Introduction
Introduction
 Description
Description
The “class” type is used to define the concrete methods of the application and can also define abstract method which is known as abstract class. Following is the syntax.
[java]class ClassName
{
concreateMethods();
}[/java]
The following is an example.
[java]Class Splessons{
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Stop thinking Start coding");
}
}[/java]
In the above example, Splessons is the name of the class and void is the return type and println is used to print the statement.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]Stop thinking Start coding[/java]
 Description
Description
The “interface” type is used to define only the abstract method,it can’t be used to develop concrete methods. Following is the syntax.
[java]interface InterfaceName
{
abstract methods();
}[/java]
The following is an example for the interface.
[java]package com.splessons;
interface printable{
void print();
}
class Sample implements printable{
public void print(){System.out.println("Welcome To Splessons");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Sample obj = new Sample();
obj.print();
}
} [/java]
In the above example, Printable interface has only one method, its implementation is provided in the Sample class.
Output: Now compile the code result will be as follows.
[java]Welcome To Splessons[/java]
 Description
Description
“Enum” type is used to declare the constant values. Following is the syntax.
[java]enum EnumName
{
Constant data;
}[/java]
Enum is sort safe user can not assign whatever else other than predefined Enum constants to an Enum variable. It is a compiler blunder to allot something else, unlike the public static final variables used in Enum int pattern and Enum String pattern. For more detailed overview on enum Click Here .
 Description
Description
The “annotation” type is used to define or develop predefined keyword. Following is the syntax.
[java]@interface AnnotationName
{
Userdefined keyword;
}[/java]
The annotation is same as interface with small differences as follows.
- ‘@’ is added just before interface keyword.
- There are no parameters for methods.
- Throws clause is not there for methods.
- The default value can be assigned to a method.
 Description
Description
Programs developed by using Java involves 3 steps.They are:
1)Coding
2)Compilation
3)Execution
 Description
Description
 More Info
More Info
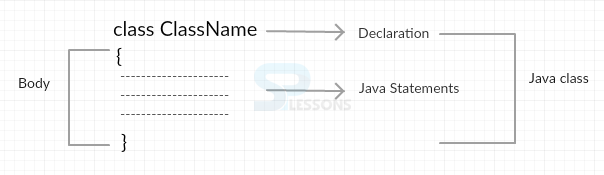
The above structure consists of 2 main sections
- Class Declaration, done by using a keyword “class”.
- Class Definition, enclosed between flower braces { }.
 Description
Description
Compilation is a process of translating a Java file into a class file (. class). This translation is done by the Java compiler. The compiler reads each gave statements at a time and translates Java statements into byte code.
• Bytecode is saved in a file with the extension ".class".The filename of the .class is same as class name.
• The file with .class extension is known as class file. Compiler by default stores the class file in the location where the java file is saved.Following is the syntax.
[java]javac filename.java[/java]
Note
Before starting compilation the working dir should be set to the folder where the java file is saved. Description
Description
The process of running Java class file is known as execution. JVM of Java software is capable of running the class file and giving the output based on the class file.
 Syntax
Syntax
java classname  More Info
More Info
JVM executes each statement sequentially because it is an interpreter. The JVM can start the execution of a class file, if the class file contains the byte code of the main method otherwise the JVM throws error.
Note
JAVA program can also be written without main method. The program can be compiled, but not executed, since to execute Java program JVM needs main method. Description
Description
A Java statement is built with the following programming elements.
Keywords are predefined reserved words and all keywords should be in lower case.
Eg: class,void,abstract,public etc
Identifiers are the names provided by the programmer to identify any methods or variables.All Identifiers should start with an alphabetic character,or an underscore( _ ) after that you can use alphanumeric.
Eg: classname,variable name,method name. For example, int empID;
Litterals are the values used in program.
Numeric Literals: 12, 12.34
String Literals: "SPLessons"
Boolean Literals: true/false
For example, int empID=108;
 Description
Description
Whenever a Java program is compiled, the compiler generates a class file, only if the program doesn’t violate the syntax and the rules of the compiler. Then the compiler throws an error without generating .class file. Errors occurring at the compilation time is known as compile time error. Any error occurring during execution is known as runtime error. It generally occurs because of logical or flow mistakes.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Class can be defined as a box, inside of this developer can write methods and functions.
- The annotation will consist of some meta data that utilized to reduce the code.