Description
Description
Java String Format, The Java string format() method is utilized to return the formatted string, if developer does not declare the locale in String.format() then Locale.getDefault() method will be called defaultly. Generally in Java printf() method is used to format the String. Following are the two methods of Java String Format method.
[java]public static String format(String format, Object... args) [/java]
[java]public static String format(Locale locale, String format, Object... args) [/java]
In Java String Format, the above two methods may throw following two exceptions.
- The locale specifies the locale to be applied on the format() method.
- The args arguments for the format string, it may be zero.
- The format parameter represents the format of the string.
- IllegalFormatException->If the format String contains any illegal syntax or code then it will be thrown.
- NullPointerException-> If the format is null then it will be thrown.
 Example
Example
Following is an example which describes how to format a particular String.
StringFormat.java
[java]package Splesson;
public class StringFormat{
public static void main(String args[]){
String name="SPLESSON";
String sf1=String.format("Name is %s",name);
System.out.println(sf1);
double piVal = Math.PI;
/* returns a formatted string using the specified format
string, and arguments */
System.out.format("%f\n", piVal);
}}
[/java]
Where developer used String.format() method to print the name.
[java]String sf1=String.format("Name is %s",name); [/java]
Output
When compile code result will be as follows.
[java]Name is SPLESSON
3.141593
[/java]
 Description
Description
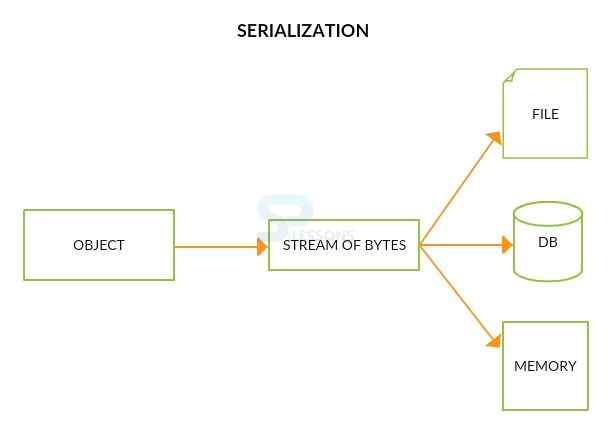
Java Serialization, serialization is a process of changing the present state of an object in the form of byte streams. After doing serialization process one can read an object from the file, deserialization is used to recreate the exist state of an object. Here one interesting point is that total process is JVM independent. To serialize or deserialize an object, a developer needs to use two classes as follows, these classes consist the complete methods of serialization and deserialization.
The ObjectOutputStream class will have write methods to serializes an object and sends it to the output stream, ObjectInputStream class also contains the method to deserialize an object as follows.
[java]public final void writeObject(Object x) throws IOException[/java]
[java]public final Object readObject() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException[/java]
 Description
Description
Java Serialization, Following is an example to understand the concept of serialization, here first developer is going to create one class with the name Employee as follows.
Employee.java
[java]package serialization;
public class Employee implements java.io.Serializable
{
public String name;
public String address;
public transient int SSN;
public int number;
public void mailCheck()
{
System.out.println("Hello Splesson " + name + " " + address);
}
}[/java]
While working with serialization then the class should implement java.io.Serializable interface. In the following example developer is going to assign the name, address.
SerializeDemo.java
[java]package serialization;
import java.io.*;
public class SerializeDemo
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Employee e = new Employee();
e.name = "SPLESSONS";
e.address = "Texas, US";
e.SSN = 123456;
e.number = 111;
try
{
FileOutputStream fileOut =
new FileOutputStream("E:/SAI/employee.ser");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOut);
out.writeObject(e);
out.close();
fileOut.close();
System.out.printf("Serialized data is saved in given folder");
}catch(IOException i)
{
i.printStackTrace();
}
}
}[/java]
As earlier discussed ObjectOutputStream is used to serialize an object, FileOutputStream is going to write the data to a file.
Output
When compile the code following is the result will be generated.
[java]Serialized data is saved in given folder[/java]
Now check the data in the folder, it will be as follows.
[java]¬í sr serialization.Employee™…µ\—c I numberL addresst Ljava/lang/String;L nameq ~ xp ot Texas, USt SPLESSONS[/java]
 Description
Description
In Java Serialization -> deserialization is the process of rebuilding the current state of an object. Based on the above example now the following code is going to deserialize an object.
DeserializeDemo.java
[java]package serialization;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class DeserializeDemo
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
Employee e = null;
try
{
FileInputStream fileIn = new FileInputStream("E:/SAI/employee.ser");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(fileIn);
e = (Employee) in.readObject();
in.close();
fileIn.close();
}catch(IOException i)
{
i.printStackTrace();
return;
}catch(ClassNotFoundException c)
{
System.out.println("Employee class not found");
c.printStackTrace();
return;
}
System.out.println("Deserialized Employee, Object state is normal now");
System.out.println("Name: " + e.name);
System.out.println("Address: " + e.address);
System.out.println("SSN: " + e.SSN);
System.out.println("Number: " + e.number);
}
}
[/java]
As discussed earlier ObjectInputStream is used to deserialized an object. FileInputStream is used to read the stream of characters.
Output
When compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]Deserialized Employee, Object state is normal now
Name: SPLESSONS
Address: Texas, US
SSN: 0
Number: 111
[/java]
The following is an example to count the number of words in a string.
[java]
package com;
import java.util.Scanner;
class CountTheWords
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Enter the string");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s=sc.nextLine();
String[] words = s.trim().split(" ");
System.out.println("Number of words in the string = "+words.length);
}
}
[/java]
The trim() method in java string checks this unicode value before and after the string, if it exists then removes the spaces and returns the omitted string.
Output: The following is the result will be displayed.
[java]
Enter the string
welcome to splessons
Number of words in the string = 3
[/java]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The println() is used to print a new line.
- The printf()is used to format the string.
- The split() method splits this string against given regular expression