Description
Description
AngularJS MVC explains about angular Model, View & Controller and the relation between these three angular components.
MVC is a software design pattern that is primarily used to develop web applications, which divides the components of an application to separate the responsibilities. Using MVC pattern, the various components will have a relationship defined by their interactions. Model has the data and logic and is used to represent the current state of the application. View is used to display the data and Controller is used to control the relation between Models and Views. Below is the detailed description of MVC.
 Description
Description
AngularJS framework works on MVC design pattern.
- Model: AngularJS Model is used for handling the data from server to controller and vice versa.
- View: View is a HTML page.
- Controller: Controller can control the whole application and is responsible for interaction between the view and model.
 Architecture
Architecture
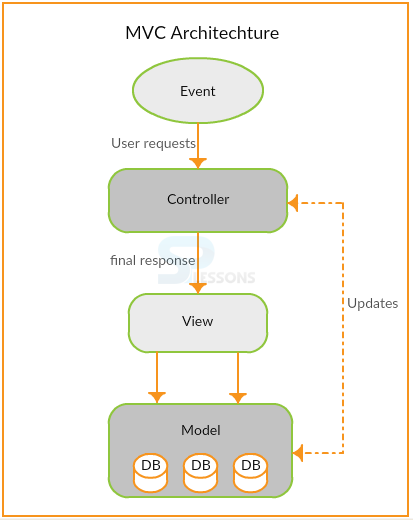
MVC can disengage the application logic from the client interface layer and supports partition of concerns. The controller gets all application requests after which it works with the model to set up any information required by the view. The information given by the controller is then used by the view to create a last response. The architecture of MVC can be graphically represented as follows:
 Description
Description
Model is responsible for the current state of application data. It will receive requests from view and follow the controller instructions. Model sends request to the server to save data in database and retrieves the data from database using server side scripting. Model can respond to view request.
 Description
Description
View is responsible for formatting the data that is prepared by the model and displays the output to the user.
In AngularJS, it is created with HTML. Most of the applications move past the single view model; in such case the HTML components that create the view will be stored in individual files. As AngularJS is famous for Single Page Application, only some part of the page represents the current view. In this case, body contents represent the view while the HTML and HEAD elements form the container for the individual views.
 Description
Description
Controller will control the entire application. It receives requests from View. Controller will combine with the model to prepare the data and respond to the view request.
 Example
Example
Step 1: Creating first controller
[javascript]
function SPController($scope) {
//code here..
}
[/javascript]
Created first controller with a name
SPController. Previously, controller is mentioned as a JavaScript constructor function. A single argument with $ sign known as scope is passed. Every controller has its particular scope. Scope binds both controller and view.
Step 2: Creating Module
Model is a JavaScript object. It lives within controller. To make model accessible in the view, a $scope object is needed.
[javascript]
myApp.controller('SPController', function($scope) {
$scope.users = [
{name:'Smith',age:23},
{name:'Mike',age:24},
{name:'John',age:26},
];
});
[/javascript]
In the above code, a model named ‘users’ is created, which is an array of objects.
Step 3: Putting it together into the view
Now, controller is set up and models are defined. To display data to the user, a view has to be created.
[html]
<h1>AngularJS MVC Architecture</h1>
<div ng-controller="SPController">
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="user in users">
{{ (user.name) + ', ' + user.age }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
[/html]
index.html
[html]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script data-require="angular.js@1.3.14" data-semver="1.3.14" src="https://code.angularjs.org/1.3.14/angular.js"></script>
<script src="http://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.4.1/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="App.js"></script>
<script src="Controller.js"></script>
</head>
<body ng-app="spApp">
<h1>AngularJS MVC Architecture</h1>
<div ng-controller="SPController">
<ul>
<li ng-repeat="user in users">
{{ (user.name) + ', ' + user.age }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
[/html]
App.js
[html]
var myApp = angular.module("spApp", []);
[/html]
Output:
 Key Points
Key Points
- MVC is a software design pattern with model, view and controller.
- Model is responsible for the current state of application data, View displays the output and Controller handles the interaction between View and Model.