Description
Description
Struts 2 Type Conversion, When user gives any request, the HTTP will take the request as String by the protocol. When one give int, booleans, dates, decimals values, the system take the request as String type. As a result, Struts contain some predefined type converter classes.
For example, if one have an integer attribute in their action class, Struts automatically converts the request parameter to the integer attribute without doing anything. By default, Struts comes with a number of type converters. By giving some predefined converters one can write and use any converter logic.
Some times by using custom data types, it is not possible to use any predefined converters.
- Integer, Float, Double, Decimal
- Date and Datetime
- Arrays and Collections
- Enumerations
- Boolean
- BigDecimal
 Example
Example
let's take one example like
1. Create the project directory structure and later create the index.jsp page.
2. Create one environmental class with property name, like view page property name.
3. Create the action class, which contains information about the system. In this example, the Environment to " Development" and the Operating system to "Windows XP SP3" are used.
4. After creating the action class, forward the result into JSP page. Now, create a JSP file with the name System.jsp to display the Environment and the Operating System information.
The project directory structure
index.jsp
[java]<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
Type conversion using Struts2.
</head>
<body>
<form action="system">
<s:textfield name="name" label="Enter your Name" />
<input type="submit" value="Register"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
[/java]
Environment.java
[java]package com.splessons;
public class Environment
{
private String name;
public Environment(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
}
[/java]
This is an extremely straightforward class that has a attribute called name.
SystemDetails.java
[java]package com.splessons;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class SystemDetails extends ActionSupport
{
private Environment environment = new Environment("Development");
private String operatingSystem = "Windows XP SP3";
public String execute()
{
return SUCCESS;
}
public Environment getEnvironment() {
return environment;
}
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
public String getOperatingSystem() {
return operatingSystem;
}
public void setOperatingSystem(String operatingSystem) {
this.operatingSystem = operatingSystem;
}
}
[/java]
struts.xml
[xml]<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd">
<struts>
<constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" />
<package name="helloworld" extends="struts-default">
<action name="system" class="com.splessons.SystemDetails" method="execute">
<result name="success">/System.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
[/xml]
Where success is a predefined result type. action element is the sub component of package. It speaks to an activity to be conjured for the approaching request. It has name, class and method attributes. In the event that you don’t determine name property as a matter of course execute() technique will be summoned for the predetermined actiion class.
System.jsp
[java]<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>System Details</title>
</head>
<body>
Environment: <s:property value="environment"/>
Operating System:<s:property value="operatingSystem"/>
</body>
</html>
[/java]
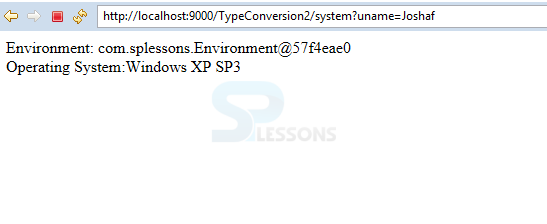
create a simple JSP file System.jsp to display the Environment and the Operating System information. Run the application in server, then one get the output as shown below.
 Description
Description
Struts know how to display and convert the string "Windows XP SP3" and other built-in data types, but it don't know what to do with the property of environment type. Then, one need to override the toString() in converter class and create the converter class for the Environment class.
EnvironmentConverter.java
[java]package com.splessons;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.struts2.util.StrutsTypeConverter;
public class EnvironmentConverter extends StrutsTypeConverter
{
@Override
public Object convertFromString(Map context, String[] values,
Class class1)
{
Environment environment1 = new Environment(values[0]);
return environment1;
}
@Override
public String convertToString(Map context, Object value) {
Environment environment1 = (Environment) value;
return environment1 == null ? null : environment1.getName();
}
}[/java]
The class extends the StrutsTypeConvertor class. StrutsTypeConvertor provides two methods like convertFromString() and convertToString(), If one override those two methods Struts will automatically convert Environment to a String. Register the converter class before to create a property files with the name as [actionclass name]-conversion.properties.
 Description
Description
[java]environment=com.splessons.EnvironmentConverter.[/java]
Here "environment" is the property of SystemDetails.java class and it tells the converter class converting this property. One need to deploy the application in server and start the server.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Struts 2 Type Conversion -
struts 2.util.StrutsTypeConverter;package needs to be imported while working with typeconversion - Struts 2 Type Conversion - Struts 2 has the capability to handle conversion of arguments into primitives.
- Struts 2 Type Conversion - Adding the custom converters is the great capability of the struts2.