Introduction
Introduction
What is meant by Thermal Engineering? Thermal Engineering is controlling heating or cooling processes in an enclosed environment or an open environment using various equipment's. It involves the science of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, heat and mass transfer.
Thermal Engineering Practice Quiz article, is exceedingly important for candidates preparing for RRB Junior Engineer Recruitment, SSC Junior Engineer Recruitment, GATE, UPSC (Civil services exam including IAS) and all Mechanical Engineering Exams in India. In this article, candidates can find different types of questions with solutions related to the Thermal Engineering Practice Quiz topic. The article Thermal Engineering Practice Quiz, will assist the students in understanding the type of questions expected from the topic Thermal Engineering .
 Quiz
Quiz
1. A closed system is one, which
- A. permits the passage of energy and matter across the boundaries
B. does not permit the passage of energy and matter across the boundaries
C. permits the passage of energy across the boundary but does not permit the passage of matter
D. permits the passage of matter across the boundary but does not permit the passage of energy
- A. permits the passage of energy and matter across the boundaries
B. permits the passage of energy only
C. does not permit the passage of energy and matter across it
D. permits the passage of matter only
- A. open system
B. closed system
C. homogeneous system
D. heterogeneous system
- A. the volume, shape and position with respect to an observer are fixed
B. material flow across the boundary
C. both (a) and (b)
D. none of theses
- A. specified mass
B. fixed region in the space
C. closed system
D. none of the above
- A. by unit degree of a substance
B. by unit degree of a unit mass
C. of a unit mass by 10
D. none of the above
- A. varies with temperature
B. varies with pressure
C. is always constant
D. none of the above
- A. temperature only
B. temperature and pressure
C. temperature, pressure and specific heats
D. none of the above
- A. increases
B. decreases
C. first decreases to minimum then increases
D. remains constant
- A. enthalpy
B. entropy
C. internal energy
D. temperature
- A. Total mass
B. Total internal energy
C. Total volume
D. Temperature
- A. density
B. pressure
C. temperature
D. all of these
- A. even
B. thermodynamic cycle
C. thermodynamic property
D. none of these
- A. isolated system
B. open system
C. non-uniform system
D. heterogeneous system
- A. conversion of work into heat
B. conversion of heat into work
C. conservation of work
D. conservation of heat
- A. first kind is possible
B. first kind is impossible
C. second kind is impossible
D. second kind is possible
- A. possible according to first law of thermodynamics
B. impossible according to first law of thermodynamics
C. impossible according to second law of thermodynamics
D. possible according to second law of thermodynamics
- A. specific heat of molecules reduces to zero
B. kinetic energy of molecules reduces to zero
C. volume of gas reduce to zero
D. pressure of gas reduce to zero.
- A. increases
B. remains constant
C. decreases
D. none of the above
- A. same
B. more
C. less
D. none of the above
1. In isothermal expansion, work done by gas depends upon
- A. atomicity of gas only
B. expansion ratio only
C. adiabatic index
D. both (a) and (b)
- A. isothermal
B. isentropic
C. polytropic
D. hyperbolic
- A. isothermal process
B. isentropic process
C. polytropic process
D. adiabatic process
- A. [latex]\frac{{v}_{1}}{{v}_{2}}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{{v}_{2}}{{v}_{1}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{{v}_{1} + {v}_{2}}{{v}_{1}}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{{v}_{1} + {v}_{2}}{{v}_{2} - {v}_{1}}[/latex]
- A. [latex]\frac{{p}_{1}{v}_{1}- {p}_{2}{v}_{2}}{(n - 1)}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{{p}_{2}{v}_{2}- {p}_{1}{v}_{1}} {(n - 1)}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{{p}_{1}{v}_{1}- {p}_{2}{v}_{2}} {n}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{{p}_{2}{v}_{2}- {p}_{1}{v}_{1}} {n}[/latex]
- A. [latex]\frac{log(\frac{{p}_{2}}{{p}_{1}})}{log(\frac{{v}_{1}}{{v}_{2}})}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{log(\frac{{v}_{1}}{{v}_{2}})}{log(\frac{{p}_{1}}{{p}_{2}})}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{log(\frac{{p}_{1}}{{p}_{2}})}{log(\frac{{v}_{1}}{{v}_{2}})}[/latex]
D. None of the above
- A. W = 0
B. E = 0
C. H = 0
D. all of the above
- A. enthalpy remains constant
B. entropy remains constant
C. some heat transfer occurs
D. internal energy remains constant
- A. constant pressure process
B. constant volume process
C. constant temperature process
D. none of
- A. constant pressure process
B. constant volume process
C. constant temperature process
D. none of these
- A. constant pressure process
B. constant volume process
C. constant temperature process
D. none of these
- A. 0
B. 1
C. [latex]\gamma[/latex]
D. infinite
- A. [latex]({\frac{{p}_{1}}{{p}_{2}}})^{\frac{y - 1}{y}}[/latex]
B. [latex]({\frac{{p}_{2}}{{p}_{1}}})^{\frac{y - 1}{y}}[/latex]
C. [latex]({\frac{{V}_{1}}{{V}_{2}}})^{\frac{y - 1}{y}}[/latex]
D. [latex]({\frac{{V}_{2}}{{V}_{1}}})^{\frac{y - 1}{y}}[/latex]
- A. must pass through a continuous series of equlibrioum states
B. leaves no history of the events in surroundings.
C. must pass through the same states on the reversed path as on the forward path.
D. all of these.
- A. reversible adiabatic flow
B. irreversible adiabatic flow
C. friction less fluid flow
D. none of the above.
- A. free expansion of gas
B. expansion of a gas in a cylinder under constant pressure
C. rapid compression of a gas in a cylinder.
D. gradual compression of a gas in a cylinder
- A. [latex]{C}_{p}\triangle T[/latex]
B. [latex]{C}_{v}\triangle T[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{{C}_{p}}{{C}_{v}}\triangle T[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{{C}_{v}}{{C}_{p}}\triangle T[/latex]
- A. 10 K/s
B. 100 K/s
C. 1000 K/s
D. 10000 K/s
- A. 50 cc of water at 25º C are mixed with 150 cc of water at 25º C
B. 500 cc of milk at 15º C are mixed with 100 cc of water at 15º C
C. 5 kg of wet steam at 100º C is mixed with 50 kg of dry and saturated steam at 100º C
D. 10 cc of water at 20º C are mixed with 10 cc of sulphuric acid at 20º C.
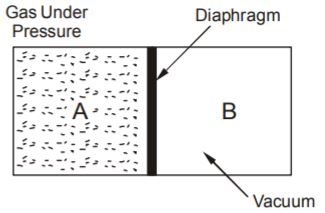
- A. A free expansion is a non-quasi static process
B. The pressure and volume of gas are not related through the equation of states
C. The process is irreversible
D. The energy is transferred to the system.
1. In a thermodynamic system, a process in which volume remains constant is called _____ process.
- A. isobaric
B. isometric
C. adiabatic
D. isotropic
- A. 40 %
B. 85 %
C. 15
D. 35
- A. same thermal energy
B. same entropy
C. same temperature
D. same molecular energy
- A.
B.
C.
D.
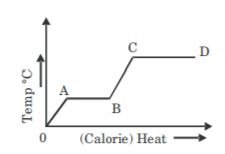
- A. OA
B. AB
C. BC
D. CD
- A. Ice
B. Ammonium chloride
C. Naphthalene
D. Camphor
- A. Stick to the walls of the container
B. Lose their kinetic energy
C. Get accelerated towards the wall
D. Change their momentum due to collision with the wall.
- A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Work
D. Momentum
- A. The pressure of a gas varies directly with temperature at constant volume i.e. P[latex]\alpha[/latex]T.
B. The product of pressure and volume of a given mass of a gas is constant at constant
C. The volume of a gas varies directly with temperature at constant pressure i.e. V[latex]\alpha[/latex]T.
D. The pressure of a gas varies directly with
volume at constant temperature i.e. P[latex]\alpha[/latex]V.
- A. Minimum
B. Zero
C. Average
D. Maximum
- A. 100°
B. -40°
C. 0°
D. 40°
- A. There is no energy or mass transfer across the boundary
B. There is no mass transfer, but energy transfer exists
C. There is no energy transfer, but mass transfer exists
D. Both energy and mass transfer take place across the boundary, but mass transfer is controlled by valves
- A. at a temperature of –273 K
B. under vacuum condition
C. at the earth's centre
D. when molecular momentum of system becomes zero
- A. Two thermodynamic systems are always in thermal equilibrium with each other
B. If two systems are in thermal equilibrium, then the third system will also be in thermal
equilibrium
C. Two systems not in thermal equilibrium with a third system will also not be in thermal
equilibrium with each other
D. When two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system they are in thermal equilibrium with each other
- A. Elevation
B. Pressure
C. Velocity
D. Velocity potential
- A. move away from the shore
B. remain stationary
C. move towards the shore
D. Sink
- A. absolute humidity value to the amount of humidity actually present
B. increase of humidity/absolute humidity
C. amount of humidity actually present to the absolute humidity
D. None of these
- A. Pressure
B. Heat capacity
C. Temperature
D. Specific volume
- A. Conservation of heat
B. Conservation of heat
C. Conservation of heat into work
D. Conservation of work into heat
- A. Kaplan turbine
B. Francis turbine
C. Pelton Wheel turbine
D. Propeller turbine
1. A system and its environment put together constitute
- A. An adiabatic system
B. An isolated system
C. A segregated system
D. A homogeneous system
- A. [latex]\frac{{C}_{p}}{T}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {T}{{C}_{p}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{{C}_{v}}{T}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac {T}{{C}_{v}}[/latex]
- A. Pressure
B. Temperature
C. Heat exchange
D. Work
- A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
B. First law of thermodynamics
C. Second law of thermodynamics
D. Law of entropy
- A. Carnot cycle
B. Otto cycle
C. Diesel cycle
D. Dual cycle
- A. A fixed region in space
B. A specified mass
C. An isolated system
D. A reversible process only
- A. Mass
B. Density
C. Pressure
D. Temperature
- A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remains the same
D. First decreases then increases
- A. Conservation of heat
B. Conservation of momentum
C. Conservation of mass
D. Conservation of energy
- A. Boyle’s law
B. Charle’s law
C. Gay-lussac’s law
D. Avogadro’s law
- A. Energy
B. Temperature
C. Entropy
D. Enthalpy
- A. 600 K
B. 650 K
C. 625 K
D. 700 K
- A. Zero
B. Positive
C. Negative
D. Maximum
- A. A function of temperature only
B. A function of pressure
C. A function of volume
D. Both pressure and volume
- A. Isobaric
B. Isothermal
C. Isentropic
D. Isochoric
- A. flue gases
B. intake air
C. steam
D. feed water
- A. Propeller turbine
B. Francis turbine
C. Kaplan turbine
D. Pelton wheel turbine
- A. du – PdV
B. du + PdV
C. du – VdP
D. du + VdP
- A. First law of thermodynamics
B. Second law of thermodynamics
C. Third law of thermodynamics
D. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
- A. Mass of substance cross the boundary
B. Energy of substance cross the boundary
C. Both mass and energy of substance cross the boundary
D. Both mass and energy substance does not cross the boundary
1. The thermal diffusivity of a substance is given by :
- A. [latex]\frac{K \rho}{C}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {K}{C \rho}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{K C}{\rho}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{C \rho}{K}[/latex]
- A. Heat transfer area
B. Heat transfer coefficient
C. Temperature gradient
D. Mechanical strength of the equipment
- A. Insulated pipes carrying hot water
B. Refrigerator freezer coil
C. Boiler furnaces
D. Condensation of steam in a condenser
- A. Conduction
B. Convection
C. Radiation
D. Conduction and Radiation put together
- A. Lattice vibration
B. Transportation of free electrons
C. Collisions and diffusion
D. No heat conducted
- A. Both bodies must be solids
B. Both bodies must be in contact
C. Temperatures of the two bodies must be different
D. Temperatures of the two bodies must be same
- A. Gray body
B. White body
C. Black body
D. Blue body
- A. Insulated pipe carrying hot water
B. Refrigerator freezer coils
C. Melting of ice
D. Boiler furnaces
- A. Conduction
B. Convection
C. Radiation
D. Combined mode of heat transfer of conduction and convection
- A. W/mK
B. [latex]{W}^{2}[/latex] /mK
C. W/[latex]{m}^{2}k[/latex]
D. W/m
- A. Reflected
B. Refracted
C. Transmitted
D. Absorbed
- A. Irregular surfaces
B. Non-uniform temperature surfaces
C. One dimensional cases only
D. Two dimensional cases only
- A. For a polished body
B. Under thermal equilibrium
C. At one particular temperature
D. At shorter wavelengths
- A. Their atoms collide frequently
B. Their atoms are relatively far apart
C. They contain free electron
D. They have high density
- A. Electromagnetic waves
B. Motion of electrons
C. Mixing motion of the different layers of the gas
D. Elastic impact of molecules
- A. Conduction
B. Convection
C. Radiation
D. Does not flow
- A. One which absorbs total radiant energy
B. Black in colour
C. One which does not reflect the radiant energy
D. One which absorbs all radiant energy at all wavelengths
- A. Conduction
B. Convection
C. Radiation
D. Scattering
- A. Boiling water
B. Steam
C. Solid ice
D. Rain water
- A. Prandtl number
B. Schmidt number
C. Lorentz number
D. Lewis number
1. The effectiveness of a fin will be maximum in an environment with
- A. Free convection
B. Forced convection
C. Radiation
D. Convection and radiation
- A. Convection
B. Conduction
C. Radiation
D. Conduction and Convection
- A. It acts as an insulator
B. It acts as conductor and insulator
C. It acts as a superconductor
D. It acts as afin
- A. Gray body
B. Black body
C. White body
D. Specular body
- A. Lead
B. Copper
C. Water
D. Air
- A. 2
B. 3
C. 4
D. 5
- A. [latex]1 - \frac{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{1} + {Q}_{2}}[/latex]
B.[latex]1 - \frac{{T}_{1}}{{T}_{2}}[/latex]
C. [latex]1 - \frac{{T}_{1}}{{T}_{1} + {T}_{2}}[/latex]
D. [latex]1 - \frac{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}}[/latex]
- A. 10 Watts
B. 100 Watts
C. 500 Watts
D. 1 kW
- A. Zeroth
B. First
C. Second
D. Third
- A. Le Chatelier's Principle
B. Law of Mass Action
C. Vander Waals Principle
D. None of these
- A. Less than zero
B. Greater than zero
C. Equal to zero
D. Any one of these
- A. Rankine
B. Carnot
C. Otto
D. Joule
- A. Mono-atomic Gases
B. Diatomic Gases
C. Ideal Gases
D. Real Gases
- A. [latex]{C}_{v} \triangle T[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac {{C}_{p}}{{C}_{v}} \triangle T[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac {{C}_{v}}{{C}_{p}} \triangle T[/latex]
D. [latex]{C}_{p} \triangle T[/latex]
- A. 54°C
B. 108°C
C. 327°C
D. 600°C
- A. Pressure measurement
B. Temperature measurement
C. Density measurement
D. Viscosity measurement
- A. Ideal process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Isothermal process
D. Isobaric process
- A. h = pv+RT
B. h = u+pT
C. h = u+pv
D. h = u-pv
- A. 0
B. 1
C. Infinite
D. 2
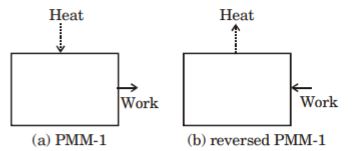
- A. PMM -I
B. PMM -II
C. PMM -III
D. Heat engine
1. The device in which the work is done by the fluid at the expense of its enthalpy is known as
- A. Compressor
B. Throttling device
C. Turbine
D. Heat exchanger
- A. Diffuser
B. Nozzle
C. Throttling device
D. Heat transfer
- A. [latex]{P}_{r} \gg 1[/latex]
B. [latex]{P}_{r} \ll 1[/latex]
C. [latex]{P}_{r} \approx 1[/latex]
D. [latex]{P}_{r} = 0[/latex]
- A. In compressible
B. Uniform
C. Compressible
D. Non-linear
- A. Cavitation
B. Corrosion
C. Gasification
D. Boiling
- A. Thermal Energy Reservoir (TER)
B. Mechanical energy reservoir (MER)
C. Thermometer
D. Heat pump
- A. First law of thermodynamics
B. Second law of thermodynamics
C. Third law of thermodynamics
D. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
- A. [latex]{Q}_{L} - {Q}_{H}[/latex]
B. [latex]{Q}_{L} + {Q}_{H}[/latex]
C. [latex]{Q}_{H} - {Q}_{L}[/latex]
D. [latex]2{Q}_{L}[/latex]
- A. Refrigerator
B. Heat pump
C. Heat engine
D. Throttling
- A. Surface tension
B. Specific energy
C. Specific heat
D. Suction energy
- A. Cross sectional area
B. Hydraulic gradient
C. Coefficient of permeability
D. Porosity of the soil
- A. 0%
B. 50%
C. 75%
D. 100%
- A. Refrigerator
B. Source
C. Sink
D. Heat engine
- A. [latex]1 - (\frac{{Q}_{2}}{{Q}_{1})}[/latex]
B. [latex]2 - \frac{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}}[/latex]
C. [latex]1 *(\frac{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}})[/latex]
D. [latex]4 - \frac{{Q}_{1}}{{Q}_{2}}[/latex]
- A. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
B. First law of thermodynamics
C. Second law of thermodynamics
D. Third law of thermodynamics
1. Radiation of a black body, in terms of its temperature follows:
- A. Newton's law of cooling
B. Plank's law
C. Stefan's law
D. Einstein Bose equation
- 1) Temperature gradient is more in A than in B
2) The heat flow is determined by Fourier's law
3) Area under the curve represent s heat dissipation rate.
- A. T, T, T
B. T, T, F
C. T, F, T
D. F, F, T
- A. Conduction
B. Convection
C. Radiation
D. All of these
- A. Coefficient of linear expansion
B. Thickness
C. Thermal conductivity
D. Elastic properties
- A. negligible flow of heat
B. no difference of temperature between the bodies
C. constant heat flow rate i.e. heat flow rate independent of time
D. uniform rate in temperature rise of a body
- A. Free convection in air
B. Forced convection in air
C. Free convection in water
D. Condensation of steam
- A. 1353 kW/[latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
B. 1353 W/[latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
C. 1353 J/[latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
D. 135 kJ/[latex]{m}^{2}[/latex]
- A. Kirchhoff's law
B. Wien's displacement law
C. Maxwell's theory
D. Stefan Boltzmann law
- A. High rate of heat diffusion
B. Low rate of heat diffusion
C. High rate of mass diffusion
D. Low rate of mass diffusion
- A. k/h
B. 2k/h
C. k/2h
D. k/4h
- A. [latex]{T}^{4}[/latex]
B. [latex]{T}^{5}[/latex]
C. [latex]{T}^{\frac{5}{2}}[/latex]
D. [latex]{T}^{3}[/latex]
- A. ultraviolet radiation
B. infrared radiation
C. thermal radiation
D. visible radiation
- A. [latex]{r}_{insulation thickness} \gg {r}_{critical}[/latex]
B. [latex]{r}_{insulation thickness}\ll {r}_{critical}[/latex]
C. [latex]{r}_{insulation thickness} = {r}_{critical}[/latex]
D. [latex]{r}_{insulation thickness} = 0[/latex]
- A. color
B. distance
C. intensity
D. temperature
- A. Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
B. First Law of Thermodynamics
C. Second Law of Thermodynamics
D. Third Law of Thermodynamics.