Introduction
Introduction
EPFO Assistant – Mains Examination, conducted in online Mode, has: a duration of 2 hours 45 Minutes, a total of 100 questions, a maximum score of 230 marks, and consists of 5 sections, namely – Reasoning/ Intelligence, General/Economy/Financial Awareness, English Language, Quantitative Aptitude, and Descriptive Paper (English Language with emphasis on comprehension and analysis).
The article EPFO Assistant Quantitative Aptitude presents the EPFO Assistant Quantitative Aptitude section wise questions and answers.
 Pattern
Pattern
| EPFO Assistant Exam Pattern - Mains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. | Name of the Test (Objective Tests) | No. of Questions | Maximum Marks | Duration | Version |
| 1. | Reasoning/ Intelligence | 40 | 60 | 35 Minutes | Bilingual |
| 2. | General/Economy/Financial Awareness | 40 | 40 | 20 Minutes | |
| 3. | English Language | 30 | 40 | 30 Minutes | |
| 4. | Quantitative Aptitude | 40 | 60 | 35 Minutes | English |
| 5. | Descriptive Paper (English Language with emphasis on comprehension and analysis) | 3 (letter, précis’, comprehension) | 30 | 45 Minutes | English |
| Total | 153 Questions | 230 Marks | 2 hours 45 Minutes | ||
 Syllabus
Syllabus
| S.NO | Topics |
|---|---|
| 1. | Computation of whole numbers |
| 2. | Decimals |
| 3. | Fractions and relationships between numbers |
| 4. | Percentage |
| 5. | Ratio & Proportion |
| 6. | Square roots |
| 7. | Averages |
| 8. | Interest |
| 9. | Profit and Loss |
| 10. | Discount |
| 11. | Partnership Business |
| 12. | Mixture and Alligation |
| 13. | Time and distance |
| 14. | Time & Work |
| 15. | Basic algebraic identities of School Algebra & Elementary surds, Graphs of Linear Equations |
| 16. | Triangle and its various kinds of centres |
| 17. | Congruence and similarity of triangles |
| 18. | Circle and its chords |
| 19. | Tangents |
| 20. | Angles subtended by chords of a circle |
| 21. | Common tangents to two or more circles |
| 22. | Triangle, Quadrilaterals |
| 23. | Regular Polygons |
| 24. | Circle |
| 25. | Right Prism |
| 24. | Right Circular Cone |
| 25. | Right Circular Cylinder |
| 26. | Sphere |
| 27. | Hemispheres |
| 28. | Rectangular Parallelepiped |
| 29. | Regular Right Pyramid with triangular or square base |
| 30. | Trigonometric ratio |
| 31. | Degree and Radian Measures |
| 32. | Standard Identities, |
| 33. | Complementary angles |
| 34. | Heights and Distances |
| 35. | Histogram |
| 36. | Frequency polygon |
| 37. | Bar diagram & Pie chart |
 Samples
Samples
Computation of whole numbers:
1. Which one of the following numbers is exactly divisible by 11?
-
A. 235641
B. 245642
C. 315624
D. 415624
-
A. .0025
B. .0256
C. .00027
D. .000126
-
A. 35
B. 36
C. 45
D. 54
-
A. 1
B. 14
C. 20
D. 21
-
A. Rs. 500
B. Rs. 1500
C. Rs. 2000
D. None of these
-
A. 213444
B. 214344
C. 214434
D. 231444
-
A. Rs. 4991
B. Rs. 5991
C. Rs. 6001
D. Rs. 6991
-
A. Rs. 650
B. Rs. 690
C. Rs. 698
D. Rs. 700
-
A. Rs. 2.50
B. Rs. 3
C. Rs. 3.75
D. Rs. 4
-
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
-
A. Rs. 20
B. Rs. 21.81
C. Rs. 22
D. Rs. 18.33
-
A. Rs. 1900
B. Rs. 2660
C. Rs. 2800
D. Rs. 2840
-
A. 26.34 litres
B. 27.36 litres
C. 28 litres
D. 29.16 litres
-
A. 9
B. 10
C. 12
D. 20
-
A. 40
B. 50
C. 54
D. 60
-
A. 45
B. 60
C. 75
D. 90
-
A. 12 kg
B. 60 kg
C. 72 kg
D. 96 kg
-
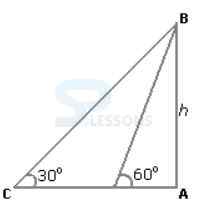
A. 43 units
B. 8 units
C. 12 units
D. Data inadequate
-
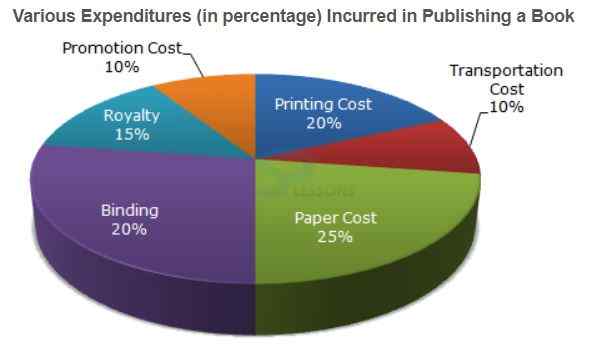
A. Binding Cost and Promotion Cost
B. Paper Cost and Royalty
C. Binding Cost and Printing Cost
D. Paper Cost and Printing Cost
-
A. Rs. 152.50
B. Rs. 157.50
C. Rs. 162.50
D. Rs. 167.50
-
A. Rs. 20,000
B. Rs. 22,500
C. Rs. 25,500
D. Rs. 28,125
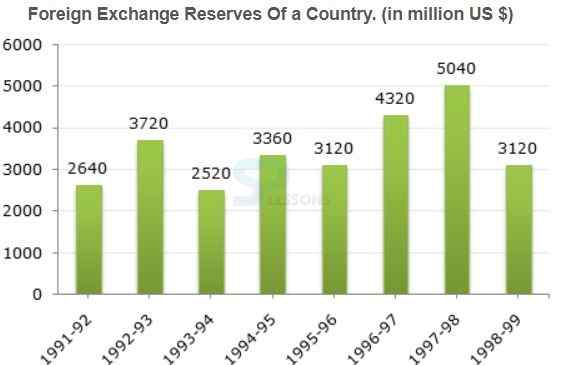
-
A. 2:6
B. 3:4
C. 3:5
D. 4:4
-
A. 0.7
B. 1.2
C. 1.4
D. 1.5
-
A. 100
B. 150
C. 200
D. 620