Introduction
Introduction
DRDO MTS Tier - 1 Examination consisting of Objective Tests for 100 marks will be conducted online. This test would be of 90 minutes duration consisting of 3 Sections as follows. There is no separate timing for each section. DRDO MTS Quantitative Aptitude presents the samples related to Quantitative Aptitude sections.
 Pattern
Pattern
Tier - 1 Examination consisting of Objective Tests for 100 marks will be conducted online. This test would be of 90 minutes duration consisting of 3 Sections as follows. There is no separate timing for each section.
| S. No. | Name of Test | Number of Questions | Maximum Marks | Time allotted for each test (Separately timed) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | General Intelligence & Reasoning Ability | 35 | 35 | 90 minutes |
| 2 | General Awareness | 30 | 30 | |
| 3 | Quantitative Aptitude & Numerical Ability | 35 | 35 |
Note:
- The provisional selection will be based on the merit obtained in Tier-I examination depending upon the post/category/sub-category of the candidate. The minimum qualifying marks for Tier-I is 40% for UR/ESM/OBC candidates and 35% for SC/ST candidates.
- SC, ST, OBC-NCL, EWS, ESM, MSP and PWD candidates, who are selected on their own merit without relaxed standards, will be considered against the unreserved vacancies as per extant Govt. of India orders.
- The reserved vacancies will be filled up separately from amongst the eligible SC, ST, OBC-NCL, EWS, ESM, MSP and PWD candidates.
- Shortlisted candidates will be called for Tier-II
 Syllabus
Syllabus
| S. No. | Name of the topic |
|---|---|
| 1 | Number Systems |
| 2 | Whole Numbers. |
| 3 | Decimals |
| 4 | Fractions |
| 5 | Arithmetical operations. |
| 6 | Percentages |
| 7 | Profit and Loss. |
| 8 | Interest. |
| 9 | Discount. |
| 10 | Averages. |
| 11 | Area |
| 12 | Pictorial Representation. |
| 13 | Ratio and Proportion. |
| 14 | Time and Work. |
| 15 | Ratio and Time. |
| 16 | Time and Distance. |
| 17 | Mixtures & Allegations. |
| 18 | Mensuration. |
| 19 | Data Interpretation etc. |
 Samples
Samples
1. How many of the following numbers are divisible by 132 ?
264, 396, 462, 792, 968, 2178, 5184, 6336
-
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
1. What decimal of an hour is a second ?
-
(A) .0025
(B) .0256
(C) .00027
(D) .000126
1. [latex]\frac{.009 }{0? }[/latex] = .01
-
(A) .0009
(B) .09
(C) .9
(D) 9
1. The two's complement system is to be used to add the signed numbers 11110010 and 11110011. Determine, in decimal, the sign and value of each number and their sum.
-
(A) –14 and –13; –27
(B) –113 and –114; 227
(C) –27 and –13; 40
(D) –11 and –16; –27
1. What percentage of numbers from 1 to 70 have 1 or 9 in the unit's digit?
-
(A) 1
(B) 14
(C) 20
(D) 21
1. In a certain store, the profit is 320% of the cost. If the cost increases by 25% but the selling price remains constant, approximately what percentage of the selling price is the profit?
-
(A) 30%
(B) 70%
(C) 100%
(D) 250%
1. A sum of money at simple interest amounts to Rs. 815 in 3 years and to Rs. 854 in 4 years. The sum is:
-
(A) Rs. 650
(B) Rs. 690
(C) Rs. 698
(D) Rs. 700
1. If Rs. 10 be allowed as true discount on a bill of Rs. 110 due at the end of a certain time, then the discount allowed on the same sum due at the end of double the time is:
-
(A) Rs. 20
(B) Rs. 21.81
(C) Rs. 22
(D) Rs. 18.33
1. A grocer has a sale of Rs. 6435, Rs. 6927, Rs. 6855, Rs. 7230 and Rs. 6562 for 5 consecutive months. How much sale must he have in the sixth month so that he gets an average sale of Rs. 6500?
-
(A) Rs. 4991
(B) Rs. 5991
(C) Rs. 6001
(D) Rs. 6991
1. A and B together can do a piece of work in 30 days. A having worked for 16 days, B finishes the remaining work alone in 44 days. In how many days shall B finish the whole work alone?
-
(A) 30 days
(B) 40 days
(C) 60 days
(D) 70 days
1. The fourth proportional to 5, 8, 15 is:
-
(A) 18
(B) 24
(C) 19
(D) 20
1. The fourth proportional to 5, 8, 15 is:
-
(A) 18
(B) 24
(C) 19
(D) 20
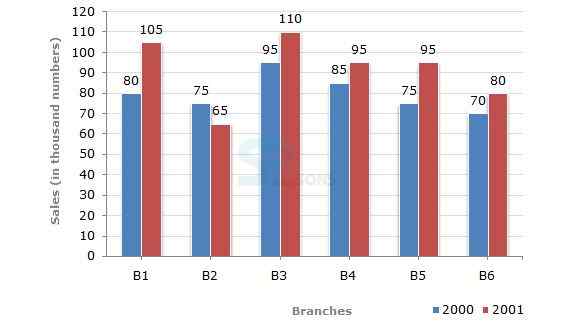
The bar graph given below shows the sales of books (in thousand number) from six branches of a publishing company during two consecutive years 2000 and 2001.
Sales of Books (in thousand numbers) from Six Branches - B1, B2, B3, B4, B5 and B6 of a publishing Company in 2000 and 2001.
1. What is the ratio of the total sales of branch B2 for both years to the total sales of branch B4 for both years?
-
(A) 2:3
(B) 3:5
(C) 4:5
(D) 7:9