Description
Description
Hibernate One To One relationship means when One class object is stored into another class, it is called hibernate object relationship. To apply Hibernate One To One relationship between two classes the primary key of the one object should be copied to primary key of the another object, foreign generator class will be used in one-to-one relationship. In Hibernate One-To-One Relationship can be applied in two ways.
To put the one-to-one relationship with a Foreign Key column in the child table, duplicate values and null values must not be allowed in the Primary Key column. Map a Foreign Key column in a mapping file, after Configuring the
- one-to-one with Primary key.
- one-to-one with Foreign key.
<> tag with unique="true" & not-null = true attributes.  Description
Description
Apply one-to-one relationship and make Primary Key of a child record same as Primary Key value of parent record, then one need to choose one-to-one with Primary Key.
- In Primary Key, column acts as a foreign key is child table.
- In order to copy Primary Key of a parent record to the Primary key of child record, hibernate is given generator class as foreign generator class.
 Example
Example
For example, take one Person containing a Pan card. Then, the Person class Primary Key column is stored to Pan card class.
 Step 2
Step 2
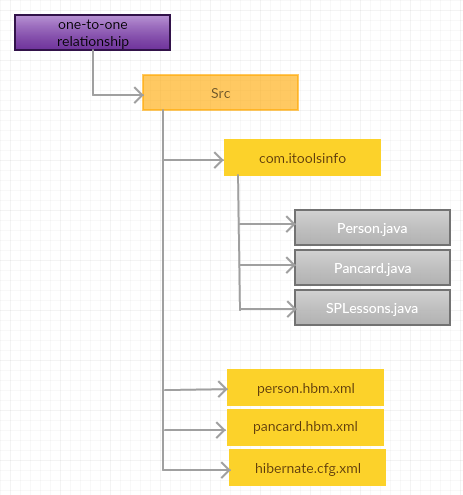
Create the Persistance classes.
Person.java
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
public class Person
{
private int id;
private String address;
private Pancard pancard;
public Pancard getPancard() {
return pancard;
}
public void setPancard(Pancard pancard) {
this.pancard = pancard;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
[/java]
Here the developer created the class Person and given their variables such as id, address, pancard. Set and Get methods are used to set and get person variables.
Pancard.java
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
public class Pancard {
private int pancardNumber;
private String name;
private Person person;
public Person getPerson() {
return person;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPancardNumber() {
return pancardNumber;
}
public void setPancardNumber(int pancardNumber) {
this.pancardNumber = pancardNumber;
}
}
[/java]
Here the developer created the class Pancard and given their variables such as pancardNumber, name. Set and Get methods are a pattern of data encapsulation. Instead of accessing class member variables directly, one can define get methods to access these variables, and set methods to modify them. As every one know that this keyword is used to refer the current object.
 Step 3
Step 3
Map the persistence classes in mapping file.
person.hbm.xml
[xml]
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC “-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN” “http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd”>
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name=”com.itoolsinfo.Person” table=” person” >
<id name=”id” column=”personId”>
<generator class=”increment”>
</generator>
</id>
<property name=”address”/>
<one-to-one name=”pancard” />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
[/xml]
The generator class subelement of id utilized to produce the unique identifier for the objects of persistence class. There are numerous generator classes characterized in the Hibernate Framework. All the generator classes actualizes the org.hibernate.id.IdentifierGenerator interface.
pancard.hbm.xml
[xml]
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC “-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN”“http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd”>
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name=”com.itoolsinfo.Pancard”table=” pancard” >
<id name=”pancardNumber” column=”pancardNumber”>
<generator class=”foreign”>
<param name=”property”>person>/param>
</generator>
</id>
<property name=”name”/>
<one-to-one name=”person” cascade=”all”/>
</class>
[/xml]
 Step 4
Step 4
Configure all the mapping files in Configuration file.
hibernate.cfg.xml
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC “-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN””http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd”>
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name=”connection.driver_class”>oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver</property>
<property name=”connection.url”>jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:XE</property>
<property name=”connection.username”>system</property>
<property name=”connection.password”>system</property>
<property name=”dialect”>org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialect</property>
<property name=”hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto”>create</property>
<property name=”show_sql”>true</property>
<mapping resource=”person.hbm.xml”/>
<mapping resource=”pancard.hbm.xml”/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
[/xml]
 Step 5
Step 5
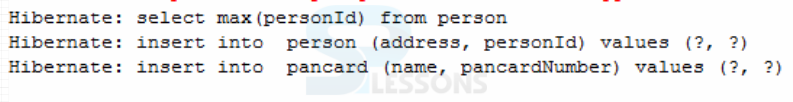
Create the SPLessons class and store the POJO class objects to perform the Database operations.
SPLessons.java
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class SPLessons {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SessionFactory factory=new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
Session session=factory.openSession();
Transaction transaction=session.beginTransaction();
Person person=new Person();
person.setAddress("itoolsinfo");
Pancard pancard=new Pancard();
pancard.setName("Jhon");
person.setPancard(pancard);
pancard.setPerson(person);
session.save(pancard);
session.save(person);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
}
[/java]
Create the SPLessons class and store the POJO class objects to perform the Database operations. Application acquires session objects from Session Factory. SessionFactory is for the most part arranged as Singleton in application, SessionFactory stores produce SQL statements and other mapping metadata that Hibernate utilizes at runtime.
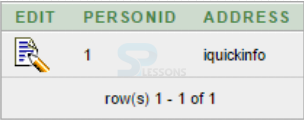
 Output
Output
 Description
Description
To put the one-to-one relationship with a Foreign Key column in the child table, duplicate values and null values must not be allowed in Primary Key column.
Map a Foreign Key column in a mapping file, after Configure the
<> tag with unique="true" & not-null = true attributes.  Example
Example
For Example, Let's take the Two class relations between one-to-one with Foreign key column.
 Step 2
Step 2
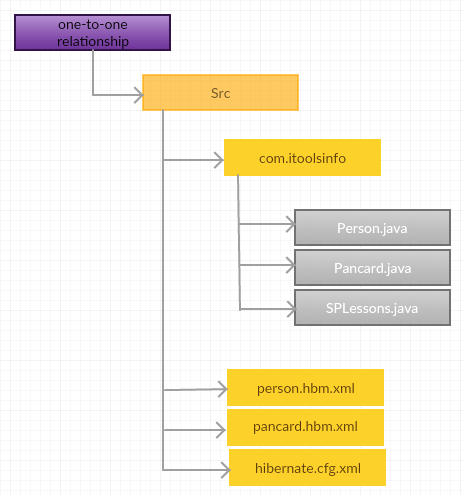
Create the Persistance classes.
Person.java
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
public class Person
{
private int id;
private String address;
private Pancard pancard;
public Pancard getPancard() {
return pancard;
}
public void setPancard(Pancard pancard) {
this.pancard = pancard;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
[/java]
Here the developer created the class Person with the variables address and pancard. Set and Get methods are a pattern of data encapsulation. Instead of accessing class member variables directly, one can define get methods to access these variables, and set methods to modify them.
Pancard.java
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
public class Pancard {
private int id;
private String name;
private Person person;
public Person getPerson() {
return person;
}
public void setPerson(Person person) {
this.person = person;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
[/java]
Here the developer created the class Pancard with address and person variables. This keyword is used to refer the current object.
 Step 3
Step 3
Map the Persistance class properties in mapping file.
person.hbm.xml
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd>>
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.itoolsinfo.Person" table="person1" >
<id name="id">
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<property name="address"/>
<many-to-one name="pancard" class="com.itoolsinfo.Pancard" cascade="all" unique="true" />
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
[/xml]
pancard.hbm.xml
[xml]
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-mapping>
<class name="com.itoolsinfo.Pancard" table="pancard1" >
<id name="id">
<generator class="increment"/>
</id>
<property name="name"/>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
[/xml]
[/xml]
 Step 4
Step 4
Configure all mapping files in Configuration file.
hibernate.cfg.xml
[xml]<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN”“http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd”>
<!-- Generated by MyEclipse Hibernate Tools.
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name=”hbm2ddl.auto”>update</property>
<property name=”dialect”>org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle9Dialect</property>
<property name=”connection.url”>jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe</property>
<property name=”connection.username”>system</property>
<property name=”connection.password”>system</property>
<property name=”connection.driver_class”>oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver</property>
<mapping resource=”person.hbm.xml”/>
<mapping resource=”pancard.hbm.xml”/>
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
[/xml]
| Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| hibernate.connection.driver_class | The JDBC driver class. |
| hibernate.dialect | This property makes Hibernate generate the suitable SQL for the picked database. |
| hibernate.connection.url | The JDBC URL to the database instance. |
| hibernate.connection.username | The database username. |
| hibernate.connection.password | The database password. |
| hibernate.connection.pool_size | Limits the number of connections waiting in the Hibernate database connection pool. |
| hibernate.connection.autocommit | Allows autocommit mode to be used for the JDBC connection. |
 Step 5
Step 5
Create the SPLessons class and store the all POJO class objects to perform the database operations.
SPLessons.hbm.xml
[java]package com.itoolsinfo;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.Transaction;
import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration;
public class SPLessons {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SessionFactory factory=new Configuration().configure("hibernate.cfg.xml").buildSessionFactory();
Session session=factory.openSession();
Transaction transaction=session.beginTransaction();
Person person=new Person();
person.setAddress("itoolsinfo");
Pancard pancard=new Pancard();
pancard.setName("Jhon");
person.setPancard(pancard);
pancard.setPerson(person);
//session.save(pancard);
session.save(person);
transaction.commit();
session.close();
}
}
[/java]
Here the class SPLesson has been created to perform database operations.
 Output
Output
 Key Points
Key Points
- Hibernate One To One - foriegn generator class is used only in Hibernate One To One relation ship.
- The guid generator class works on MS SQL Server and MySQL.