Description
Description
Moving a Swing Windows on the screen is like a small entertaining game.User can change the place of the window application any where on the screen, while moving Swing Windows from one place to another place user can get the same result of an application then the resolution of the system will not be visible. In moving Swing Windows the resolution of the system will be visible that can be visible via x-axis and y-axis direction. The complete logic behind the moving window has been shown in below example.
 Example
Example
This example describes what is technique behind the moving window.
 Step-1
Step-1
Create a package and import all the required packages to hire the properties.
[java]package swing;//create the package
import java.awt.Container;//import all the required packages.
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.event.ComponentEvent;
import java.awt.event.ComponentListener;
import javax.swing.GroupLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
[/java]
 Step-2
Step-2
Create a class with the name SwingMovingWindow that should extend from the JFrame and should implement the ComponentListener. The functionality of ComponentListener is to receive the events.
[java]public class SwingMovingWindow extends JFrame
implements ComponentListener[/java]
 Step-3
Step-3
Create labels x and y and create constructor with name of class name.
[java]private JLabel labelx;
private JLabel labely;
public SwingMovingWindow() {
initUI();
}[/java]
 Step-4
Step-4
Create the object to the group layout and create the layout to the container pane and add listeners that performs on components as follows.
[java]Container pane = getContentPane();
GroupLayout gl = new GroupLayout(pane);
pane.setLayout(gl);
addComponentListener(this);[/java]
 Step-5
Step-5
Create the labels x and y, add font size, set the bounds.
[java]labelx = new JLabel("x: ");
labelx.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 14));
labelx.setBounds(20, 20, 60, 25);
labely = new JLabel("y: ");
labely.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 14));
labely.setBounds(20, 45, 60, 25);[/java]
 Step-6
Step-6
Set the gaps between the components.
[java]gl.setAutoCreateContainerGaps(true);
gl.setAutoCreateGaps(true);[/java]
 Step-7
Step-7
Create horizontal group layout and vertical group layout with parallel and sequential modes and components should add labels x, y by providing gaps between the components as follows.
[java] gl.setHorizontalGroup(gl.createParallelGroup()
.addComponent(labelx)
.addComponent(labely)
.addGap(250)
);
gl.setVerticalGroup(gl.createSequentialGroup()
.addComponent(labelx)
.addComponent(labely)
.addGap(130)[/java]
 Step-8
Step-8
Set the title to the window and write the method to close the window.
[java]setTitle("Moving window");
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);[/java]
 Step-9
Step-9
Create the three methods and here used componetmoved() remaining methods are empty methods.
[java] @Override
public void componentShown(ComponentEvent e) {
}[/java]
 Step-9
Step-9
Here get the components of x and y.
[java]labelx.setText("x: " + x);
labely.setText("y: " + y);[/java]
SwingMovingWindow.java
[java]package swing;
import java.awt.Container;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.event.ComponentEvent;
import java.awt.event.ComponentListener;
import javax.swing.GroupLayout;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
public class SwingMovingWindow extends JFrame
implements ComponentListener {
private JLabel labelx;
private JLabel labely;
public SwingMovingWindow() {
initUI();
}
private void initUI() {
Container pane = getContentPane();
GroupLayout gl = new GroupLayout(pane);
pane.setLayout(gl);
addComponentListener(this);
labelx = new JLabel("x: ");
labelx.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 14));
labelx.setBounds(20, 20, 60, 25);
labely = new JLabel("y: ");
labely.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.BOLD, 14));
labely.setBounds(20, 45, 60, 25);
gl.setAutoCreateContainerGaps(true);
gl.setAutoCreateGaps(true);
gl.setHorizontalGroup(gl.createParallelGroup()
.addComponent(labelx)
.addComponent(labely)
.addGap(250)
);
gl.setVerticalGroup(gl.createSequentialGroup()
.addComponent(labelx)
.addComponent(labely)
.addGap(130)
);
pack();
setTitle("Moving window");
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void componentResized(ComponentEvent e) {
}
@Override
public void componentMoved(ComponentEvent e) {
int x = e.getComponent().getX();
int y = e.getComponent().getY();
labelx.setText("x: " + x);
labely.setText("y: " + y);
}
@Override
public void componentShown(ComponentEvent e) {
}
@Override
public void componentHidden(ComponentEvent e) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
SwingMovingWindow ex = new SwingMovingWindow();
ex.setVisible(true);
}
});
}
}
[/java]
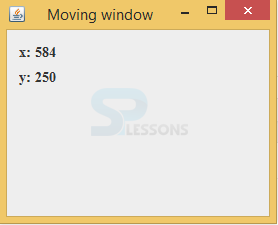
Output:
Output will be as follows.When user move the window then resolution of the application will be shown via x and y axis.
 Key Points
Key Points
- ComponentShown, ComponentHidden, ComponentMoved, ComponentResized will be in
ComponentListener interface. - To place the location of an application on the screen
setLoc