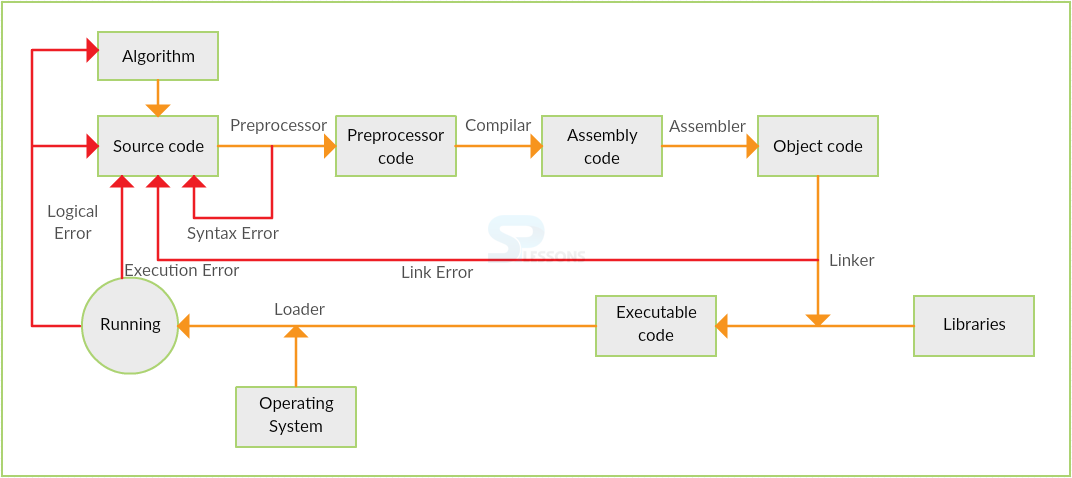
Introduction
Introduction
"Structure of C Program" chapter gives clear explanation of various sections of C-programs.
Any program is written and executed in various steps to give a desired output.Even if a small program is coded, it requires a structure.
 Description
Description
Any C program need to follow a structure which consists of certain rules. The Structure of C Program can be as follows which has various sections.Some of the sections are essential and some of them are optional.
 Sections
Table
Sections
Table
| Sections in Structure of C Program |
|---|
| Documentation Section |
| Link Section |
| Definition Section |
| Global Declaration Section |
| Main Function Section |
| Sub-programming Section |
 Description
Description
Documentation section is used for giving the comments regarding the title, author,more detailed information about the program etc.
Eg:
Single line comments
[html]//sum of two numbers[/html]
Multi-line comments
[html]/*Welcome to SPLessons
You are reading C-programming tutorial
This program is about summing of two numbers*/[/html]
 Description
Description
Link section is used to link the compiler to the library function using header files.
Eg:
[html]#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>[/html]
 Description
Description
Definition section consists of symbolic constants.
Eg:
[c]#define true 1[/c]
 Description
Description
The variables used anywhere in the program are called as global variables. In this section, global variables are declared which can be also used in user-defined functions.
Eg:
[c]int x=10;[/c]
 Description
Description
Main function section is the main part of the program. It mainly consists of two parts which are written between the braces {} and every line have to end with a semicolon(;).
Declaration Section: In declaration section, all the required variables are declared which can be used in the executable part.
Executable Section: In executable section, statements are given which are helpful in executing the program and giving the output.
Eg:
[c]
{
Function 1
Function 2
.
.
}[/c]
 Description
Description
Sub-programming section consists of user-defined functions.These functions are called by the main function section.
 Example
Example
[c]
/*C basic structure example
to find sum of two numbers */ //documentation section
#include<stdio.h> //Link section
int total; //Global declaration section
int sum(int,int); //Function declaration section
void main() //Main section
{
int a,b;
printf("\n Enter the two numbers : ");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b); /* taking two numbers as input*/
total = sum(a,b); /* calling function.The value returned by the function is stored in total */
printf("\n The sum of two numbers is : %d ",total);
getch();
}
int sum ( int num1,int num2) //User defined section
{
int result; /* defining variable, its scope lies within function */
result = num1 + num2 ; /*adding two numbers*/
return (result) ; //definition section
}[/c]
Output:
[c]
Enter the two numbers : 1 2
The sum of two numbers is : 3
[/c]
All the rules should be followed in every section to get a successful output from a program.
 Key Points
Key Points
- C-Structure is built-up based on 6 sections.
- Execution starts from main section.
- Sub-programming section and definition sections are optional.
 Programming
Tips
Programming
Tips
Using documentation section(comments) is the best practice because it explains the program clearly .