Introduction
Introduction
BITSAT 2020 – Entrance Examination, conducted in online Mode, has: a duration of 3 Hours and consists of 4 parts, namely – Physics, Chemistry, English Proficiency & Logical Reasoning and Mathematics/ Biology. The 4 sections are not separately timed and there is no break in between the sections. There is a Negative marking in BITSAT 2020 exam and 1 mark is deducted for each wrong answer. The below sections gives the detailed information about BITSAT Physics part.
 Pattern
Pattern
| Parts | Subject | No of Questions | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part I | Physics | 40 | 3 hours (Without break) |
| Part II | Chemistry | 40 | |
| Part III | (a) English Proficiency and | 15 | |
| (b) Logical Reasoing | 10 | ||
| Part IV | Mathematics or Bilogy (For B.Pharm candidates) | 45 | |
| Total | 150 | ||
Note:
There is no time limit for individual parts of the test. The candidate can go back and change any of his/her answers among the 150 questions.
If a candidate answers all the 150 questions (without skipping any question), the candidate will have an option of attempting 12 (twelve) extra questions, if there is still time left.
These extra questions will be from Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics/ Biology only; four questions from each part. Further, once the candidate has opted for extra questions, he/ she cannot go back for correction of any of the earlier answered 150 questions.
The BITSAT Chemistry section, has 40 objective questions. Below mentioned are the different categories of expected questions in the BITSAT Chemistry Section.  Syllabus
Syllabus
BITSAT 2020 Exam Syllabus
Note:
Each correct answer fetches 3 marks, while each incorrect answer has a penalty of 1 mark (-1mark). No marks are awarded for questions not attempted. While the candidate can skip a question, the computer will not allow the candidate to choose more than one option as correct answer. There will be 150 questions in all.
 Samples
Samples
1. If a gas expands at constant temperature, it indicates that:
- A. Number of the molecules of gas increases
B. Kinetic energy of molecules decreases
C. Pressure of the gas increases
D. Kinetic energy of molecules remains the same
- A. 0.4 atm
B. 0.3 atm
C. 0.2 atm
D. 0.1 atm
- A. increased by 10%
B. increased by 1%
C. decreased by 10%
D. decreased by 1%
- A. 0.071 g
B. 0.0355 g
C. 0.02 mole
D. 6.023 × [latex]{10}^{21}[/latex] molecules
- A. kinetic energy of [latex]{O}_{2}[/latex] > kinetic energy of [latex]{SO}_{2}[/latex]
B. kinetic energy of [latex]{O}_{2}[/latex] < kinetic energy of [latex]{SO}_{2}[/latex]
C. kinetic energy of both are equal.
D. None of these
1. A beryllium atom has 4 protons, 5 neutrons, and 4 electrons. What is the mass number of this atom?
- A. 4
B. 5
C. 8
D. 9
- A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
- A. atomic number
B. atomic mass
C. total number of electrons
D. number of electrons in the outer energy level
- A. +1
B. +2
C. +3
D. +4
- A. s
B. p
C. d
D. f
1. In allene [latex]{C}_{3}[/latex][latex]{H}_{4}[/latex], the type(s) of hybridisation of the carbon atoms is (are)
- A. sp and [latex]{sp}_{3}[/latex]
B. sp and [latex]{sp}_{2}[/latex]
C. Only [latex]{sp}_{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]{sp}_{2}[/latex] and [latex]{sp}_{3}[/latex]
- A. square planar geometry
B. Tetrahedral geometry
C. Trigonal bipyramidal geometry
D. Octahedral geometry
- A. [latex]{N}_{2}[/latex]
B. NO
C. CO
D. [latex]{O}_{3}[/latex]
- A. [latex]{MgCL}_{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]{FeCL}_{2}[/latex]
C. [latex]{SnCL}_{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]{AlCL}_{3}[/latex]
- A. Two sigma, two pi
B. One sigma, two pi
C. One sigma, one pi
D. Two sigma, one pi
1. The condition for a reaction to occur spontaneously is
- A. ΔH must be negative
B. ΔS must be negative
C. (ΔH-TΔS) must be negative
D. (ΔH+TΔS) must be negative
- A. [latex]{Br}_{2}[/latex](g)
B. [latex]{Cl}_{2}[/latex](g)
C. [latex]{H}_{2}[/latex]O(g)
D. [latex]{Ch}_{4}[/latex](g)
- A. Work is a state function
B. Temperature is a state function
C. Change in the state is completely defined when the initial and final states are specified
D. Work appears at the boundary of the system
- A. Surroundings and system change into each other
B. There is no boundary between system and surroundings
C. The surroundings are always in equilibrium with the system
D. The system changes into the surroundings spontaneously
- A. work-producing machine like an engine or turbine
B. work-absorbing machine like a pump or a compressor
C. both of the mentioned
D. none of the mentioned
1. The formation of ammonia from [latex]{N}_{2}[/latex](g) and [latex]{H}_{2}[/latex](g) is a reversible reaction
[latex]{N}_{2}[/latex](g) + [latex]{3H}_{2}[/latex] ⇌ [latex]{2NH}_{3}[/latex](g) + Heat
What is the effect of increase of temperature on this equilibrium reaction
- A. equilibrium is unaltered
B. formation of ammonia is favoured
C. equilibrium is shifted to the left
D. reaction rate does not change
- A. increase in pressure
B. decrease in pressure
C. increase in volume
D. none of these
- A. for a system at equilibrium, Q is always less than the equilibrium constant
B. equilibrium can be attained from either side of the reaction
C. presence of catalyst affects both the forward reaction and reverse reaction to the same extent
D. Equilibrium constant varied with temperature
- A. Equilibrium is possible only in a closed system at a given temperature
B. The opposing processes occur at the same rate and there is a dynamic but stable condition
C. All the physical processes stop at equilibrium
D. All measurable properties of the system remains constant
- i. Liquid ⇌ Vapour
ii. Solid ⇌ Liquid
iii. Solid ⇌ Vapour
iv. Solute (s) ⇌ Solute (Solution)
- 1. melting point
2. Saturated solution
3. Boiling point
4. Sublimation point
5. Unsaturated solution
- A. i:1, ii:2, iii:3, iv:4
B. i:3, ii:1, iii:4, iv:2
C. i:2, ii:1, iii:3, iv:4
D. i:3, ii:2, iii:4, iv:5
1. Process in which substance gains electrons is called
- A. oxidation
B. hydrogenation
C. sublimation
D. reduction
- A. NaOH
B. NaCl
C. NaO
D. [latex]{NH}_{3}[/latex]
- A. Alloying
B. Tinning
C. Galvanizing
D. all of above
- A. sulphide ore
B. stannous sulphate
C. hydrogen sulphate
D. sodium chloride
- A. chemical reaction
B. physical reaction
C. no reaction
D. biochemical reaction
1. In a zero-order reaction for every 10° rise of temperature, the rate is doubled. If the temperature is increased from 10°C to 100°C, the rate of the reaction will become
- A. 64 times
B. 128 times
C. 256 times
D. 512 times
- A. 0.1
B. 0.01
C. 0.001
D. 0.02
- A. Molecularity and order of reaction both are 2
B. Molecularity is 2 but order of reaction is 1
C. Molecularity is 1 but order of reaction is 2
D. Moecularity is 1 and order of reaction is also 1
- A. 5 years
B. 2 years
C. 3 years
D. 10 years
-
A. Rate of reaction
B. Rate constant
C. Half-life
- A. A only
B. C only
C. A and B only
D. B and C only
1. What is the colloidal mixture of solid with solid called?
- A. Solid sol
B. Liquid sol
C. Sol
D. Gel
- A. Sol
B. Gel
C. Foam
D. Form
- A. Foam
B. Form
C. Emulsification
D. Solid sol
- A. Aerosol
B. Gel
C. Sol
D. Emulsion
- A. Liquid in solid
B. Solid in liquid
C. Gas in gas
D. Gas in solid
1. Hydrogen has 3 isotopes. Which of the following is NOT one of them?
- A. Proton
B. Deuterium
C. Tritium
D. Protium
- A. s block
B. d block
C. p block
D. f block
- A. Urea > Ammonium chloride > Ammonium nitrate > Ammonium nitrite
B. Urea > Ammonium nitrate > Ammonium nitrite > Ammonium chloride
C. Urea > Ammonium nitrite > Ammonium nitrate > Ammonium chloride
D. Urea > Ammonium nitrite > Ammonium chloride > Ammonium nitrate
- A. Weak oxidising agent
B. Weak reducing agent
C. Strong oxidising agent
D. Strong reducing agent
- A. Hydrogen gas is more expensive.
B. Hydrogen gas is highly flammable.
C. Hydrogen gas is toxic.
D. Hydrogen gas is less available.
1. Which one of the following exists in the oxidation state other than +3?
- A. B
B. Al
C. Ce
D. Ga
- A. [latex]{Sc}^{3+}[/latex]
B. [latex]{Ni}^{2+}[/latex]
C. [latex]{ti}^{4+}[/latex]
D. [latex]{Zn}^{2+}[/latex]
- A. [latex]{C}_{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]{N}_{2}[/latex]
C. [latex]{O}_{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]{S}_{2}[/latex]
- A. Zero to – 1 and zero to +3
B. Zero to + 1 and zero to –3
C. Zero to + 1 and zero to –5
D. Zero to – 1 and zero to +5
- A. Hypophosphorous acid
B. Phosphorous acid
C. Pyrophosphoric acid
D. Orthophosphoric acid
1. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds with element
- A. Hydrogen
B. Oxygen
C. Carbon
D. Both hydrogen and carbon
- A. Aromatic
B. Alkanes
C. Alkynes
D. Alkenes
- A. Methanol
B. Methane
C. Formaldehyde
D. Formic acid
- A. Potassium formate
B. Potassium succinate
C. Potassium acetate
D. Potassium fumarate
- A. Friedel craft reaction
B. Wurtz reaction
C. Wurtz fitting reaction
D. Debey Huckel reaction
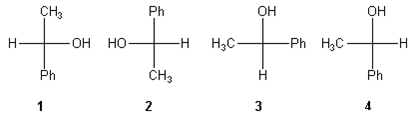
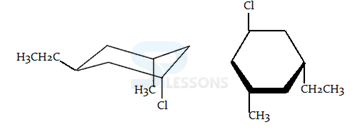
1. Compounds which have different arrangements of atoms in space while having same atoms bonded to each other are said to have
- A. position isomerism
B. functional group isomerism
C. chain isomerism
D. stereoisomerism
- A. heat
B. temperature
C. polarized light
D. pressure
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. Geometrical isomers
B. Enantiomers
C. Diastereomers
D. Identical
- A. This compound is optically active because it has stereogenic centers that create cis-trans isomers
B. This compound is optically active because the compound contains a center, plane, or axis of chirality
C. This compound is not optically active since there are no stereogenic centers
D. This compound is not optically active because of its symmetry
1. Organic compounds are broadly classified as
- A. Open chain compounds and acyclic compounds
B. Open chain compounds and linear chain compounds
C. Cyclic compounds and alicyclic compounds
D. alicyclic compounds and acyclic compounds
- A. Acyclic compounds
B. Alicyclic compounds
C. Ring compounds
D. Closed chain compounds
- A. Alcohol
B. Aldehyde
C. Halide
D. Benzene
- A. Ester
B. Aldehyde
C. Ether
D. Ketone
- A. Alicyclic compounds
B. Heterogeneous compounds
C. Branched chain compounds
D. Aromatic compounds
1. What is called for the pollution that can be traced directly to industrial activity?
- A. Soil pollution
B. Water pollution
C. Air pollution
D. Industrial pollution
- A. Dumping of various waste products from industries
B. Taking water bodies places to built industries
C. Industries which uses all the water from the water bodies and cause scarcity of water
D. Building of purification unit in the industries
- A. CO
B. [latex]{O}_{3}[/latex]
C. [latex]{CH}_{4}[/latex]
D. [latex]{H}_{2}[/latex]O Vapour
- A. Its main components are produced by the action of sunlight on
emissions of automobiles and factories.
B. Produced in cold and humid climate.
C. It contains compounds of reducing nature.
D. It contains smoke, fog and sulphur dioxide.
- A. Thiamine
B. Riboflavin
C. Folic acid
D. Ascorbic acid
1. Electronic thermometers
- A. are mercury in glass thermometer
B. alcohol in glass thermometer
C. are used to reduce the risk of mercury poisoning if broken
D. are greatly replaced by alcohol in glass thermometer
- A. ccm
B. cdm
C. liters
D. tones
- A. 0.01g
B. 0.001 g
C. 0.1g
D. Both A and B
- A. measuring cylinder
B. beaker
C. volumetric flask
D. burette
- A. data punching devices
B. devices used to draw graph of temperature against time
C. are a form of stop watch
D. have replaced gas syringes