Description
Description
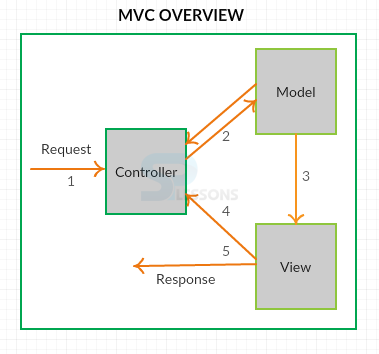
Struts 2 MVC Architecture, Struts2 framework is defined in most of the MVC (Model View Controller) based applications, before that user should have an idea about what MVC is. Model View Controller is the popular design pattern which is utilized to build web applications and it consists of three parts where each one will have its own functionality, where controller is the responsibility for carrying the little code through which request will be sent to the server, when the server takes the request model is the responsibility to check the data availability and view is utilized to expose the data to an user. Following is the conceptual figure which describes functioning of each module.
Model:Model is responsible to carry data and it is the low level of the pattern.
View:View is responsible to expose the carried data to an user.
Controller:Controller will provide interaction between the model and view. Controller will have the code, requests and responses will be handled from here.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
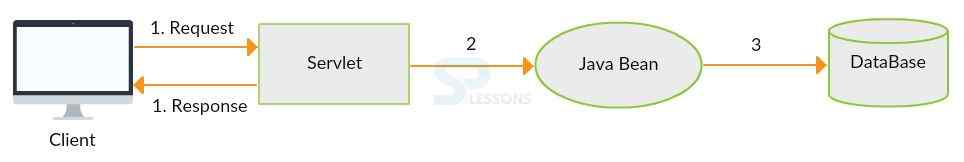
In a servlet, the presentation logic and persistence logic are defined, then servlet will act as a controller and view pages. If any changes occurred in a browser, the application will be deployed on the server, which is the drawback of MVC1.
- In MVC1, the presentation logic and persistence logic both are in Servlet. Business logic is defined in JavaBean classes.
- If the user gives the request from a browser to a servlet, the servlet will get the request from the browser and it will access the JavaBean classes and invokes the business logic.
- JavaBean goes into Database and performs any database operations. After the data is read or saved, JavaBean class will give the result into the servlet.
- The servlet will give the result into browser and display the output on Browser page.
 Conceptual
figure
Conceptual
figure
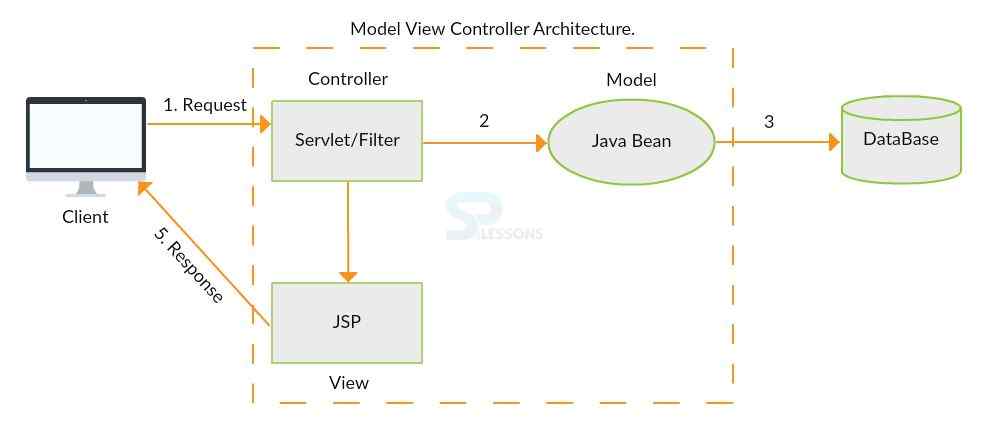
In MVC2, Controller and views are defined separately.
- If the user gives the request from a browser to a Servlet/Filter, then servlet will act as a Controller.
- The Controller will get the request from the browser and it will access the JavaBean (Model) class. Then the JavaBean class is defined in business logic and persistence logic.
- Javabean goes into a database and performs any database operations. After that, the data will be read or saved. JavaBean class will give the result on Controller in object format.
- The Controller goes to View pages in JSP which are defined in Presentation logic.
- JSP gives the response into the browser page.
- In MVC2, business logic and presentation logic are written separately. But, both are maintained in one controller.
- If one uses the JSP in views, if any modifications have occurred in the browser page, one can change the JSP page after running the program. Again, one cannot deploy the application in the server.
 Key Points
Key Points
- Struts 2 MVC Architecture - MVC is the design pattern utilized to build web applications.
- Struts 2 MVC Architecture - The big drawback of Servlet is that if any modification is done.
- Struts 2 MVC Architecture - The drawback of Servlet will be overcome by JSP.