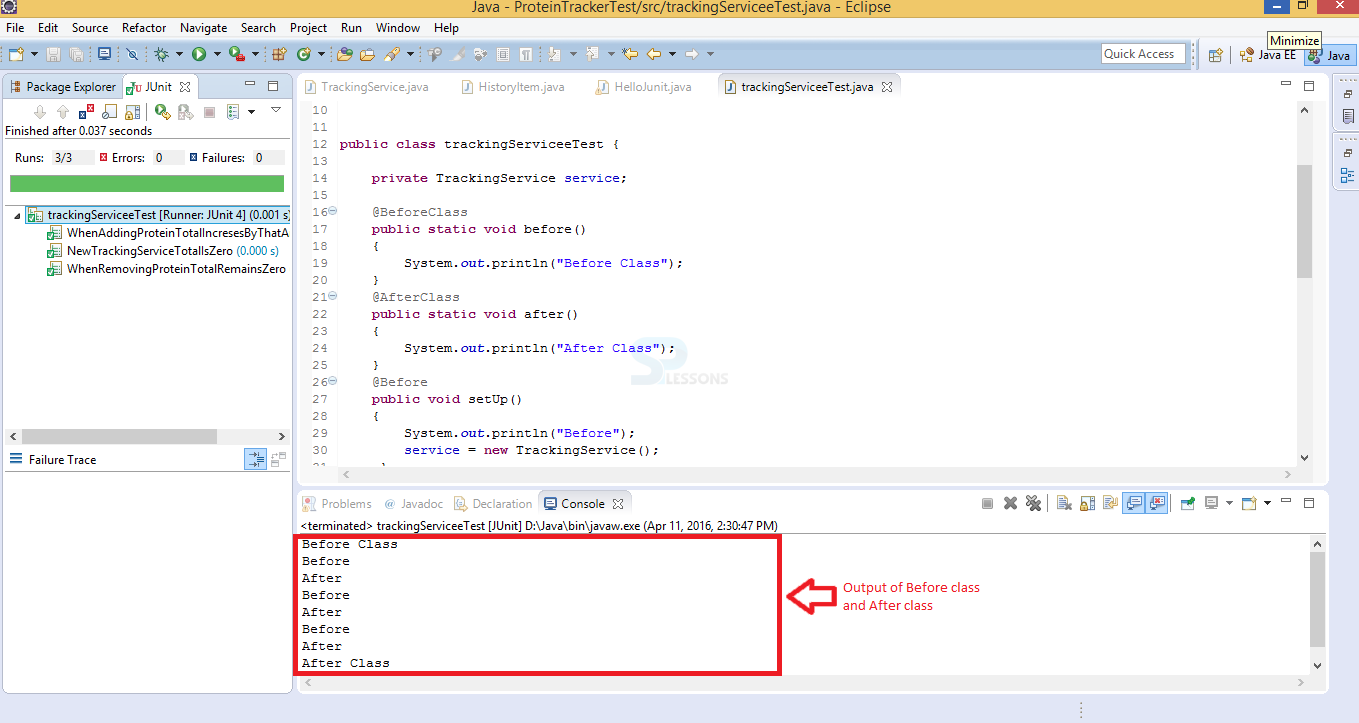
If user run the above generated code it will run all mentioned methods and annotations successfully and which displays the output in green colour as shown in below image.
 Description
Description
Parameterized Tests used to pass a set of inputs and expected outputs into a test class and runs against those inputs and check to the expected results without creating a test case for each pair. In order to create simple parameterized JUnit test user need to create static method with parameters annotation which returns a collection of arrays that have one item for input and another one is for expected output. Below image demonstrate the Parameterized test.
Creating Parameterized Tests
Following are the steps to create Parameterized Tests.
- In order to create the parameterized test user need to create parameters annotations that return back collection of arrays which have one item for item and the another item for an expected result.
- User can create a class which contain a constructor that takes an input and Expected result, and set of those values into a fields in a class.
- Finally user create tests that rely on the inputs and expected result values stored in the fields of created class.
 Examples
Examples
The below code demonstrate to create a test to specify the series of input for Protein that either going to add or remove.
[c]import java.utill.Arrays;
import java.utill.List;
import org.junit.runner.Runwith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
import com.simpleprogrammer.proteintracker.Trackingservice;
@Runwith(Parametrized.class)
public class PrametrizecTests {
Private static Tracking Service=new TrackingService();
@Parameters
public static List<Object[]> data(){
return Arrays.osList(new Object[][]){
{5, 5},
{5, 10},
{-12, 0},
{50, 50},
{1, 51}
})
}
public ParametrizedTests(int input, int expected){
this.input = input;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Test
public voi tst(){
if(input <=0)
service.addProtein(input);
else
service.removeProtein(-input);
}
}
[/c]
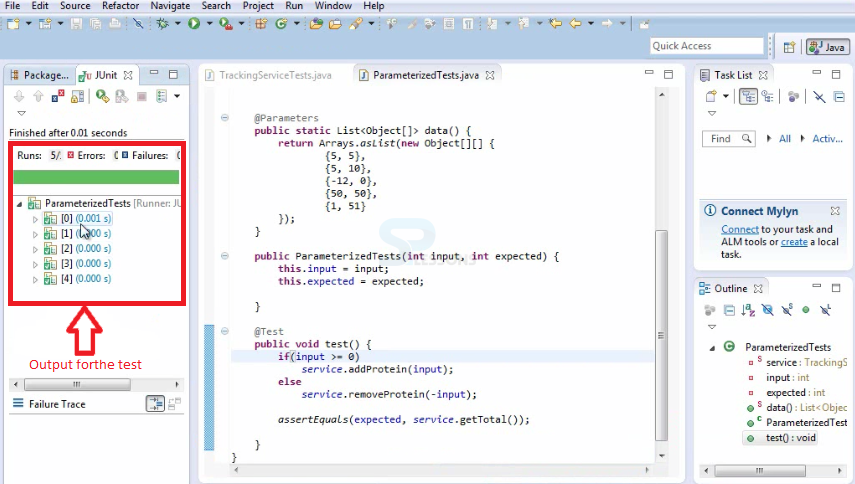
The output for the above program is shown below.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Junit Test Class - User can pass set of inputs to Parameterized test.
- While creating tests follow the naming conventions.
- Output shows the executed procedure by using annotations.
- Parameterized tests will run against the expected outputs.