Description
Description
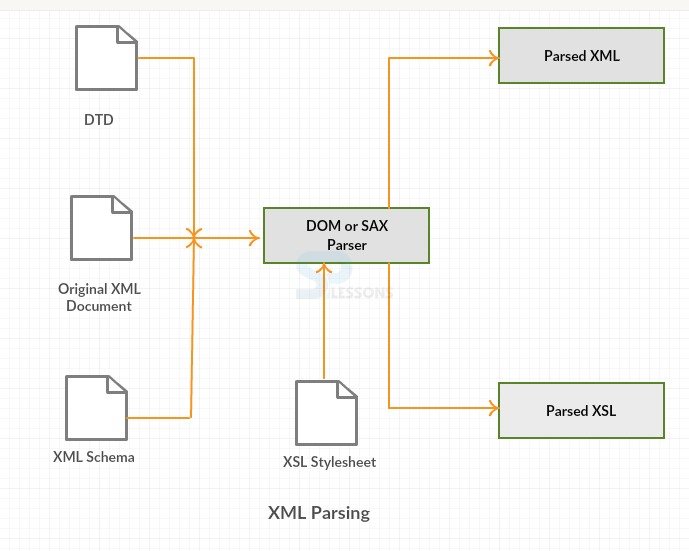
XML Parser: Parser is a program part which represents the physical form of a data and converts it into storage form for the program. The one which reads XML Data in a XML file is referred to as XML Parser. Until unless the code is copied as a unit block blindly, every XML program should call the XML Parser.
The world working in XML with Java is not alphabet soup of acronyms such as DOM, JDOM, JAXP and so on. One of the frequently used JavaXML Parsers is
JAXP whcih stands for java api for xml processing that describes the requirements for the xml api’s which are blanketed in java SE like:
DOM : DOM characterizes a rigid of interfaces to the parsed adaptation of a xml record. the parser peruses inside the total archive and assembles an in-memory tree.
DOM is platform browser and language neutral. It does not assume anything about what platform is running on what browser turning on and there are several language implementations of the DOM that can be used to work with. One of the most common languages that people work with the DOM is JavaScript.
JDOM : Java-based Document Object Model parses the XML document same as DOM but in easier manner.
Schemas give the capacity to characterize a component’s sort and much better limitations. DTDs uphold a strict requesting of components; constructions have a more adaptable scope of alternatives. At long last schema’s are composed in XML, while DTDs have their own particular syntax.
SAX: The SAX interface for xml characterizes the exercises and interfaces used to connect with a sax-agreeable xml parser.
StAX: Streaming API for XML is a pull process where only data is looked and only call methods that are meaningful.
XPATH: XML Path Language defines locations for XML documents which can be used in XSLT style sheets.
JAXB: Java for xml restricting minimizes get right of passage to a xml record from a java program with the guide of granting the xml document to this framework in a java organize.  Description
Description
To decide the programming interface that best suites for the application one ought to understand the design factors of all the interfaces, and functionality of application with the xml files which are being parsed. Below are the issues that outcomes in finding the exceptional api.
- If the application is written in Java, JAXP is the best option that works with DOM, SAX, and JDOM by differentiating the code from the implementation details of numerous parsers.
- On the off chance that the utility is sent as java applet, then sax parser is the excellent option since it minimizes the amount of downloaded code, consider that sax parsers are littler than dom parsers.
- If there is a requirement to access that data in XML document many times, then DOM is the best choice because it saves the data automatically.
- Suppose, only some things are required from the XML source, the sax is the proper preference because it doesn't create items for everything in the supply file.
- If working on a device with less memory space, then SAX is the best choice.
 Key Points
Key Points
- JAXP describes the standards for the XML API’s that are included in Java SE.
- SAX is the mostly used Java XML Parser.