Description
Description
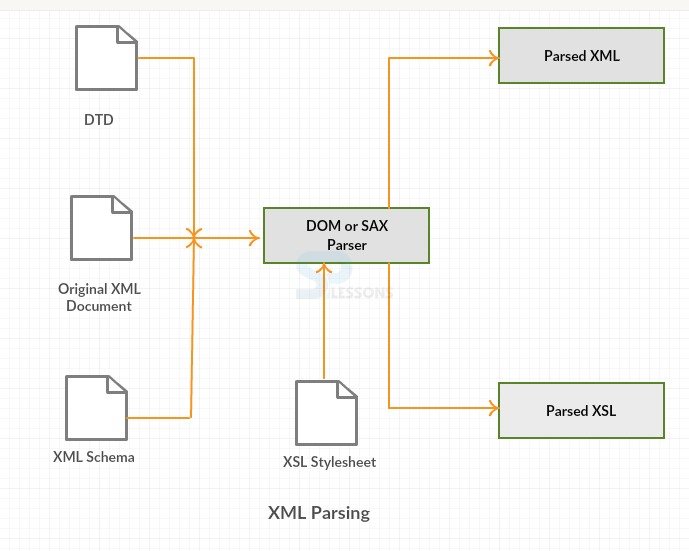
XML Parser: Parser is a program part which represents the physical form of a data and converts it into storage form for the program. The one which reads XML Data in a XML file is referred to as XML Parser. Until unless the code is copied as a unit block blindly, every XML program should call the XML Parser.
The world working in XML with Java is not alphabet soup of acronyms such as DOM, JDOM, JAXP and so on. One of the frequently used JavaXML Parsers is
JAXP whcih stands for Java API for XML Processing that describes the standards for the XML API's that are included in Java SE like:
DOM : Document Object Model defines a set of interfaces to the parsed version of an XML document. The parser reads in the entire document and builds an in-memory tree.
DOM is platform browser and language neutral. It does not assume anything about what platform is running on what browser turning on and there are several language implementations of the DOM that can be used to work with. One of the most common languages that people work with the DOM is JavaScript.
JDOM : Java-based Document Object Model parses the XML document same as DOM but in easier manner.
Schemas give the capacity to characterize a component’s sort and much better limitations . DTDs uphold a strict requesting of components; constructions have a more adaptable scope of alternatives. At long last schema’s are composed in XML, while DTDs have their own particular syntax.
SAX : The Simple API for XML defines the events and interfaces used to interact with a SAX-compliant XML parser.
StAX : Streaming API for XML is a pull process where only data is looked and only call methods that are meaningful.
XPATH : XML Path Language defines locations for XML documents which can be used in XSLT style sheets.
JAXB : Java Architecture for XML Binding minimizes access to an XML document from a Java program by presenting the XML document to the program in a Java format.  Description
Description
The XML Document Type Declaration, ordinarily known as DTD (Document Type Definition), DTD is an approach to portraying XML dialect definitely. DTDs check vocabulary and legitimacy of the structure of XML archives against syntactic principles of proper XML dialect. An XML DTD can be either indicated inside the archive, or it can be kept in a different record and after that enjoyed independently. Following is the basic syntax of the DTD.
[xml]
<!DOCTYPE element DTD identifier
[
declaration1
declaration2
declaration3
........
]>
[/xml]
Where The DTD begins with
<!DOCTYPE delimiter. DTD identifier is an identifier for the document type definition, which might be the way to a document on the framework or URL to a record on the web. On the off chance that the DTD is indicating outside way, it is called External Subset. The square brackets [ ] are internal subsets. An element advises the parser to parse the record from the predetermined root element.
 Description
Description
The developer can compose manages inside XML record utilizing declaration. The extent of this DTD inside this report. Usage is archive approved independent from anyone else without outer reference. Following is the syntax.
[xml]<!DOCTYPE root-element [element-declarations]>[/xml]
Where
root-element is nothing but the name of root element. The following is an example.
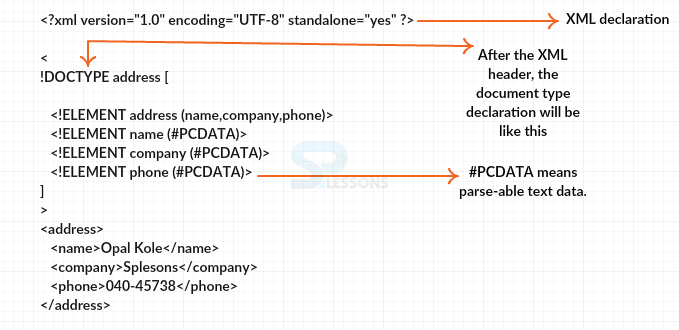
[xml]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes" ?>
<!DOCTYPE address [
<!ELEMENT address (name,company,phone)>
<!ELEMENT name (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT company (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT phone (#PCDATA)>
]>
<address>
<name>Opal Kole</name>
<company>Splesons</company>
<phone>040-45738</phone>
</address>
[/xml]
In the above example, #PCDATA means parse-able text data. Following is the image description of the above code.
Following are the some rules need to be remind.
- The type of the document declaration must show up toward the begin of the report, it is not allowed anyplace else inside the archive.
- Like the DOCTYPE presentation, the component affirmations must begin with an exclamation mark.
- The Name in the report type announcement must match the component type of the root component.
 Description
Description
External DTD is shared between numerous XML reports. Any progressions are redesign in DTD record impact or upgraded go to an all XML reports. External DTD will have two types as follows.
Private DTD distinguish by the SYSTEM keyword. Access for single or gathering of clients. The developer can indicates rules in external DTD document as .dtd type. Later in XML document presentation to connecting this DTD record. Following is the syntax declaration.
[xml]<!DOCTYPE root_element SYSTEM "dtd_file_location">[/xml]
Following is an example.
external_dtd.dtd
[xml]<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no" ?>
<!DOCTYPE address SYSTEM "address.dtd">
<address>
< <name>Opal Kole</name>
<company>Splesons</company>
<phone>040-45738</phone>
</address>[/xml]
address.dtd
[xml]
<!ELEMENT address (name,company,phone)>
<!ELEMENT name (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT company (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT phone (#PCDATA)>
[/xml]
Public DTD distinguishes by the PUBLIC keyword. Get to any clients and XML editors are know the DTD. Some normal DTD Web DTD, XHTML, MathML and so on. Following is the syntax.
[xml]<!DOCTYPE root_element PUBLIC "dtd_name" "dtd_file_location">[/xml]
Following is an example.
[xml]<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
...
</head>
<body>
...
...
</body>
</html>[/xml]
 Key Points
Key Points
- The DTD is used to check the structure of the XML document.
- The scope of internal DTD is with in the document.