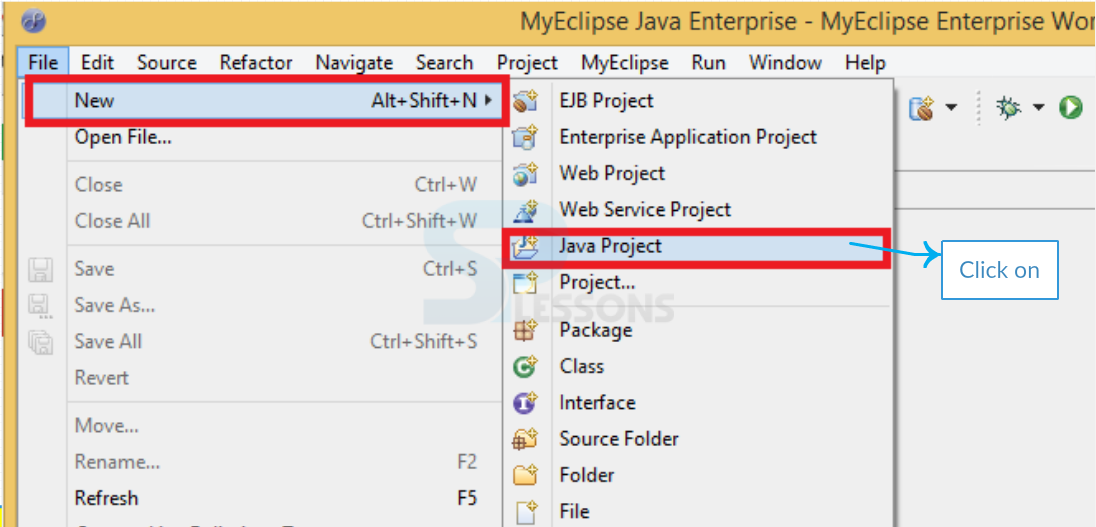
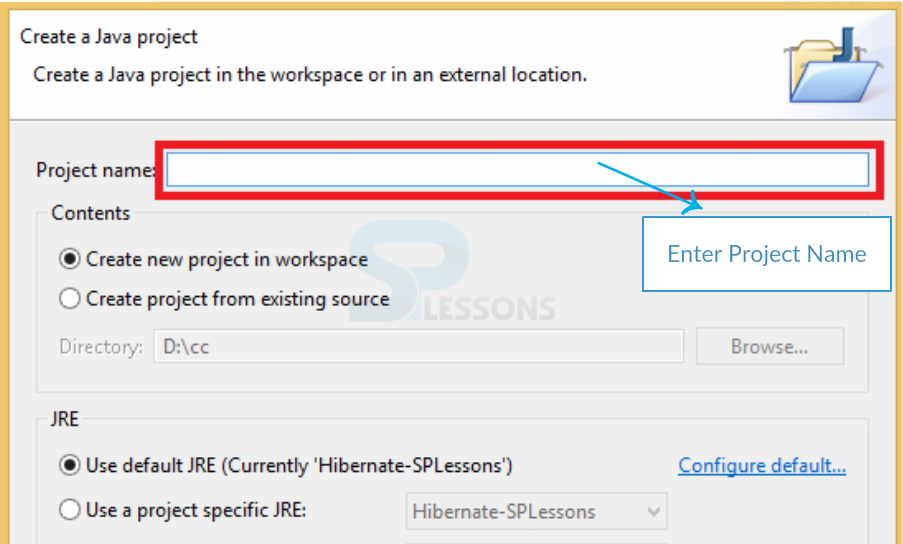
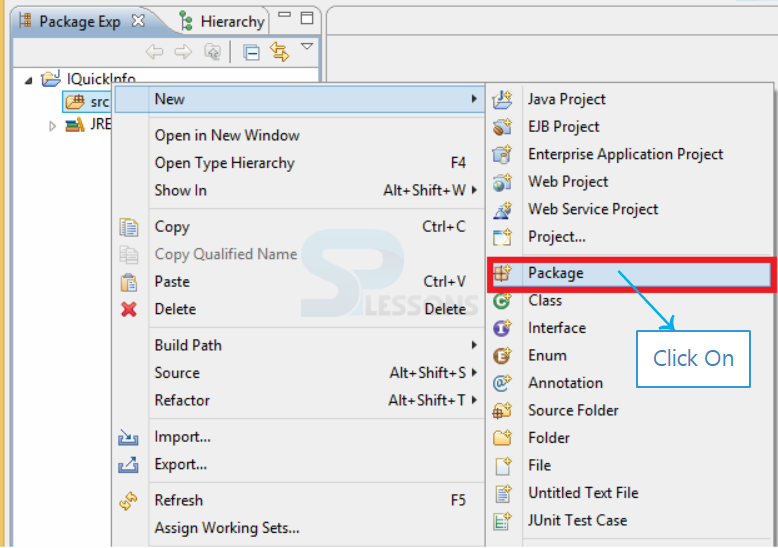
Step-1
Step-1
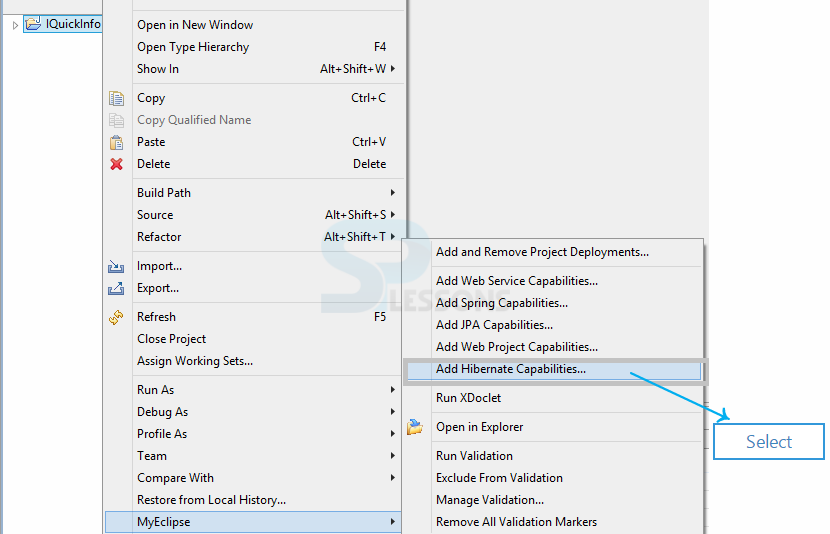
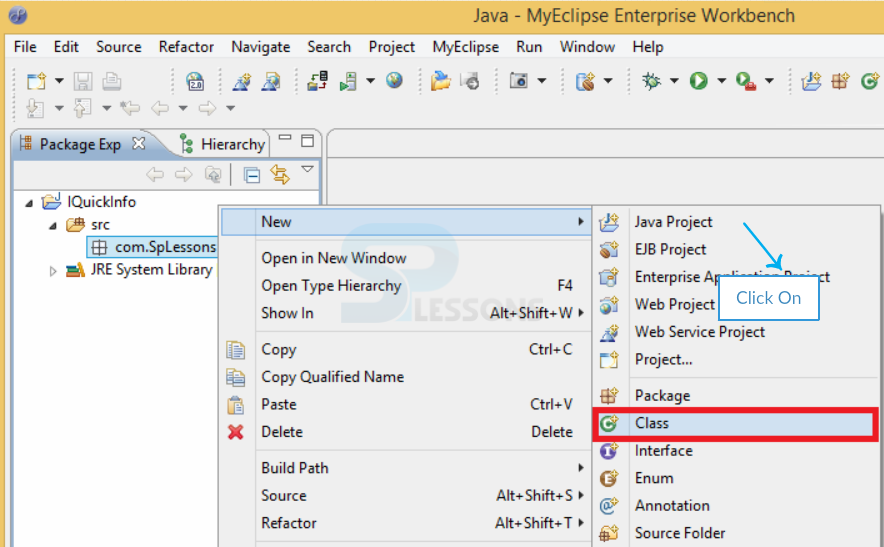
 Step-3
Step-3
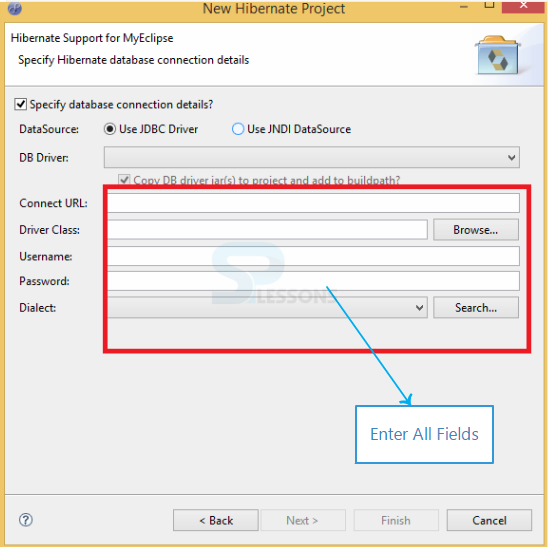
 Step-4
Step-4
 Example
Example
Employee.java
[java]package com.abc;
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String firstName,lastName;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
}
[/java]
Set and Get methods are a pattern of data encapsulation. Instead of accessing class member variables directly, one can define get methods to access these variables, and set methods to modify them. By encapsulating them in this manner, one can have control over the public interface
StoreData.java
[java]package com.abc;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class StoreData {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//creating configuration object
Configuration cfg=new Configuration();
cfg.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml");//populates the data of the configuration file
//creating seession factory object
SessionFactory factory=cfg.buildSessionFactory();
//creating session object
Session session=factory.openSession();
//creating transaction object
Transaction t=session.beginTransaction();
Employee e1=new Employee();
e1.setId(122);
e1.setFirstName("sonoorrr");
e1.setLastName("jaiswalrrrr");
session.persist(e1);//persisting the object
t.commit();//transaction is commited
session.close();
System.out.println("your data has been stored successfully, please check in your data base.");
}
}
[/java]
persist() is like recovery (with exchange) and it adds the entity object to the persistent context, so any further changes are followed. In the event that the article properties are changed before the exchange is commited or session is flushed, it will likewise be spared into database.
employee.hbm.xml
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.abc.Employee" table="emp1000">
<id name="id">
<generator class="assigned"></generator>
</id>
<property name="firstName"></property>
<property name="lastName"></property>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>[/xml]
The generator classsubelement of id utilized to produce the unique identifier for the objects of persistence class. There are numerous generator classes characterized in the Hibernate Framework. All the generator classes actualizes the org.hibernate.id.IdentifierGenerator interface.
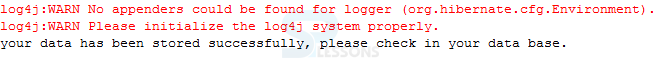
Output will be as follows. While compiling the application following output will be displayed, Information will be stored in database.
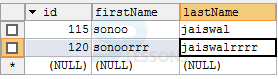
The following output will be displayed in data base browser(SQLyog).
hibernate.cfg.xml
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<!-- Generated by MyEclipse Hibernate Tools. -->
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<property name="dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test</property>
<property name="connection.username">root</property>
<property name="connection.password">root</property>
<property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<mapping resource="employee.hbm.xml"/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>[/xml]
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| hibernate.connection.driver_class | The JDBC driver class. |
| hibernate.dialect | This property makes Hibernate generate the suitable SQL for the picked database. |
| hibernate.connection.url | The JDBC URL to the database instance. |
| hibernate.connection.username | The database username. |
| hibernate.connection.password | The database password. |
| hibernate.connection.pool_size | Limits the number of connections waiting in the Hibernate database connection pool. |
| hibernate.connection.autocommit | Allows autocommit mode to be used for the JDBC connection. |
 Key Points
Key Points
- Hibernate Eclipse - Configuration file and Mapping file both are needed for the application.
- Hibernate Eclipse - One hibernate application may have more mapping files.