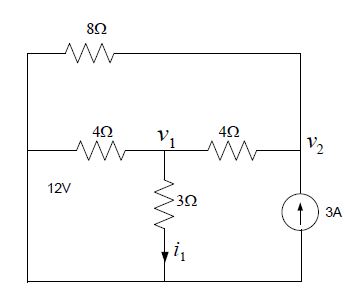
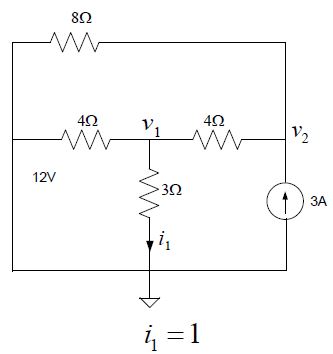
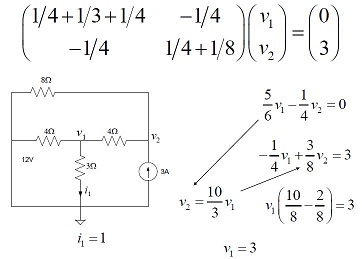
Introduction
Introduction
Superposition theorem is one of those strokes of genius that takes a complex subject and simplifies it in a way that makes perfect sense. A theorem like Millman’s certainly works well, but it is not quite obvious why it works so well. Superposition, on the other hand, is obvious.
 Definition
Definition
The circuit is linear we can find the response of the circuit to each source acting alone, and then add them up to find the response of the circuit to all sources acting together. This is known as the superposition principle.
The Superposition Principle states that the voltage across (or the current through) an element in a linear circuit is the algebraic sum of the voltages across (or currents through) that element due to each independent source acting alone.
 Concepts
Concepts
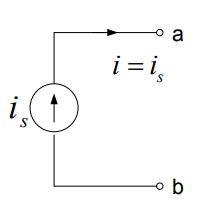
1. Current Source:
- We replace it by a current source where [latex]{i}_{S}[/latex] = 0
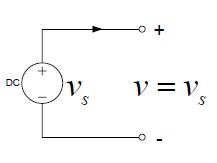
- We replace it by a voltage source where [latex]{v}_{S}[/latex] = 0
 Key Points
Key Points
- This theorem is applicable to only for linear network i.e the networks with R,L,C, transformer and Linear controlled sources as elements.
- The presence of dependent sources makes the network an active and hence SPT is used for the both active as well as passive networks.