Description
Description
Struts 2 Spring was developed by Rod Johnson in June 2003 on Apache 2.0 version that provides robust and secure applications. The latest version of Spring 4.2.1 was released in September 2015. Struts 2 Spring objects are loosely coupled objects and it can be used for development of real time applications unlike struts and hibernates.here struts can be used for developing front end applications like web applications. Hibernates can be used for developing database related operations. ContextLoaderListener is the main assert of spring frame work to communicate with the other frameworks, this listener will be placed in the web.xml.While integrating spring with Struts 2 required jar files needs to be inserted to the project. Following are the required files which describes how to integrate spring framework with Struts 2.
- index.jsp
- error.jsp
- welcome.jsp
- web.xml
- Login.java
- struts.xml
- applicationContext.xml
 Example
Example
Following is an example which shows how to do the an application by integrating with spring.
index.jsp
[java]<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<s:form action="login">
<s:textfield name="userName" label="UserName" ></s:textfield>
<s:password key="password" />
<s:submit ></s:submit>
</s:form>
[/java]
error.jsp
[java]Sorry man! [/java]
welcome.jsp
[java]<%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%>
<h1><font color="green">Welcome, <s:property value="userName"/><br/>
${message}
${link}</font>
[/java]
web.xml
[xml]<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="2.5"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<filter>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<filter-class>
org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
</filter-class>
</filter>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts2</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
</web-app> [/xml]
The ContextLoaderListener is used to integrate Spring with other web application.
Login.java
[java]package mypack;
public class Login {
private static final String UserName = null;
private String userName,message,link;
char Password;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getLink()
{
return link;
}
public void setLink(String link)
{
this.link = link;}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public char getPassword()
{
return Password;
}
public void setPassword(char password)
{this.Password =password;
}
public String execute(){
return "success";
}
} [/java]
Here just created the data members and also performed SET and GET methods on those members.
struts.xml
[xml]<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.1//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.1.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="abc" extends="struts-default">
<action name="login" class="login">
<result name="success">welcome.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts> [/xml]
applicationContext.xml
Message and link data has written here.
[xml]<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd">
<bean id="login" class="mypack.Login">
<property name="message" value="Hey man stay tuned to splessons and get stuff."></property>
<property name="link" value="http://www.splessons.com/"></property>
</bean>
</beans> [/xml]
The Application Context is spring's more best in class compartment. Like BeanFactory it can stack bean definitions, wire beans together and apportion beans upon solicitation. Also it includes more undertaking particular usefulness, for example, the capacity to determine literary messages from a properties document and the capacity to distribute application occasions to intrigued occasion audience members. This compartment is characterized by the org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext interface.
The ApplicationContext incorporates all usefulness of the BeanFactory, it is by and large suggested over the BeanFactory. BeanFactory can in any case be utilized for light weight applications like cell phones or applet based applications.
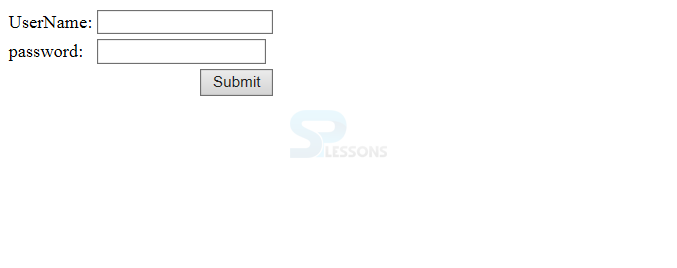
Output
When compile the program following page will be displayed in the browser.
When click on submit button following message will be displayed.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Struts 2 Spring - The spring framework uses an applicationContext.xml file.
- Struts 2 Spring - applicationContext.xml file will be placed at WEB-INF.
- Spring configuration file will be loaded by ContextLoaderListener.