Introduction
Introduction
In mechanics of materials, the strength of a material is its ability to withstand an applied load without failure or plastic deformation. The field of strength of materials deals with forces and deformations that result from their acting on a material. Strength of Materials is an important topic in Mechanical Engineering subjects. Strength of Materials Practice Quiz article, is exceedingly important for candidates preparing for RRB Junior Engineer Recruitment, SSC Junior Engineer Recruitment, GATE, UPSC (Civil services exam including IAS) and all Mechanical Engineering Exams and etc. In this article, candidates can find different types of questions with solution related to the Strength of Materials topic. The article Strength of Materials Practice Quiz, will assist the students understanding of the type of questions expected from the topic Strength of Materials.
 Quiz
Quiz
1. [latex]{\sigma}_{x}, {\sigma}_{y} and {\tau}_{xy}[/latex] are rectangular stress components at a point. The radius of Mohr’s circle is
- A. [latex]\sqrt{{{\sigma}_{x}}^{2} - {{\sigma}_{y}}^{2} + {{\tau}_{xy}}^{2}} [/latex]
B. [latex]\sqrt{{(\frac{{\sigma}_{y} + {\sigma}_{x}}{2}})^{2} + {{\tau}_{xy}}^{2}} [/latex]
C. [latex]\sqrt{{{\sigma}_{y}}^{2} - {{\sigma}_{x}}^{2} + {{\tau}_{xy}}^{2}} [/latex]
D. [latex]\sqrt{{(\frac{{\sigma}_{y} - {\sigma}_{x}}{2}})^{2} + {{\tau}_{xy}}^{2}} [/latex]
- A. modulus of elasticity
B. radius of gyration about the minor axis
C. span/length of the beam
D. ratio of overall depth to thickness of the flange
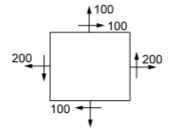
- A. [latex]25 \sqrt{5} [/latex]
B. [latex]50 \sqrt{5} [/latex]
C. [latex]100 \sqrt{5} [/latex]
D. [latex]200 \sqrt{5} [/latex]
- A. related to the length
B. directly proportional to the slenderness ratio
C. inversely proportional to the slenderness ratio
D. non-linearly to the slenderness ratio
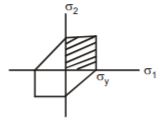
- A. [latex]\frac {{\sigma}_{1} - {\sigma}_{2}}{2} = \pm \frac{{\sigma}_{yp}}{2}[/latex]
B. [latex] \frac{{\sigma}_{1}}{2} = \pm \frac{{\sigma}_{yp}}{2}[/latex]
C. [latex] \frac{{\sigma}_{2}}{2} = \pm \frac{{\sigma}_{yp}}{2}[/latex]
D. [latex] {\sigma}_{1} = \pm 2{\sigma}_{yp}[/latex]
- 1. Shear stress is zero
2. Normal stress is zero
3. Shear stress is maximum
4. Normal stress is maximum
- A. 1 and 2 are correct
B. 2 and 3 are correct
C. 1 and 4 are correct
D. 3 and 4 are correct
- A. pure shear
B. uni-axial stress only
C. equal and opposite axial stresses on two mutually perpendicular planes, the planes being free of shear
D. equal axial stresses on two mutually perpendicular planes, the planes being free of shear.
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
- A. the diameter of the Mohr’s circle
B. half the diameter of the Mohr’s circle
C. one-third the diameter of the Mohr’s circle
D. one-fourth the diameter of the Mohr’s circle
- A. the material is rigid
B. the material is perfectly plastic
C. there is no longitudinal strain in the material
D. none of these
1. The plane of maximum shear stress has normal stress that is
- A. maximum
B. minimum
C. zero
D. None of these
- A. length
B. cross-section
C. volume
D. none of these
- A. a straight line path
B. a circular path
C. a parabolic path
D. an elliptical path
- A. [latex]\frac{{\pi}^{2} EI}{{L}^{2}}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{2 {\pi}^{2} EI}{{L}^{2}}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{3 {\pi}^{2} EI}{{L}^{2}}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{4 {\pi}^{2} EI}{{L}^{2}}[/latex]
- A. Torque in each shaft is the same
B. Shear stress in each shaft is the same
C. Angle of twist of each shaft is the same
D. Torsional stiffness of each shift is the same
- A. [latex]\frac{Effective length}{Least radius of gyration}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{Actual length}{Moment of inertia}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{Moment of inertia}{Actual length}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{Actual length}{Radius of gyration}[/latex]
- A. [latex]\frac{0.002}{L}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{2}{L}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{0.2}{L}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{L}{0.002}[/latex]
- A. 0
B. 0.5
C. 1.0
D. 0.25
- A. [latex]E = \frac{KC}{K + C}[/latex]
B. [latex]E = \frac{2KC}{2K + C}[/latex]
C. [latex]E = \frac{9KC}{3K + C}[/latex]
D. [latex]E = \frac{3KC}{K + 2C}[/latex]
- A. Elasticity
B. Plasticity
C. Ductility
D. Malleability
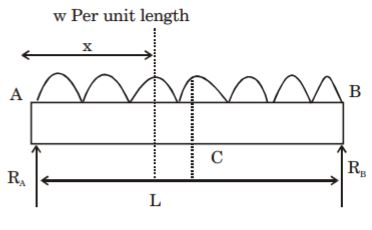
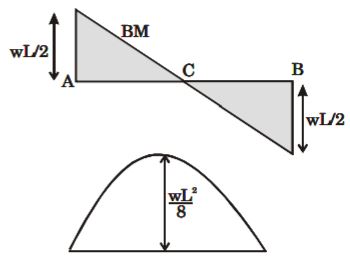
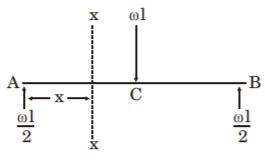
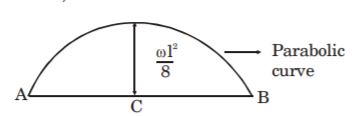
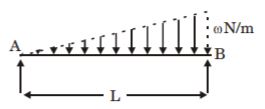
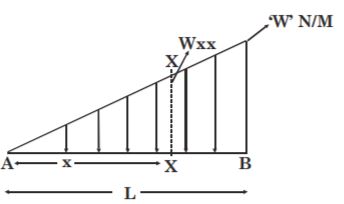
- A. [latex]\frac{\omega{L}^{2}}{4}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{\omega{L}^{2}}{8}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{\omega{L}^{2}}{2}[/latex]
D. [latex]\omega{L}^{2}[/latex]
- A. Electrical conduction
B. Sonorous in nature
C. dullness
D. ductility
1. In S.I system, unit of stress is:
- A. [latex]\frac{kg}{{cm}^{2}}[/latex]
B. N
C. [latex]\frac{N}{{m}^{2}}[/latex]
D. Watt
- A. Cam and rocker arm
B. Connecting rod and piston
C. Crankshaft and piston
D. None of these
- A. [latex]\frac{cm}{kg}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{m}{kg}[/latex]
C. no units
D. None of these
- A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
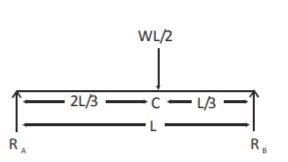
- A. [latex]\frac{L}{2}[/latex]
B. [latex]\frac{L}{4}[/latex]
C. [latex]\frac{L}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
D. [latex]\frac{L}{3}[/latex]
- A. Wear Resistance
B. Elasticity
C. Shear Strength
D. Tensile Strength
- A. axle
B. drive shaft
C. crank shaft
D. cam shaft
- A. Cams
B. Fly wheel
C. Gudgeon pin
D.
- A. Young's modulus
B. Shear modulus
C. Poisson's ratio
D. Bulk modulus of elasticity
- A. rod caps
B. cap bolts
C. small end bearings
D. gudgeon pins