Description
Description
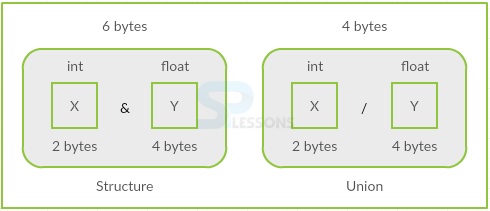
Unions in C are very similar to structures. The keyword used is "union". Union is used mainly to save the memory space and to store the values dynamically. The differences between Unions in C and structure is,
- Structure allocates memory for every member of it separately. Whereas union allocates a single shared storage space for all of its members which will be the size of its biggest data member.
- Manipulations made on one member will not effect the other in structures. As only single member is allocated at a time in unions, manipulations done on one member will reflect on other.
 Syntax
Syntax
union union_name
{
//declarations and initializations of members;
};
 Description
Description
The union variable can be retrieved in the same manner as in the structure. To access the union variable . dot operator is used and to get the address of union variable * is used.
Unions in C are not much used when compared to structures as they does not store all the variables at a time.
[c]union example
{
char c;
int a;
float b;
} ex;
[/c]
[c]
union example
{
char c;
int a;
float b;
} ex;
ex.c;
ex.a;
ex.b;[/c]
 Example
Example
[c]
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
union car
{
int model;
float cost;
char car_name;
};
int main( )
{
union car c;
c.model = 2011;
c.cost = 100000;
c.car_name='i20';
clrscr();
printf("%d\n",c.model);
printf("%f\n",c.cost);
printf("%c\n",c.car_name);
getch();
return 0;
}[/c]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Structure "struct" keyword is replaced with "union" and is used in shareable mode.
- Unions are used to focus on memory as each member within union structure is assigned its own unique storage space.
 Programming
Tips
Programming
Tips
Do not initialize multiple members using union.The compiler gives an error.