Introduction
Introduction
IBPS RRB Officers Scale II Single Level Exam has the different patterns for General Banking Officer position and Specialist Cadre position respectively. An additional "Professional Knowledge" section is added in the Specialist Cadre Single Level exam. Below provided are the details of IBPS RRB Officers Scale II Single Level Exam for each specific position.
 Pattern
Pattern
1. IBPS RRB Officers Scale II Single Level Exam - General Banking Officer
| S.No. | (Objective) Test Name | Medium of Exam | Questions | Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reasoning Ability | Hindi/English | 40 | 50 | 2 hours |
| 2 | Quantitative Aptitude & Data Interpretation | Hindi/English | 40 | 50 | |
| 3 | Financial Awareness | Hindi/English | 40 | 40 | |
| 4 a* | English Language | English | 40 | 40 | |
| 4 b* | Hindi Language(हिंदी) | Hindi | 40 | 40 | |
| 5 | Computer Knowledge | Hindi/English | 40 | 20 | |
| Total | 200 | 200 |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
| Topic | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Syllogism | 0 - 5 |
| Input Output | 0 - 5 |
| Alphanumeric Series | 0 - 5 |
| Ranking/Direction/Alphabet Test | 0 - 5 |
| Seating Arrangement | 0 - 10 |
| Logical Reasoning | 5 - 10 |
| Puzzle | 5 - 7 |
| Coding Decoding | 0 - 5 |
| Blood Relations | 0 - 5 |
| Data Sufficiency | 0 - 5 |
| Inequalities | 0 - 5 |
- A. E is an immediate neighbour of the delegate of India
B. E is the delegate of Maldives
C. The delegate of India is an immediate neighbour of F
D. The delegate of Bhutan sits between F and delegate of Nepal
E. Shopkeeper sits second to the right of the teacher
-
A. India
B. Pakistan
C. Sri Lanka
D. Afghanistan
E. Bhutan
-
A. Immediately to the left
B. Third to the left
C. Second to the right
D. Fourth to the left
E. Second to the left
-
A. H
B. Delegate of Pakistan
C. Delegate of Nepal
D. Cannot be determined
E. F
-
A. Immediately to the left
B. Third to the left
C. Second to the right
D. Fourth to the left
E. None of these
-
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only III
D. Either II or III
E. None of these
-
A. R is the brother of P
B. K is the husband of S
C. Q is the wife of K
D. R is the sister of S
E. None of these
| Topic | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Data Interpretation | 0 - 15 |
| Permutation, Combination & Probability | 0 - 5 |
| Series & Sequence | 0 - 5 |
| Simplification | 0 - 5 |
| Ratio & Proportion, Percentage & Averages | 0 - 3 |
| Number Systems | 0 - 3 |
| Profit & Loss | 0 - 2 |
| Work & Time | 0 - 2 |
| Time & Distance | 0 - 2 |
| Simple Interest & Compound Interest & Surds & Indices | 1 - 2 |
| Sequence & Series | 1 - 2 |
| Mixtures & Alligations | 1 - 2 |
-
A. 344
B. 366
C. 354
D. 356
E. None of these
-
A. 323
B. 326
C. 324
D. 313
E. None of these
-
A. 37
B. 59
C. 62
D. 57
E. None of these
-
A. 436
B. 456
C. 454
D. 434
E. None of these
-
A. 1364
B. 1386
C. 1384
D. 1376
E. None of these
-
A. 1996
B. 1997
C. 1998
D. 1999
E. None of these
-
A. 559
B. 509
C. 584
D. 534
D. None of these
-
A. 1.45
B. 1.48
C. 1.6
D. 1.42
E. None of these
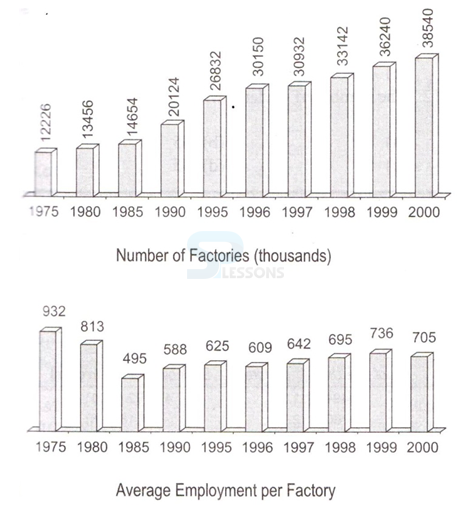
-
A. 1980-85
B. 1985-90
C. 1990-95
D. 1995-00
E. None of these
-
A. Two
B. Three
C. Four
D. Can't be determined
E. None of these
| Topics |
|---|
| Questions are asked from following General Awareness Syllabus Topics |
| Important Days/dates |
| Full forms/Abbr. |
| Current Bank Rates |
| Current Affairs, Countries Capital & Currency |
| Census |
| Banking Awareness – Indian Financial System |
| History of Indian Banking Industry – Structure of Indian Banking |
| History/Functions/roles of Regulatory Bodies like – RBI, SEBI, IRDA, PFRDA, FSDC, FMC etc |
| Monetary & Credit Policies |
| Budget Basics and Current Union Budget |
| International Organisations/ Financial Institutions |
| Credit Rating Agencies, Financial Inclusions, Teaser Rates, GAAR, Priority Sector Lending etc. |
| Capital Market & Money Market |
| Government Schemes – Bharat Nirman, Swavlamban, Swabhiman etc. |
| Other important concepts like – BASEL, Micro Finance, Base Rate, Negotiable Instruments |
-
A. Corporation Tax
B. Income Tax
C. Wealth Tax
D. Service Tax
E. None of the above
-
A. UNCTAD
B. UNICEF
C. WHO
D. World Bank
E. None of the above
-
A. Channel of Rupee Exchange
B. Customer Online Realtime Exchange
C. Centralized Online Rupee Exchange
D. Centralized Online Realtime Exchange
E. Customer Online Rupee Exchange.
-
A. Money funds
B. Share
C. Repurchase agreement
D. Commercial Paper
E. None of the above
-
A. 1 July 1949
B. 26 January 1951
C. 1 April 1935
D. 1 July 1955
E. 1 January 1949
| Topic | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Reading Comprehension | 0 - 10 |
| Cloze Test | 0 - 10 |
| Fill in the blanks | 0 - 5 |
| Paragraph Complete/ Sentence Correction | 0 - 5 |
| Para jumbles | 0 - 5 |
| Miscellaneous | 0 - 5 |
| Synonyms / Antonyms | 1 - 3 |
| Multiple Meaning / Error Spotting | 0 - 5 |
-
A. People from rural areas have a high perceived value of banking services.
B. Cost is not a valid criterion for technological pack selection for financial-inclusion initiatives.
C. The inclusion segment is a singular impoverished_ undifferentiated mass.
D. The branch timings of banks generally do not coincide with the off-work hours of the labor class in urban markets
E. All the given statements are true
-
A. Only (b)
B. Only (c)
C. All (a), (b) & (c)
D. Only (a)
E. Both (b) and (c)
-
A. Banks always prefer the cheapest package (to cut cost) while making a choice of technology to be used.
B. The Business Correspondent Agents are highly demotivated to pursue their activity as a full-time job.
C. The investments made by banks and their delivery partners are not yielding equal amounts of returns.
D. Banks do not have an adequate number of delivery partners required to tap the unbanked market.
E. Banks do not have adequate manpower to explore the diversity of the unbanked market and thereby identify the right target customers for various programs.
-
A. Both a & b
B. All a, b, & c
C. only C
D. Only A
E. Only B
-
A. Only (a)
B. Only (c)
C. Only (b)
D. All (a), (b) and (c)
E. Both (a) and (c)
-
A. Impoverished
B. Handful
C. Acknowledged
D. Plenty
E. Solitude
-
A. Quintessential
B. Popular
C. Omnipresent
D. Simplified
E. Abnormal
-
A. Emaciated
B. Pertinent
C. Cornered
D. Rejected
E. Active
-
A. a
B. b
C. d
D. c
E. f
-
A. e
B. b
C. d
D. c
E. a
-
A. c
B. a
C. b
D. e
E. d
| Topics |
|---|
| Shortcut keys |
| Computer Abbreviations |
| Internet (Concept, History, working environment, Application) |
| History of Computers |
| Software & Hardware |
| Database (introduction) |
| Number System |
| Security Tools, Virus, Hacker |
| MS Windows & MS Office |
| Communication (Basic Introduction) |
| Networking (LAN, WAN) |
| Security Tools, Virus, Hacker |
-
A. Bada
B. Safari
C. Symbian
D. MeeGo
E. WebOS
-
A. F2
B. F4
C. F6
D. F9
E. F11
-
A. Telex
B. Memex
C. CompuServe
D. Bell 103 dataset
E. Dataphone
-
A. 1st Generation
B. 2nd Generation
C. 3rd Generation
D. 4th Generation
E. 5th Generation
-
A. UPS
B. API
C. CGI
D. J2EE
E. OLE
 Pattern
Pattern
2. IBPS RRB Officers Scale II Single Level Exam - Specialist Cadre
| S.No. | (Objective) Test Name | Medium of Exam | Questions | Marks | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reasoning Ability | Hindi/English | 40 | 40 | 2 hours 3 minutes |
| 2 | Quantitative Aptitude & Data Interpretation | Hindi/English | 40 | 40 | |
| 3 | Financial Awareness | Hindi/English | 40 | 40 | |
| 4 a* | English Language | English | 40 | 20 | |
| 4 b* | Hindi Language(हिंदी) | Hindi | 40 | 20 | |
| 5 | Computer Knowledge | Hindi/English | 40 | 20 | |
| 6 | Professional Knowledge | Hindi/English | 40 | 40 | |
| Total | 200 | 200 |
 Syllabus
Syllabus
| Topic | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Syllogism | 0 - 5 |
| Input Output | 0 - 5 |
| Alphanumeric Series | 0 - 5 |
| Ranking/Direction/Alphabet Test | 0 - 5 |
| Seating Arrangement | 0 - 10 |
| Logical Reasoning | 5 - 10 |
| Puzzle | 5 - 7 |
| Coding Decoding | 0 - 5 |
| Blood Relations | 0 - 5 |
| Data Sufficiency | 0 - 5 |
| Inequalities | 0 - 5 |
-
A. 5, 3, 4, 1, 2
B. 3, 5, 4, 2, 1
C. 3, 5, 1, 4, 2
D. 5, 3, 1, 2, 4
| Topic | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Data Interpretation | 0 - 15 |
| Permutation, Combination & Probability | 0 - 5 |
| Series & Sequence | 0 - 5 |
| Simplification | 0 - 5 |
| Ratio & Proportion, Percentage & Averages | 0 - 3 |
| Number Systems | 0 - 3 |
| Profit & Loss | 0 - 2 |
| Work & Time | 0 - 2 |
| Time & Distance | 0 - 2 |
| Simple Interest & Compound Interest & Surds & Indices | 1 - 2 |
| Sequence & Series | 1 - 2 |
| Mixtures & Alligations | 1 - 2 |
| Topics |
|---|
| Questions are asked from following General Awareness Syllabus Topics |
| Important Days/dates |
| Full forms/Abbr. |
| Current Bank Rates |
| Current Affairs, Countries Capital & Currency |
| Census |
| Banking Awareness – Indian Financial System |
| History of Indian Banking Industry – Structure of Indian Banking |
| History/Functions/roles of Regulatory Bodies like – RBI, SEBI, IRDA, PFRDA, FSDC, FMC etc |
| Monetary & Credit Policies |
| Budget Basics and Current Union Budget |
| International Organisations/ Financial Institutions |
| Credit Rating Agencies, Financial Inclusions, Teaser Rates, GAAR, Priority Sector Lending etc. |
| Capital Market & Money Market |
| Government Schemes – Bharat Nirman, Swavlamban, Swabhiman etc. |
| Other important concepts like – BASEL, Micro Finance, Base Rate, Negotiable Instruments |
| Topic | Number of Questions |
|---|---|
| Reading Comprehension | 0 - 10 |
| Cloze Test | 0 - 10 |
| Fill in the blanks | 0 - 5 |
| Paragraph Complete/ Sentence Correction | 0 - 5 |
| Para jumbles | 0 - 5 |
| Miscellaneous | 0 - 5 |
| Synonyms / Antonyms | 1 - 3 |
| Multiple Meaning / Error Spotting | 0 - 5 |
| Topics |
|---|
| Shortcut keys |
| Computer Abbreviations |
| Internet (Concept, History, working environment, Application) |
| History of Computers |
| Software & Hardware |
| Database (introduction) |
| Number System |
| Security Tools, Virus, Hacker |
| MS Windows & MS Office |
| Communication (Basic Introduction) |
| Networking (LAN, WAN) |
| Security Tools, Virus, Hacker |
Topics
The section on Proffessional Knowledge will be based on the post you are applying to. There are six different posts (i.e. Information Technology Officer, Chartered Accountant, Law Officer, Treasury Manager, Marketing Officer and Agricultural Officer) under the IBPS RRB Specialist Officer Scale II grade positions. These, alongwith the nature of Professional Knowledge.
Sample Questions
1. To access the services of the operating system, the interface is provided by the:
| Post | Domain of Professional Knowledge |
|---|---|
| Information Technology Officer | Software and Computer Knowledge |
| Chartered Accountant | Accountancy & Finance |
| Law Officer | Law (especially in relation to Financial Institutions) |
| Treasury Manager | Accountancy & Finance |
| Marketing Officer | Marketing Management |
| Agricultural Officer | Agricultural Knowledge |
-
A. system calls
B. API
C. library
D. assembly instructions
E. none of the above
-
A. kernel is the program that constitutes the central core of the operating system
B. kernel is the first part of the operating system to load into memory during booting
C. kernel is made of various modules which can not be loaded in running operating system
D. kernel remains in the memory during the entire computer session
E. all are correct
-
A. time division multiplexing
B. space division multiplexing
C. both (a) and (b)
D. none of the mentioned
E. code division multiplexing
-
A. address space and global variables
B. open files
C. pending alarms, signals and signal handlers
D. all of the mentioned
E. none of the above
-
A. when process is scheduled to run after some execution
B. when process is unable to run until some task, has been completed
C. when process is using the CPU
D. none of the mentioned
E. all of the above