Description
Description
Join is a query which combines data from multiple tables. A JOIN is performed at whatever points two or more tables are joined in a SQL statement.
Join can be divided into
- Cartesian join
- Equi join
- Non equi join
- Outer join
 Description
Description
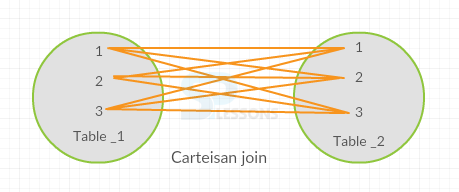
A Cartesian join is a join of every row of one table to every row of another table.
 Syntax
Syntax
Select * from <table_name1>,<table_name2>;
table_name => Any accurate table.  Examples
Examples
By viewing the below example, the concept of Cartesian join can be understood easily.
[sql]sql> select * from emp17;
+--------+--------+--------+
| emp_id | ename | deptno |
+--------+--------+--------+
| 1001 | jhon | 10 |
| 1002 | shah | 20 |
| 1003 | maddi | 10 |
| 1004 | maddie | 20 |
+--------+--------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> select * from dept13;
+--------+-----------+-----------+
| deptno | dept_name | dept_city |
+--------+-----------+-----------+
| 10 | leo | texas |
| 20 | vin | newyork |
+--------+-----------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> select * from emp17,dept13;
+--------+--------+--------+--------+-----------+-----------+
| emp_id | ename | deptno | deptno | dept_name | dept_city |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+-----------+-----------+
| 1001 | jhon | 10 | 10 | leo | texas |
| 1001 | jhon | 10 | 20 | vin | newyork |
| 1002 | shah | 20 | 10 | leo | texas |
| 1002 | shah | 20 | 20 | vin | newyork |
| 1003 | maddi | 10 | 10 | leo | texas |
| 1003 | maddi | 10 | 20 | vin | newyork |
| 1004 | maddie | 20 | 10 | leo | texas |
| 1004 | maddie | 20 | 20 | vin | newyork |
+--------+--------+--------+--------+-----------+-----------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)[/sql]
In the above example, the Cartesian join combines both emp17 table and dept13 table and update the values to all the fields based on depno, so that each and every employee will have completed details with duplicate values.
 Description
Description
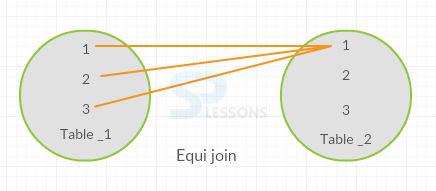
Combining data from multiple tables by specifying equal number of conditions, then each row in the first table will join with one row in the second table.
 Syntax
Syntax
select <column_list> from <table1>,<table2>where table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
table_name => Any accurate table.
column_list => All columns in the table.  Examples
Examples
By viewing the below example, the concept of equi join can be understand easily.
[sql]sql> select * from e;
+--------+-------+--------+--------+
| emp_id | ename | salary | deptno |
+--------+-------+--------+--------+
| 1001 | mike | 12000 | 10 |
| 1002 | welli | 13000 | 20 |
| 1003 | jeo | 14000 | 10 |
| 1004 | jorg | 15000 | 20 |
+--------+-------+--------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql>select * from d;
+---------+-----------+---------+
| dept_no | dept_name | city |
+---------+-----------+---------+
| 10 | jelly | texas |
| 20 | oyak | newyork |
+---------+-----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql>select e.emp_id,e.ename,d.dept_no,d.city from e,d where e.deptno=d.dept_n
o;
+--------+-------+---------+---------+
| emp_id | ename | dept_no | city |
+--------+-------+---------+---------+
| 1001 | mike | 10 | texas |
| 1002 | welli | 20 | newyork |
| 1003 | jeo | 10 | texas |
| 1004 | jorge | 20 | newyork |
+--------+-------+---------+---------+
4 rows in set (0.05 sec)[/sql]
In the above example, the equi join combines both e table and d table and update the values to all the fields based on depno, then some of the row in the first table will join with one row in the second table.
 Description
Description
Combining data from multiple tables by applying different number of conditions, then some of the rows in the first table will join with one row in the second table.
 Syntax
Syntax
SELECT *
FROM <table_name1>, <table_name2>
WHERE <table_name1>.column [> | = | <= ] <table_name2>.column;
table_name => Any accurate table.
 Examples
Examples
By viewing the below example, the concept of non equi join can be understood easily.
[sql]sql> select * from e;
+--------+-------+--------+--------+
| emp_id | ename | salary | deptno |
+--------+-------+--------+--------+
| 1001 | mike | 12000 | 10 |
| 1002 | welli | 13000 | 20 |
| 1003 | jeo | 14000 | 10 |
| 1004 | jorge | 15000 | 20 |
+--------+-------+--------+--------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> select * from d;
+---------+-----------+---------+
| dept_no | dept_name | city |
+---------+-----------+---------+
| 10 | jelly | texas |
| 20 | oyak | newyork |
+---------+-----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> select e.emp_id,e.ename,d.dept_name,d.city from e,d where e.deptno=d.dept
_no and e.salary>13000;
+--------+-------+-----------+---------+
| emp_id | ename | dept_name | city |
+--------+-------+-----------+---------+
| 1003 | jeo | jelly | texas |
| 1004 | jorge | oyak | newyork |
+--------+-------+-----------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
[/sql]
In the above example, the non equi join combines both e table and d table values based on depno, then some of the row in the first table will join with one row in the second table.
 Description
Description
Outer join gives back all rows from both the tables which fulfill the join condition along with rows which does not fulfill the join condition.
Outer join can be classified into two types:
- Left outer join
- right outer join
 Description
Description
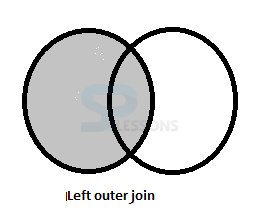
The condition is optional for the table on left size and is compulsory for the table on right side.
 Syntax
Syntax
 Examples
Examples
By viewing the below example, the concept of left outer join can be understood easily.
[sql]sql> select * from e12;
+--------+--------+---------+
| emp_id | ename | dept_no |
+--------+--------+---------+
| 1001 | jack | 10 |
| 1002 | maddi | 20 |
| 1003 | maddie | 10 |
| 1004 | max | 20 |
| 1004 | capi | 30 |
+--------+--------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> select * from d12;
+---------+-----------+----------+
| dept_no | dept_name | city |
+---------+-----------+----------+
| 10 | finance | texas |
| 20 | capital | new york |
+---------+-----------+----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql>select emp_id,ename,dept_name,city from e12 left join d12 on e12
.dept_no=d12.dept_no;
+--------+--------+-----------+----------+
| emp_id | ename | dept_name | city |
+--------+--------+-----------+----------+
| 1001 | jack | finance | texas |
| 1003 | maddie | finance | texas |
| 1002 | maddi | capital | new york |
| 1004 | max | capital | new york |
| 1004 | capi | NULL | NULL |
+--------+--------+-----------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
[/sql]
In the above example, the condition is optional for the table e12 and is compulsory for the table d12.
 Description
Description
The condition is optional for the table on right side, where as it is compulsory on the table on right side.
 Syntax
Syntax
SELECT *
FROM table1
Right [ OUTER ] JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
table_name => Any accurate table.
 Examples
Examples
[sql]sql> select * from e12;
+--------+--------+---------+
| emp_id | ename | dept_no |
+--------+--------+---------+
| 1001 | jack | 10 |
| 1002 | maddi | 20 |
| 1003 | maddie | 10 |
| 1004 | max | 20 |
| 1004 | capi | 30 |
+--------+--------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> select * from d12;
+---------+--------------+----------+
| dept_no | dept_name | city |
+---------+--------------+----------+
| 10 | finance | texas |
| 20 | capital | new york |
| 30 | manager | ausralia |
| 40 | applications | usa |
| 50 | technology | canada |
+---------+--------------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
sql> select e12.emp_id,e12.ename,d12.dept_name,d12.city from d12 right join e12 on d12.dept_no=e12.dept_no;
+--------+--------+-----------+----------+
| emp_id | ename | dept_name | city |
+--------+--------+-----------+----------+
| 1001 | jack | finance | texas |
| 1003 | maddie | finance | texas |
| 1002 | maddi | capital | new york |
| 1004 | max | capital | new york |
| 1004 | capi | manager | ausralia |
+--------+--------+-----------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
In the above example, the condition is optional for the table d12 and is compulsory for the table e12[/sql]
 Key Points
Key Points
- Join is a query which combines data from multiple tables.
- Cartesian join - All the rows in the primary table joins with every one of the rows in second table.
- Equi join - All rows in the main table will join with just only rows in the second table.
- Non equi join - A portion of the row in the first table will join with one row in the second table.
- Left outer join - The condition is optional for the table on left side and is compulsory for the table right side.
- Right outer join - The condition is optional for the table on right side and is compulsory for the table left side.