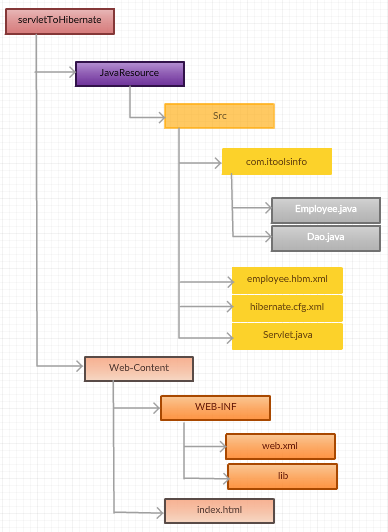
- Create the project directory structure.
- Create the HTML file and forward the request to Servlet.
index.html
[html]<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<form action="servlet">
Employee Id : <input type="text" name="id">
Employee Name : <input type="text" name="name">
Employee Salary :<input type="text" name="salary">
<input type="submit" value="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
ServletDemo.java
[java]
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.iquickinfo.Dao;
public class ServletDemo extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException
{
System.out.println("this is servlet");
int employeeId=Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("id").trim());
String employeeName=request.getParameter("name").trim();
int salary=Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("salary").trim());
Dao dao=new Dao();
boolean b=dao.saveDetails(employeeId, employeeName, salary);
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out=response.getWriter();
if(b==true)
{
out.println("<h1>Employee details sucessfully saved.</h1>");
}
else
{
out.println("<h1>Employee details already existed.</h1>");
}
out.println("");
out.close();
}
}
[/java]
In
doGet(), the parameters are appended to the URL and sent along with the header information. The
serialVersionUID is used as a version control in a Serializable class. If you do not explicitly declare a
serialVersionUID, JVM will do it for you automatically, based on various aspects of your Serializable class, as described in the Java(TM) Object Serialization Specification. Sets the
content type of the response being sent to the client, if the response has not been committed yet.The given content type may include a character encoding specification.
- Set URL Pattern in web.xml file.
web.xml
[xml]<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<display-name>ServletToHibernate</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>ServletDemo</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>ServletDemo</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/servlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
[/xml]
- Create the persistence class.
Employee.java
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
public class Employee
{
private int employeeId;
private String employeeName;
private int salary;
public int getEmployeeId() {
return employeeId;
}
public void setEmployeeId(int employeeId) {
this.employeeId = employeeId;
}
public String getEmployeeName() {
return employeeName;
}
public void setEmployeeName(String employeeName) {
this.employeeName = employeeName;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
[/java]
Set and
Get methods are a pattern of data encapsulation. Instead of accessing class member variables directly, one can define get methods to access these variables, and set methods to modify them.
- Map the persistence class in mapping file.
employee.hbm.xml
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.itoolsinfo.Employee" table="employee">
<id name="employeeId">
<generator class="assigned"></generator>
</id>
<property name="employeeName"></property>
<property name="salary"></property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
[/xml]
The
generator class subelement of id utilized to produce the unique identifier for the objects of persistence class. There are numerous generator classes characterized in the Hibernate Framework. All the generator classes actualizes the
org.hibernate.id.IdentifierGenerator interface.
- Configure the mapping file in Configuration file.
hibernate.cfg.xml
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="connection.driver_class">oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE</property>
<property name="connection.username">system</property>
<property name="connection.password">system</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">create</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping resource="employee.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
[/xml]
- Create the Dao class and store the POJO class object details which will be sent to the servlet class.
Dao.java
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class Dao
{
public boolean saveDetails(int employeeId, String employeeName, int salary)
{
boolean flag=true;
SessionFactory factory=new Configuration().configure("hibernate.cfg.xml").buildSessionFactory();
Session session=factory.openSession();
Employee employee=new Employee();
employee.setEmployeeId(employeeId);
employee.setEmployeeName(employeeName);
employee.setSalary(salary);
Transaction transaction=session.beginTransaction();
try
{
session.save(employee);
transaction.commit();
}catch(Exception e)
{
transaction.rollback();
flag=false;
}
session.close();
return flag;
}
}
[/java]
- Deployee the application in Tomcat/web apps folder, after run on server. Open the Html page.
- Enter all the details after clicking on submit button.
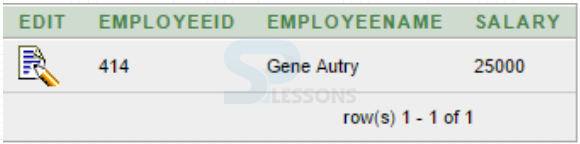
- In command prompt the output is displayed.
- Check the output in Database table also using following command.
[sql]select * from Employee;[/sql]
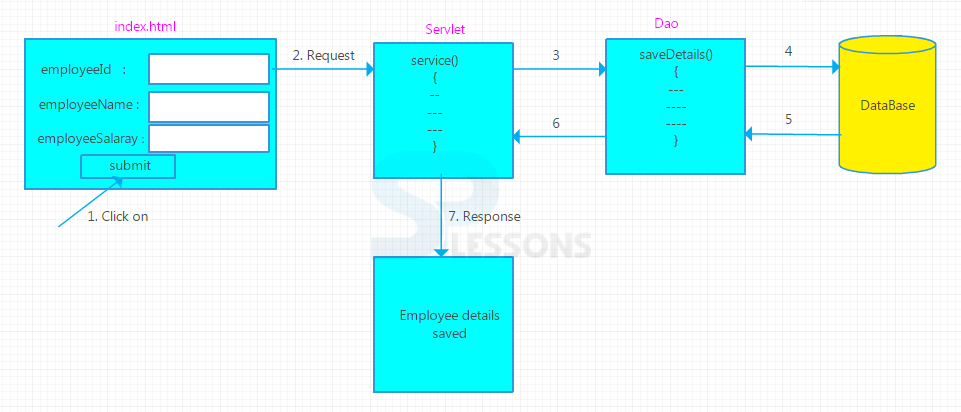
 Introduction
Introduction  Example
Example  Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure  Example
Example  Points
Points